Comprehensive Overview of Pneumonia Types and Causes
This article provides a detailed overview of pneumonia, highlighting its various types, causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and preventive measures. Understanding these aspects helps in early detection and effective management of this lung infection, which can be serious if left untreated. The piece emphasizes the importance of vaccination and prompt medical attention for better recovery outcomes.
Sponsored

Understanding the Different Forms and Origins of Pneumonia
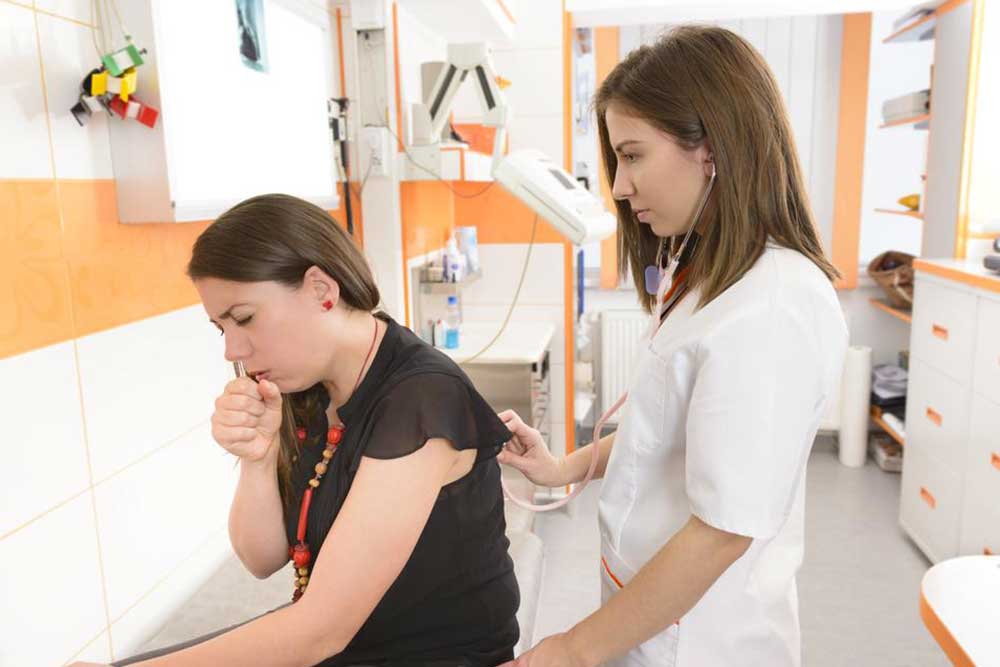
Pneumonia is a lung infection that inflames the air sacs within the lungs, leading to fluid buildup or pus formation. This condition hampers normal breathing and can be triggered by bacteria, fungi, viruses, or other pathogens. Symptoms may include cough, mucus production, chest discomfort, chills, fever, and breathing difficulty, varying based on age and pneumonia type.
Classification of pneumonia depends on the pathogen involved:
Bacterial pneumonia: Caused by bacteria like Streptococcus pneumonia, Chlamydophila pneumonia, and Legionella pneumophila.
Viral pneumonia: Often affects children and the elderly due to weakened lung resilience, caused by viruses.
Mycoplasma pneumonia: A milder form affecting those over 12 years old.
Fungal pneumonia: Occurs in immunocompromised individuals when fungi from soil or bird droppings infect the lungs.
Pneumonia can be contracted in healthcare settings (nosocomial) or community environments, with some forms resistant to standard treatments. Infection routes include ingestion, aspiration, or ventilation support. Diagnosis methods encompass blood, sputum, urine tests, CT scans, and fluid analysis. Treatment varies based on the cause, typically involving antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungal medications. Recovery may take weeks, especially in severe cases, emphasizing the importance of prompt treatment. Preventive vaccines like Prevnar 13, Pneumovax 13, and Pneumovax 23 can significantly reduce infection risk.