Understanding Lung Cancer: Types, Symptoms, and Causes
Lung cancer, a major global health concern, often develops silently but shows symptoms like cough and chest pain as it progresses. It primarily affects smokers and those exposed to hazardous substances like radon, asbestos, or radiation. There are two main types: non-small cell and small cell lung cancer. Risk factors include genetic predisposition, smoking habits, and environmental exposures. Early detection and lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, are vital for prevention. Consult healthcare professionals for screening and risk mitigation strategies.
Sponsored
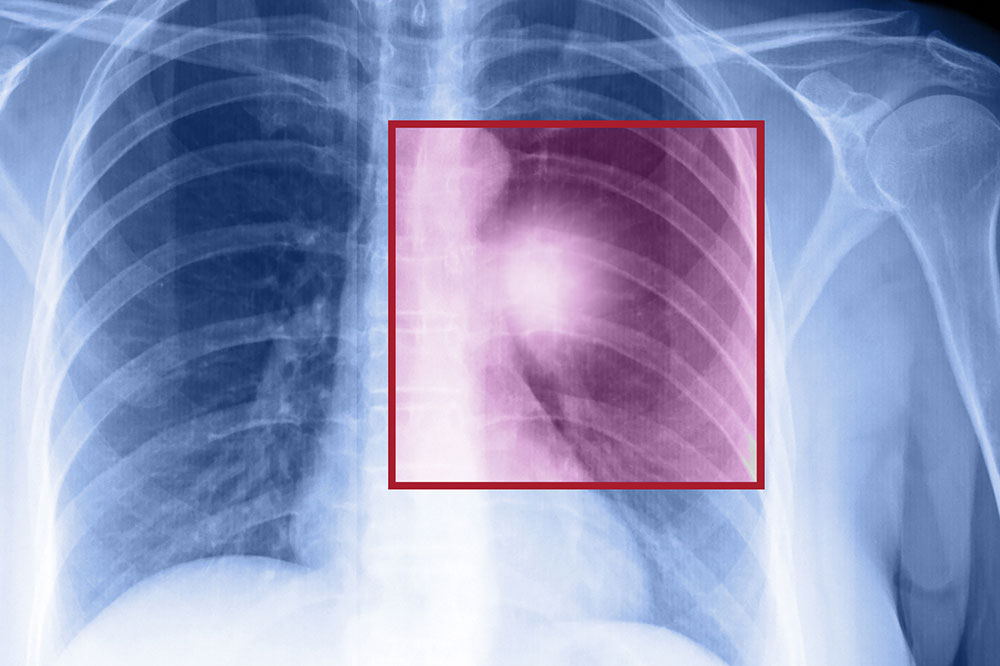
Lung cancer emerges when abnormal cell growth occurs in the lung tissue. It ranks among the leading causes of mortality globally, especially affecting smokers. This article explores the key factors related to lung cancer, including its symptoms, types, and risk causes.
Signs and Symptoms of Lung Cancer
Usually, early-stage lung cancer shows no obvious symptoms. As it advances, symptoms may include:
Persistent cough
Chest discomfort
Breathing difficulties
Blood in sputum
Unexplained weight decline
Hoarseness
Bone pain
Chronic headaches
Seeking medical advice is vital if these symptoms are observed.
Those unable to quit smoking should consult healthcare professionals for cessation strategies to lower risk.
Types of Lung Cancer
There are primarily two forms:
Non-small cell lung carcinoma: Encompasses subtypes such as squamous cell, adenocarcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
Small cell lung cancer: Mainly affects heavy smokers and is less common than non-small cell variants.
Risk Factors for Lung Cancer
Several elements increase the chance of developing lung cancer, some modifiable, others not:
Genetic predisposition: Family history of lung cancer increases personal risk.
Radon exposure: Particularly in homes or buildings with natural radon leakages from soil or water.
Chemicals and asbestos exposure: Occupational hazards in environments with carcinogenic substances.
Radiation exposure: Chest radiation treatments can heighten risk.
Smoking and secondhand smoke: Leading causes; quitting significantly reduces risk.
If you recognize these factors, consult your doctor for preventive measures.
Causes of Lung Cancer
Smoking remains the primary cause of lung cancer, introducing carcinogens that damage lung tissue. Even non-smokers can develop the disease, often through secondhand smoke or environmental exposures. Repetitive damage hampers cellular repair, prompting abnormal growth and cancer formation over time.