Comprehensive Guide to Lung Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Lung cancer, primarily stemming from epithelial cells lining the bronchi, poses significant health risks worldwide. Early diagnosis and treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation, are crucial. Key risk factors include smoking, asbestos exposure, and genetics. Symptoms often appear only in later stages and require prompt medical attention for better prognosis.
Sponsored
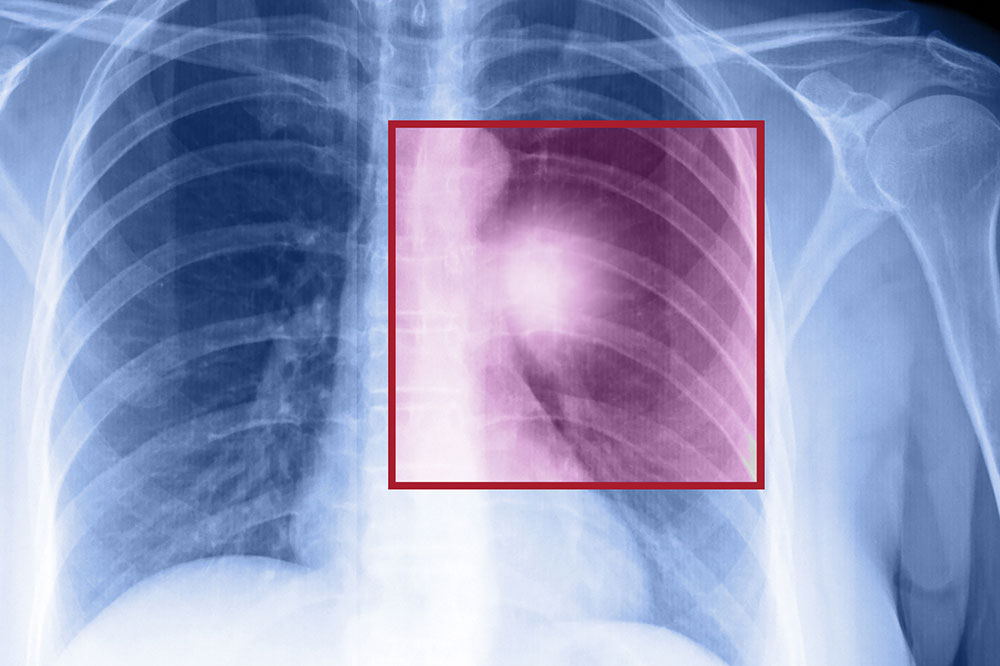
Lung cancer develops due to abnormal growth of tissues in the lungs, which can subsequently metastasize to other parts of the body, leading to critical health issues and often fatal outcomes. About 90% of lung cancers originate from the epithelial cells lining the larger bronchi and smaller bronchioles. Mainly, the cells surrounding lung tissues and blood vessels contribute to the disease. Most patients diagnosed are over 60 years of age.
Cancer can metastasize beyond the lungs, and early diagnosis is vital for successful treatment. Common therapies include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and radiosurgery, aimed at eliminating cancerous cells.
Several factors contribute to lung cancer risk. While smoking remains the primary cause, environmental influences like air pollution also significantly increase the probability of developing the disease, especially among non-smokers.
The main contributing factors include:
Smoking: The leading cause, with prolonged cigarette use responsible for approximately 90% of cases.
Asbestos exposure: Inhalation of these fibers can cause prolonged tissue damage and raise cancer risk.
Passive smoking: Non-smokers exposed to tobacco smoke face about a 25% increased risk.
Radon: Long-term inhalation of radon gas from soil sources can be a contributing factor.
Genetics: Family history of cancer can predispose individuals to lung cancer.
The symptoms often appear only in advanced stages, including persistent cough, sometimes with blood, shortness of breath, and hoarseness. Other signs involve weight loss, fatigue, neurological issues like memory loss, and increased bone fragility.
Treatment options depend on factors such as the cancer's location, stage, and patient's overall health. Surgical removal is ideal if the cancer is limited to the lungs. For advanced cases where metastasis has occurred, targeted drugs, chemotherapy, and radiation are used to control and destroy cancer cells.