Identifying Common Non-Allergic Asthma Triggers
This article explains the common non-allergic triggers of asthma, including infections, environmental factors, medications, and lifestyle influences. Recognizing these triggers helps in effective management and maintaining a normal quality of life. It emphasizes consulting healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies for non-allergic asthma.
Sponsored

Common Triggers for Non-Allergic Asthma
Understanding Non-Allergic Asthma Triggers
Non-allergic asthma affects individuals without harmful sensitivities to specific substances. If you experience asthma-like symptoms and allergy tests are negative, consult a specialist for proper diagnosis. Many believe asthma is solely allergy-related, but various other factors can cause airway inflammation and similar symptoms.
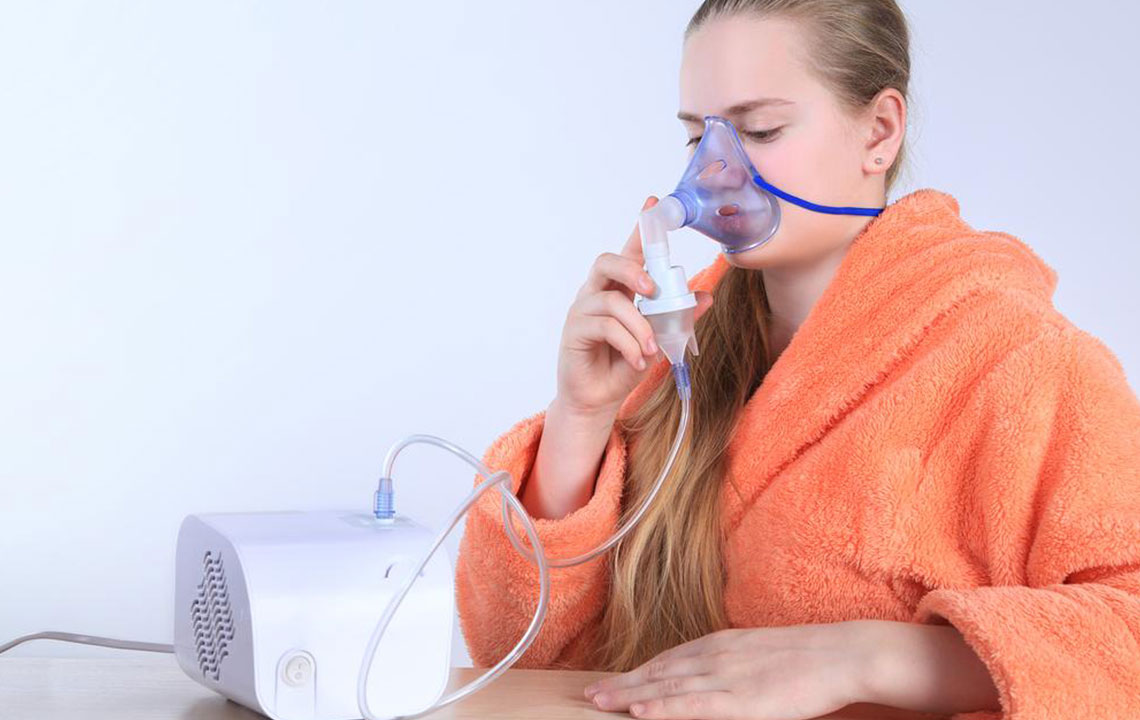
Infections and Illnesses
Common cold
Sinus or throat infections (Rhinitis)
Pneumonia
Flu
Once symptoms appear, doctors typically prescribe corticosteroids for roughly two weeks, and medication can be discontinued as symptoms resolve.
Other Causes of Non-Allergic Asthma
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) – Similar symptoms to asthma, mostly affecting smokers. Managed with inhalers and medication, with smoking cessation essential.
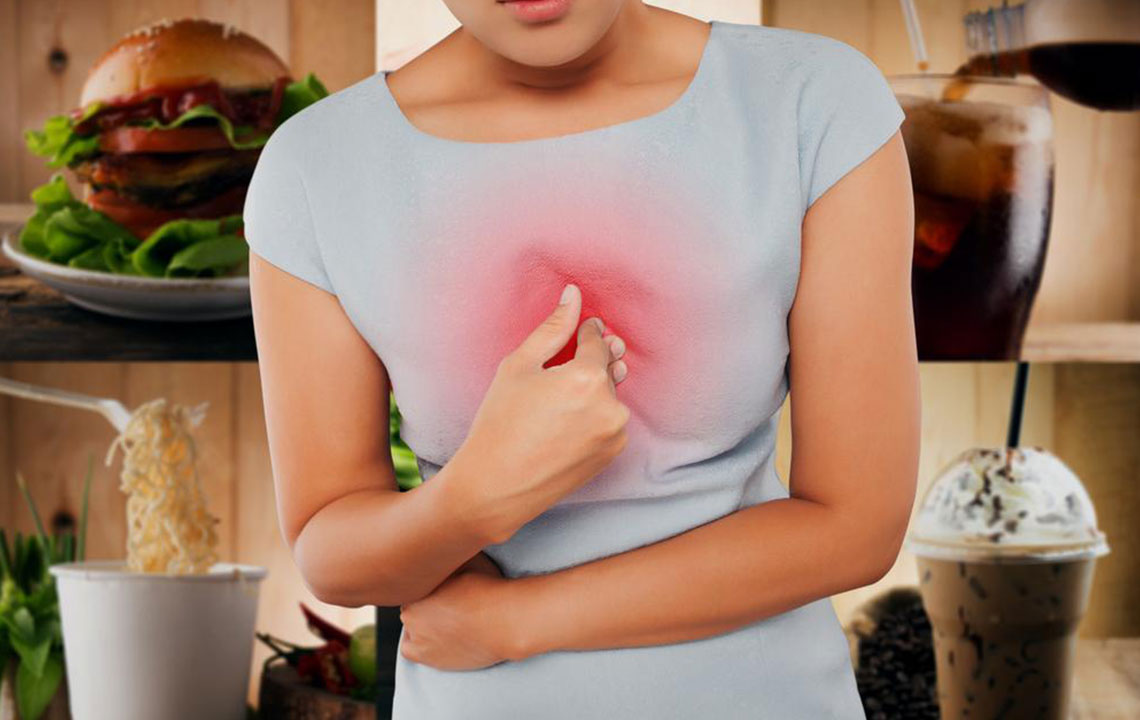
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) – Stomach acids entering the esophagus can cause cough and asthma-like signs. Managing with smaller meals, avoiding cold foods, and refraining from lying down immediately after eating helps. Medications to reduce acidity are effective.
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) – A fungal sensitivity causing asthma symptoms, treated with corticosteroids and antifungals.
Nasal polyps – Inflamed growths inside the nose linked to sinus inflammation, increasing allergen sensitivity. Treated with nasal sprays or surgically removed.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) – Breathing interruptions during sleep due to airway obstruction, often linked to obesity. Requires prompt treatment as it is a serious condition.
Medications and Environmental Factors
Certain drugs like aspirin and NSAIDs can trigger asthma symptoms. Beta-blockers used for heart issues may also cause issues—dosages are adjusted accordingly. Exposure to sudden temperature changes, heavy rain, wind, pollen, or dust clouds can act as triggers. Physical activity can induce exercise-related asthma, but with proper medication, individuals remain active. Food additives, hormonal shifts during menopause, and other environmental factors can also contribute. People with asthma should avoid triggers, adhere to prescribed medication, and follow a healthy diet for optimal management.