Comprehensive Guide to Pulmonary Infection: Pneumonia
This comprehensive overview explains pneumonia's causes, symptoms, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment options. It emphasizes preventive measures, including vaccination, lifestyle changes, and hygiene practices, essential for reducing risk. The article guides patients and caregivers on managing the illness effectively, highlighting the importance of timely medical intervention and supportive care to ensure recovery. Suitable for those seeking an in-depth understanding of pneumonia, it serves as a valuable resource for patient education and health awareness.
Sponsored

Understanding Pneumonia: Causes, Risks, and Management
Pneumonia is a prevalent respiratory condition characterized by inflammation of the lung airspaces due to infection. It can be triggered by viruses, bacteria, or fungi, affecting individuals across all age groups at any time. Typically, it involves one lung lobe, but if untreated, it can spread to both lungs, leading to serious health complications.
Learn essential information about pneumonia below.
What is pneumonia?
Pneumonia is a lung infection caused by different pathogens, resulting in inflammation of lung tissues.
It often begins with a viral, bacterial, or fungal invasion.
As the infection progresses, the lung tissues become inflamed, with fluid filling the alveoli, making breathing difficult.
Anyone can develop pneumonia, but it presents a higher risk for those over 65, young children under two, individuals with certain health conditions, and smokers.
Is pneumonia contagious?
Yes, pneumonia can spread from person to person.
The bacteria, viruses, or fungi responsible for pneumonia can be transmitted through sneezing or coughing. When healthy individuals inhale these pathogens, they can become infected, although not everyone exposed will necessarily get sick.
The contagiousness varies depending on the causative organism. Some viruses spread more easily than others. Fungal pneumonia typically transmits through environmental exposure rather than direct contact.
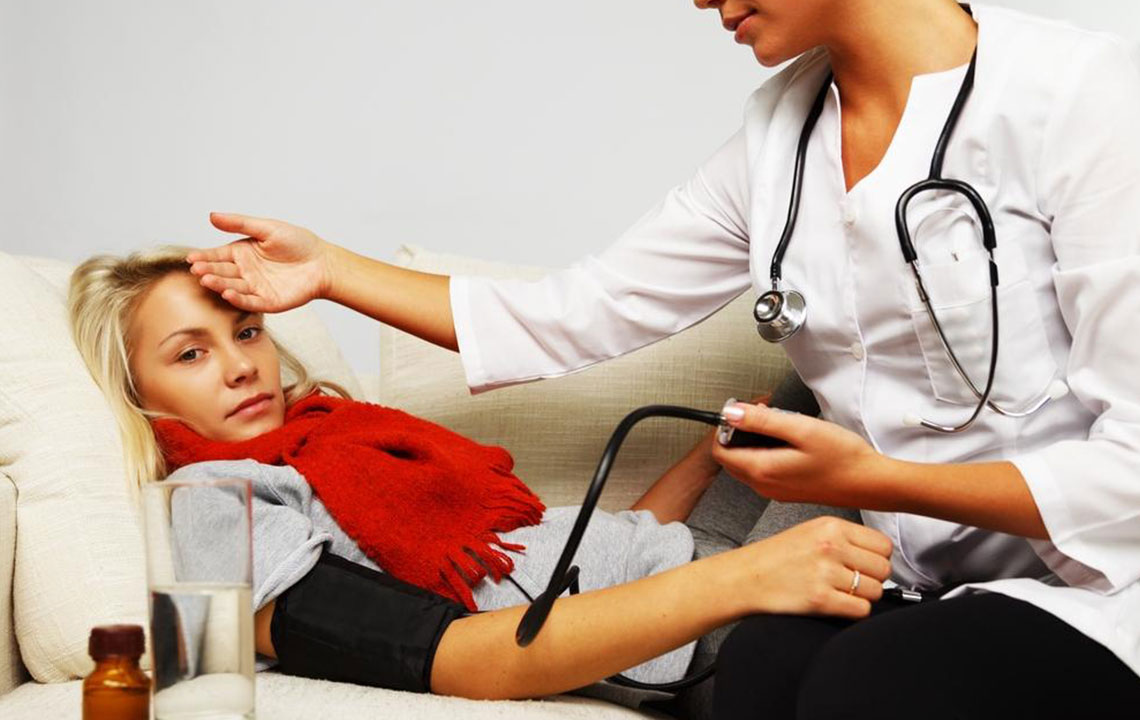
Managing pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia is commonly treated with antibiotics.
Viral pneumonia often improves with rest and supportive care.
Staying well-hydrated helps in fluid elimination and recovery.
Fungal pneumonia requires specific antifungal medications.
Vaccination can play a role in prevention and management.
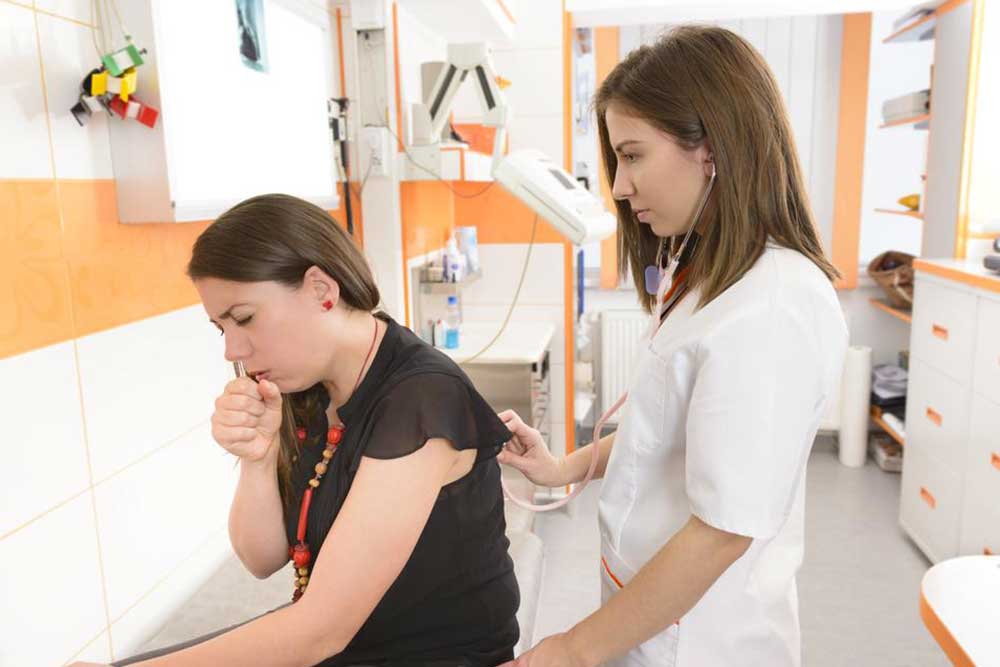
Diagnosis of pneumonia
Seek medical evaluation if symptoms emerge for accurate diagnosis.
The doctor reviews medical history and conducts physical examinations.
Chest X-rays are crucial for identifying affected areas.
Additional tests like CT scans and blood work assess severity and causative agents.
Sputum analysis helps determine the infectious organism.
Lifestyle and dietary recommendations for pneumonia patients
Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke are vital.
Reduce alcohol intake to support immune health.
Maintain a nutritious diet rich in vitamins and minerals.
Drink plenty of fluids, such as water, fruit juices, and fresh fruits.
Practice good hygiene to prevent further infections.
Follow medical advice and take prescribed medications timely.
Ensure adequate rest to boost recovery.