A Complete Guide to Understanding and Preventing Osteoporosis
This comprehensive article explains osteoporosis, its risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and prevention methods. It emphasizes lifestyle changes like diet and exercise to help manage and prevent this bone-weakening disease, especially for those at high risk such as postmenopausal women and the elderly.
Sponsored

Osteoporosis is a condition where bones become fragile and prone to fractures. It occurs when the body cannot regenerate enough new bone to replace old tissue, leading to decreased bone density and strength. Commonly affecting the hips, spine, and wrists, this disease impacts both men and women, with postmenopausal women being at higher risk. Maintaining a balanced diet, adhering to prescribed medications, and engaging in weight-bearing exercises are effective strategies to manage osteoporosis. Early detection and lifestyle modifications are key to prevention and treatment.
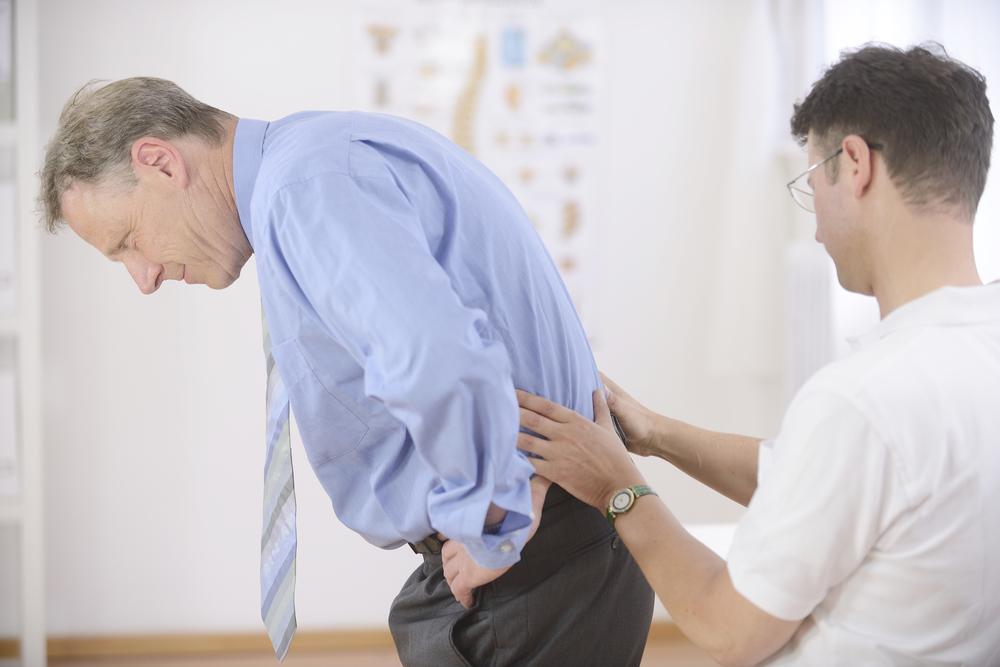
Factors increasing the risk of osteoporosis include genetic predisposition, gender, ethnicity, age, body type, existing health conditions, and previous fractures. Women over 50, especially those of Asian or Caucasian descent, are more susceptible. Bone loss begins after age 30, making early prevention important. Symptoms can include stooped posture, back pain, loss of height, and easy fractures. It’s essential to seek medical attention if severe pain or fractures occur. Diagnosis involves medical history, physical exams, blood tests, and bone density scans like DEXA. Preventive measures include quitting smoking, a calcium- and vitamin D-rich diet, regular weight-bearing exercise, and proactive health checks.