Understanding the Causes and Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
This article explores the causes and signs of hypoglycemia, emphasizing the importance of recognizing symptoms such as blurred vision, trembling, and confusion. It highlights the risks for diabetics and provides tips for prevention and management, including medication and lifestyle adjustments for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
Sponsored

Understanding the Causes and Signs of Low Blood Sugar
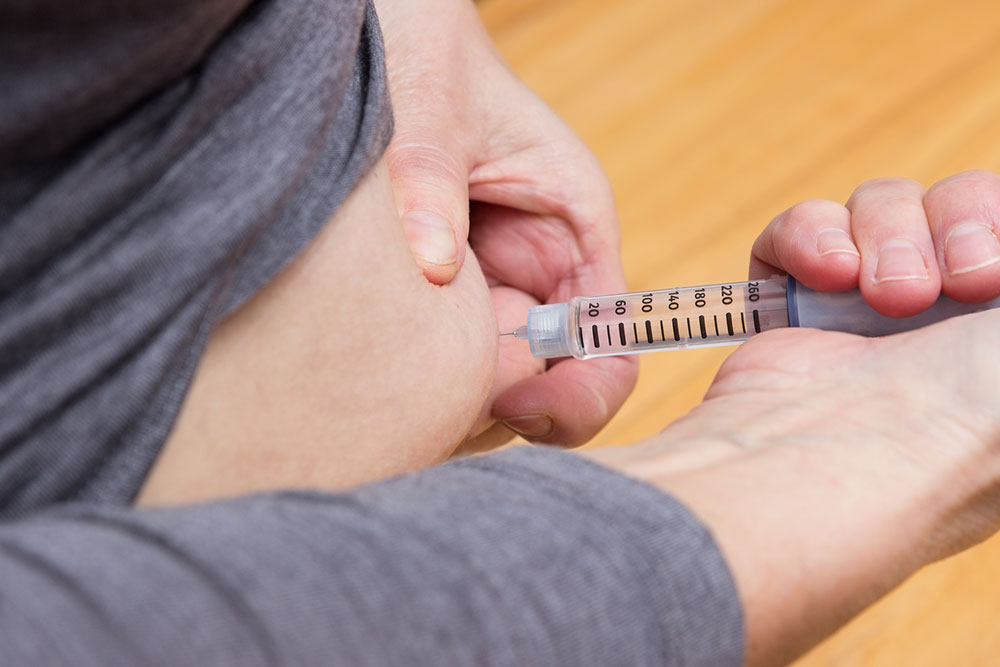
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health, especially for individuals managing diabetes with medication or insulin. Insulin, produced by the pancreas, helps break down glucose to produce energy. When insulin production is abnormal, it can lead to hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar. Excessive glucose intake stored in muscles and liver transforms into fat, serving as energy reserves. Recognizing early symptoms is vital to prevent health complications.
Common indicators of hypoglycemia include:
Blurred vision
Vision may become fuzzy, and you might feel like losing consciousness.
Pale skin
Pale skin tone is a prominent sign requiring medical attention.
Nervousness
Anxiety and emotional instability often accompany low blood sugar, causing mood swings and stress.
Persistent hunger
Feelings of constant hunger result from the body's need for glucose.
Intense tremors
Shaking episodes are linked to nervous system disruptions and catecholamine release issues.
Sleep disturbances
Nightmares and sleep disruptions can occur, sometimes leading to sleepwalking due to emotional distress.
Excessive sweating
Sudden sweating episodes without external triggers signal autonomic nervous system activity, often indicating hypoglycemia.
Skin tingling
Tingling sensations on the skin may occur, requiring consultation for proper glucose management.
Slurred speech
Speech may become unintelligible, caused by brain function impairment due to low glucose levels.
Confusion
Wandering thoughts and concentration issues can be life-threatening and need immediate attention.
Understanding these symptoms helps in early detection and treatment, primarily for those with diabetes. Medications like glucagon can be effective for managing severe hypoglycemia. Awareness of causes, such as skipped meals, excessive activity, alcohol intake, tumors producing excess insulin, kidney or liver disorders, and certain medications, can aid in prevention. Regular monitoring and consulting healthcare providers are essential for maintaining optimal health and avoiding complications.