Comprehensive Guide to Managing Type 1 Diabetes
This comprehensive guide explains type 1 diabetes, including causes, symptoms, management strategies, and potential complications. Emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and lifestyle changes, it provides essential information to help individuals control their condition and maintain health through proper treatment and regular checkups.
Sponsored

Understanding and Managing Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system targets and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This chronic illness results in the body’s inability to produce insulin, primarily affecting children but also emerging in adults. Insulin is essential for converting glucose from food into energy. Without it, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to complications. Early diagnosis and management are crucial to prevent serious health issues.
High blood sugar levels from insulin deficiency can cause immediate and long-term health problems, including organ damage and nerve issues. The exact cause remains unknown, but genetics and autoimmune responses are believed to play roles. Conditions like vitiligo and Grave’s disease may coexist with type 1 diabetes.
Excessive thirst
Dry mouth
Nausea and vomiting
Persistent hunger
Frequent urination
Extreme fatigue
Significant weight loss
Blurred vision
Recurrent infections
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent type 1 diabetes, maintaining blood sugar within recommended ranges and regular health screenings can help in early detection. Managing associated conditions like high cholesterol and blood pressure, avoiding smoking, and staying up-to-date with immunizations can reduce complications. Regular checkups are vital for effective management.
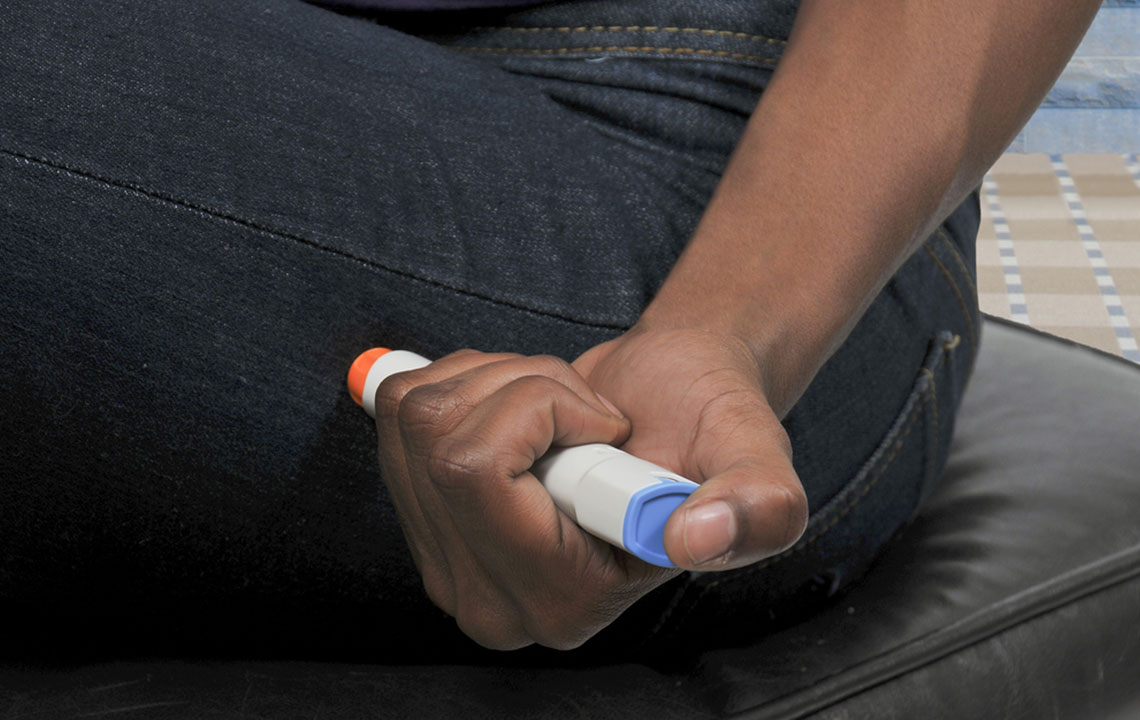
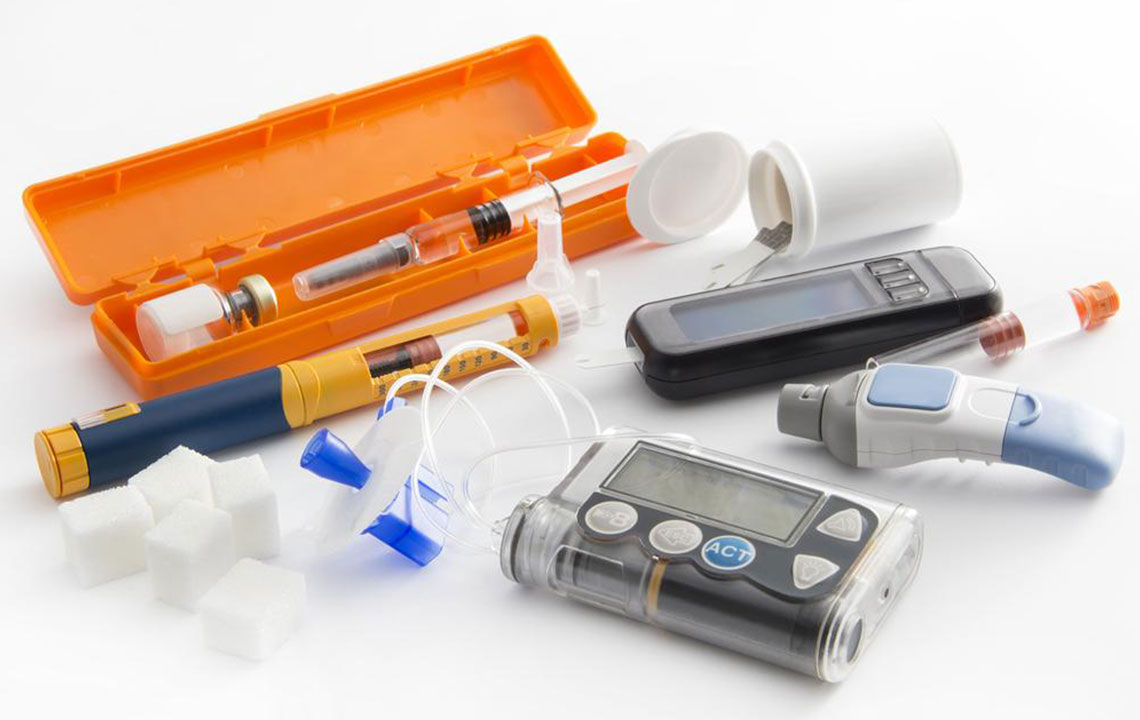
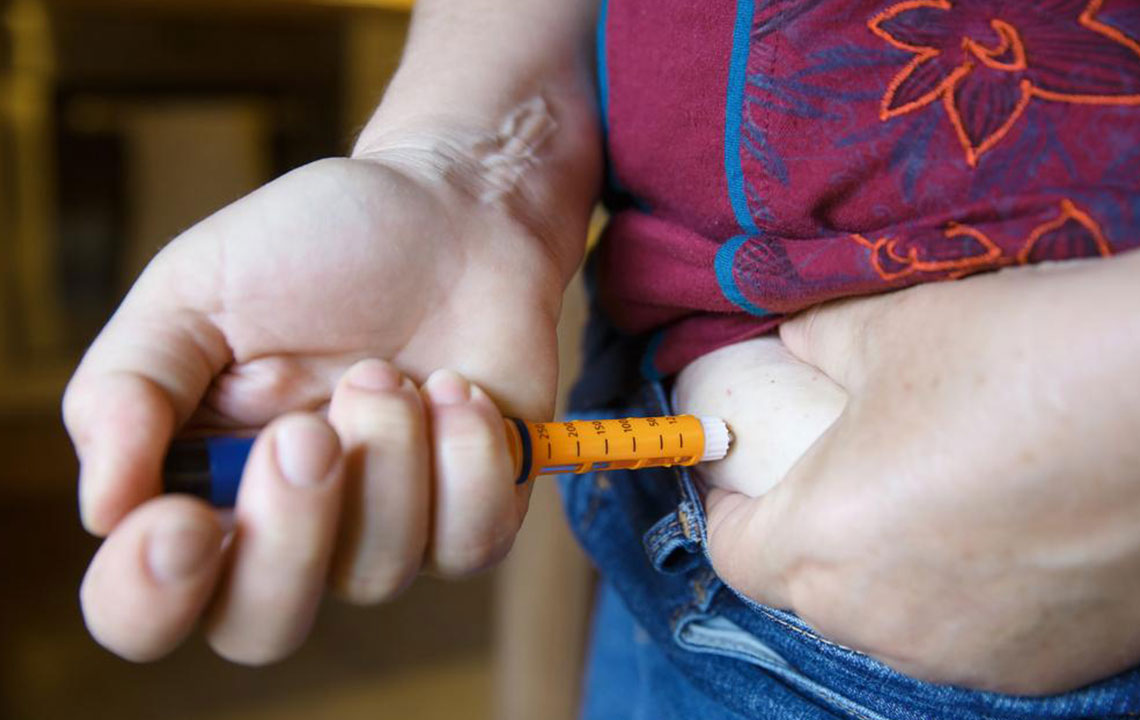
Treatment primarily involves insulin therapy, lifestyle modifications, and dietary management. Insulin can be administered via injections or an insulin pump. Combining proper nutrition and exercise helps control blood sugar levels. Monitoring glucose levels regularly ensures appropriate insulin dosing. Preventing complications like kidney disease, nerve damage, and eye problems requires diligent management and routine healthcare visits.
Overall, proactive health habits and early diagnosis can enable individuals with type 1 diabetes to lead full, healthy lives. Continuous medical support and lifestyle adjustments are essential to prevent serious health issues.