Understanding Cellulitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Types
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that can affect various body parts, including arms, face, and legs. It begins with redness, swelling, and tenderness, often caused by bacteria entering through cuts or skin conditions. Prompt treatment with antibiotics is vital, especially in cases of leg or facial cellulitis. Recognizing the symptoms early helps prevent complications. Types of cellulitis vary based on the affected area, with specific symptoms and treatment approaches. Immediate medical attention ensures effective management of this potentially serious infection.
Sponsored
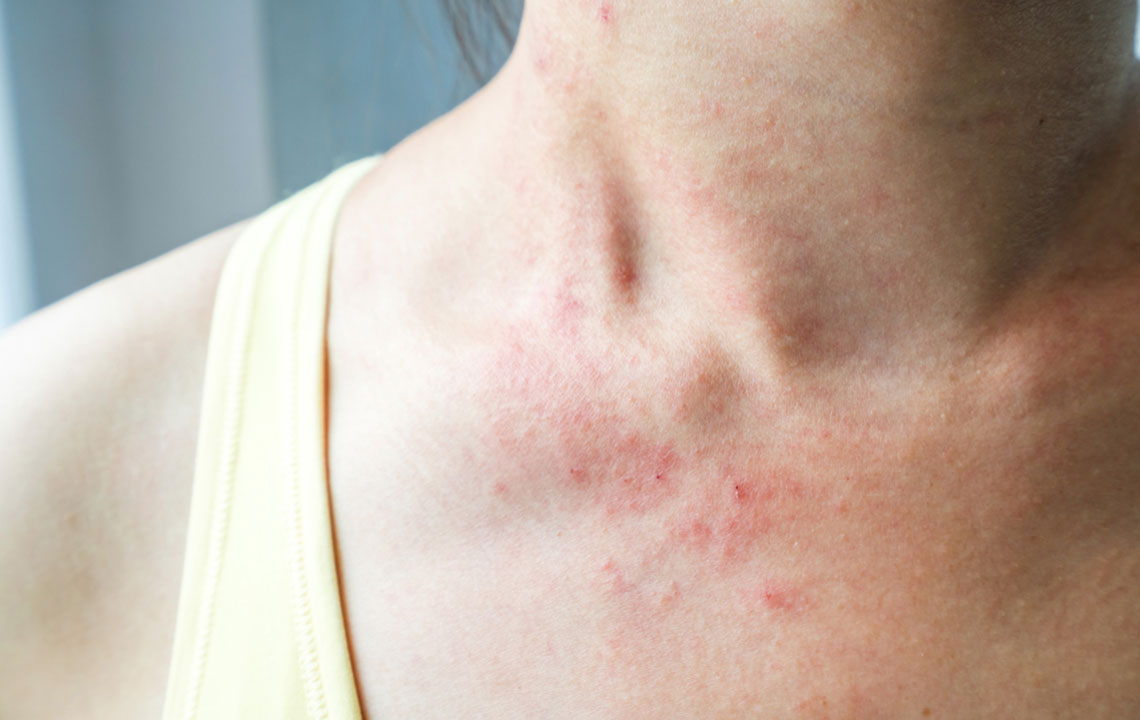
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that begins with localized redness and swelling and can escalate to a serious health concern if not treated promptly. It results when bacteria invade damaged skin, affecting the underlying dermis and subcutaneous tissues. Common culprits include Streptococcus and Staphylococcus bacteria, though fungi can occasionally cause similar infections. Leg cellulitis warrants immediate medical attention. Symptoms typically include warm, tender, swollen skin that appears red, often accompanied by blisters, spots, and fever. Various factors like cuts, bites, or skin conditions facilitate bacterial entry into the skin. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential.
Types of Cellulitis
Cellulitis can occur in different parts of the body:
Extremity cellulitis affects arms, legs, and hands, usually treated with oral antibiotics.
Facial cellulitis involves redness, swelling, and tenderness around the lips and tongue, often presenting with fever and irritability.
Periorbital cellulitis impacts the eye area, common in children and infants, involving facial swelling around the eyes.
Breast cellulitis causes redness, swelling, and pain in the breast tissue, sometimes spreading to nearby areas and accompanied by fever and fatigue.
Perianal cellulitis occurs mainly in children, especially males, causing discomfort, painful bowel movements, and possible blood in stool.






