Understanding Autoimmune Disorders: A Comprehensive Overview
This article provides an in-depth overview of autoimmune diseases, including their causes, types, diagnosis, and prevention strategies. It emphasizes lifestyle changes to reduce risk and discusses available treatments to manage symptoms effectively.
Sponsored

Understanding Autoimmune Disorders: A Complete Guide
The body's immune system is designed to defend against harmful pathogens like viruses and bacteria. Its primary role is to identify and eliminate foreign invaders. However, in autoimmune conditions, the immune system mistakenly targets the body's own healthy tissues. This leads to the production of auto-antibodies that attack specific cells, causing various health issues. Autoimmune diseases can affect multiple organs and systems, resulting in significant health complications.
Contributing Factors
While the exact causes of autoimmune diseases remain unclear, research suggests genetic predisposition plays a role. Environmental influences such as diet, infections, and exposure to chemicals may also trigger these conditions.
Common Autoimmune Conditions
There are numerous autoimmune illnesses, each targeting different body parts. Notable examples include:
Type 1 Diabetes
The immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, impairing blood sugar regulation.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
The immune response damages joint tissues, leading to soreness, stiffness, and swelling.
Multiple Sclerosis
The immune system attacks the protective myelin sheath around nerve fibers, causing neurological symptoms like numbness and mobility issues.
In addition, autoimmune diseases such as lupus, Crohn's disease, Addison’s disease, Graves’ disease, and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis are prevalent.
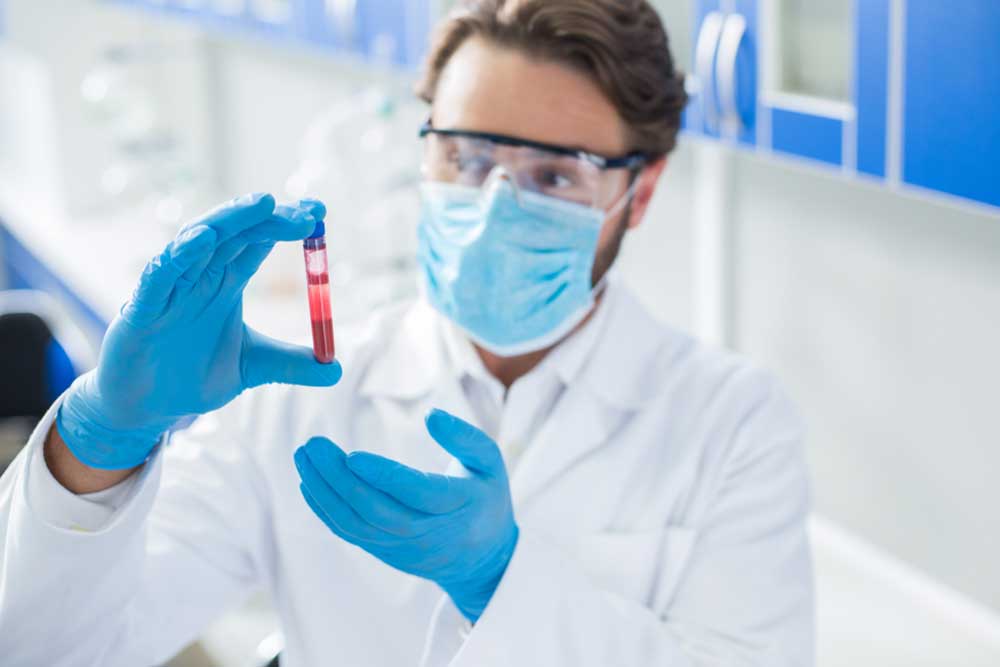
Diagnosing Autoimmune Disorders
Detecting autoimmune diseases involves multiple tests, as no single diagnostic tool is conclusive. The Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) test is commonly used to identify immune activity indicative of autoimmune conditions. Further tests analyze specific auto-antibodies and evaluate inflammation levels, assisting healthcare providers in pinpointing the exact disease.
Prevention Strategies
Though autoimmune diseases cannot always be prevented, certain lifestyle modifications can reduce risk. Avoiding toxins such as pollutants, heavy metals, pesticides, and synthetic estrogens is crucial. Abstaining from smoking, maintaining an anti-inflammatory diet, and supporting gut health through a diet rich in fruits and vegetables—while limiting sugar and grains—are beneficial. Adequate sleep and stress management also contribute to lower autoimmune risk.
While existing treatments cannot cure autoimmune diseases, medications like NSAIDs and immune suppressants help manage symptoms. These therapies control inflammation, pain, and fatigue, improving patients’ quality of life.