Understanding the Five Main Variants of Crohn's Disease
Crohn's disease presents in five distinct forms, each affecting different parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Recognizing these types—such as colitis, jejunoileitis, ileocolitis, ileitis, and gastroduodenal Crohn's—enables more targeted treatment approaches. Symptoms range from abdominal pain and diarrhea to weight loss and ulcers, emphasizing the importance of early detection. This article offers a comprehensive overview of the main Crohn's disease variants, aiding patients and healthcare providers in managing this complex condition effectively.
Sponsored
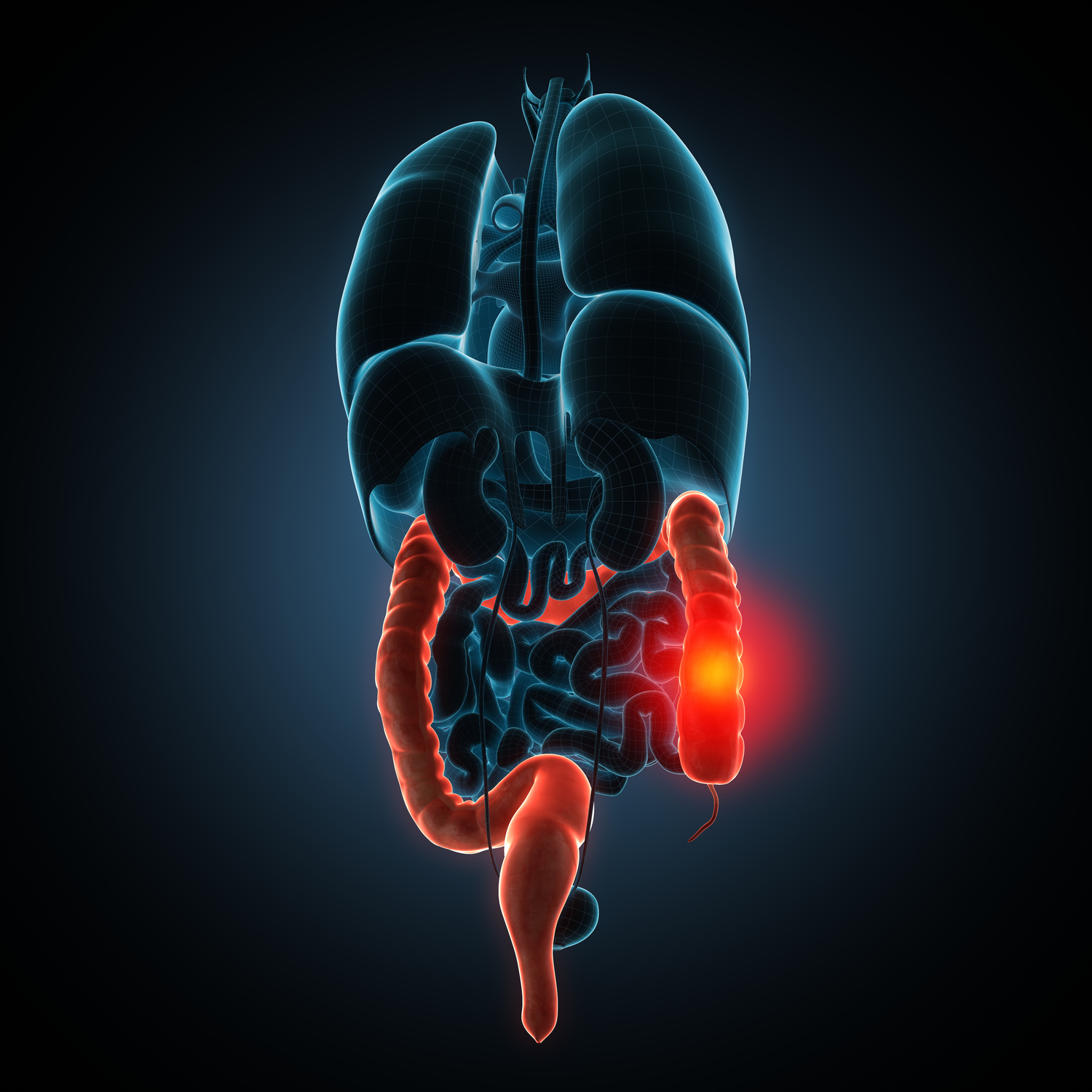
Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory condition impacting the digestive system, leading to serious complications if left untreated. It manifests in five main types, each with unique symptoms and treatment strategies. The disease primarily involves the lower small intestine and the colon, but can affect various parts of the gastrointestinal tract across different age groups, especially between 15 and 35. It damages bowel tissues, causing swelling, scarring, and ulcers, which can block the digestive passage and impair nutrient absorption, resulting in severe health issues.
Here are the five primary forms of Crohn's disease:
Colitis Crohn's: This type affects the colon, causing ulcers, fistulas, abscesses, rectal bleeding, diarrhea, joint pain, and skin changes. Symptoms range from moderate to severe discomfort.
Jejunoileitis: Impacting the upper small intestine (jejunum), it leads to cramps after eating, anal fistulas, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
Ileocolitis: The most common form, affecting the ileum and colon, resulting in weight loss, diarrhea, and cramping.
Ileitis: Focused on the ileum, with symptoms similar to ileocolitis but also prone to fistulas and abscess formation.
Gastroduodenal Crohn's Disease: Involving the stomach and duodenum, it causes nausea, loss of appetite, and weight loss.
Understanding these variants can help in early diagnosis and tailored treatment, improving patient outcomes.