Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis: Symptoms and Causes
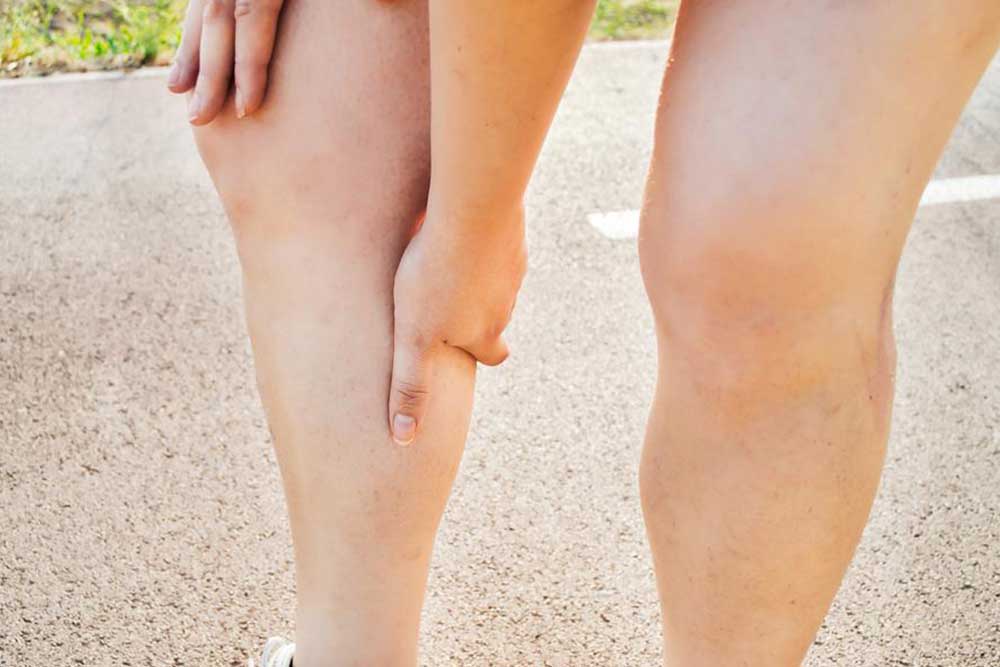
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition characterized by blood clot formation in deep veins, mainly in the legs. Recognizing symptoms like swelling, pain, and redness is vital for early diagnosis and prevention of complications like Pulmonary Embolism. Risk factors include injury, surgery, obesity, pregnancy, and prolonged immobility. Diagnostic tools such as ultrasound and MRI help confirm DVT. Staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, and regular leg movements are essential preventive strategies for at-risk populations.
Sponsored
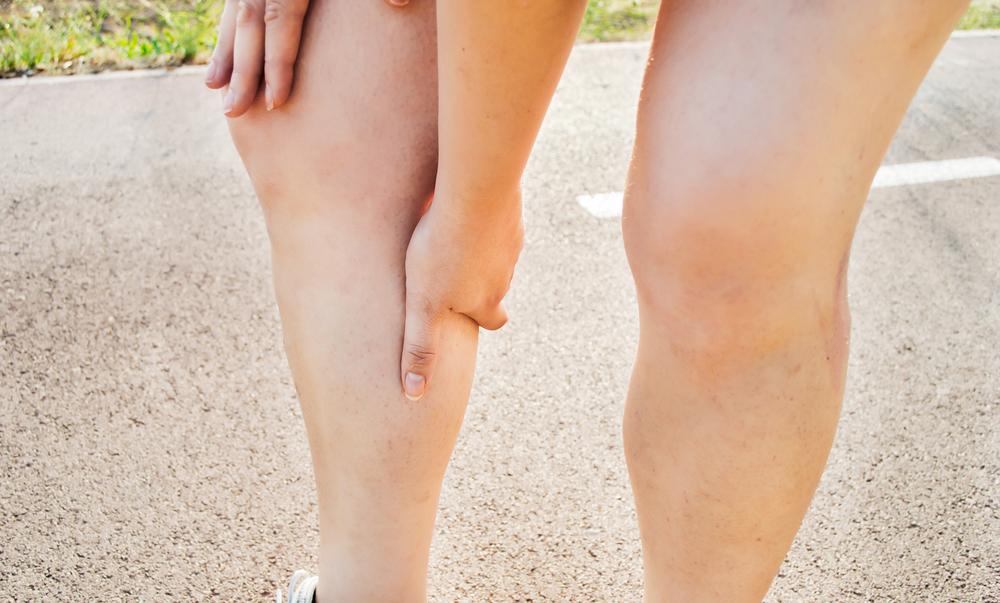
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) involves the formation of a blood clot in deep veins, predominantly in the legs. It can cause discomfort, swelling, and cramps, and poses a serious risk if the clot travels to the lungs, causing a Pulmonary Embolism. Various factors increase DVT risk, including injury, medical conditions, surgeries, obesity, pregnancy, age, heart issues, prolonged immobility, and family history.
Common DVT symptoms include sudden leg pain, swelling, warmth, redness, tenderness, and cramps, often affecting just one leg. Failure to treat DVT can lead to a life-threatening Pulmonary Embolism, characterized by shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid breathing, coughing blood, and dizziness. Accurate diagnosis via ultrasound, venography, or MRI is crucial. Preventive measures include regular movement, weight management, and staying active, especially for high-risk individuals.