Understanding Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management
Gout is a painful joint condition caused by uric acid crystals, often affecting the big toe. It results from high uric acid levels due to diet, genetics, and health factors. Effective treatment includes medication and lifestyle changes to lower uric acid and prevent flare-ups, emphasizing dietary adjustments and medical management for long-term relief.
Sponsored
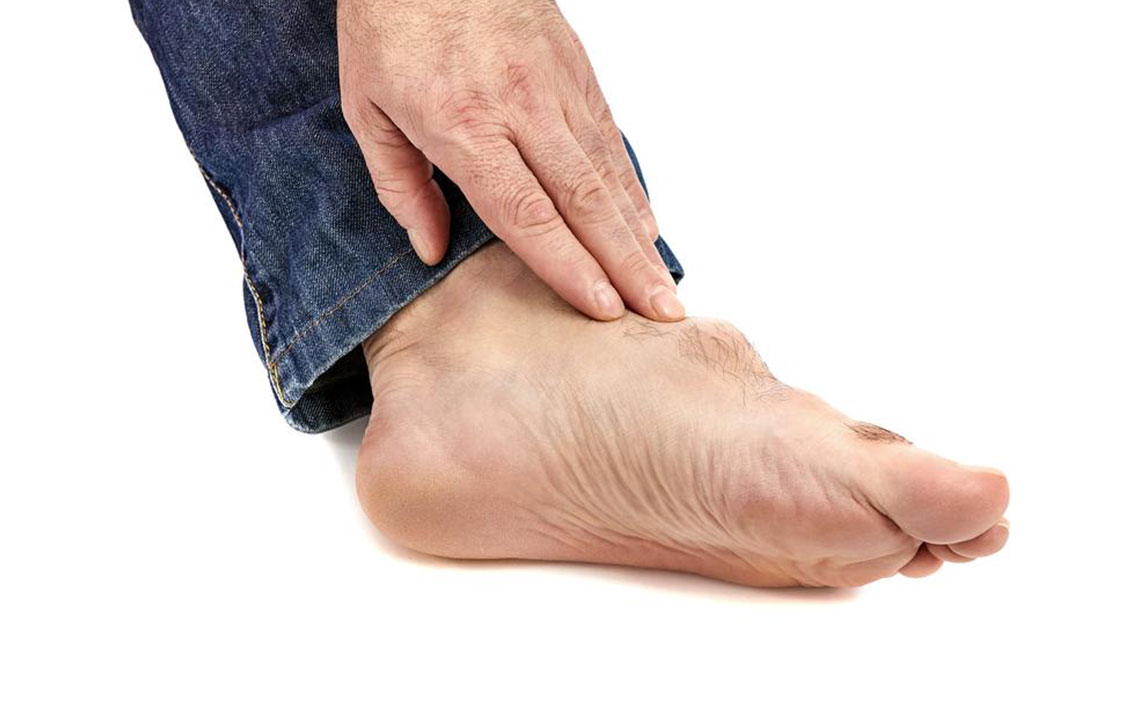
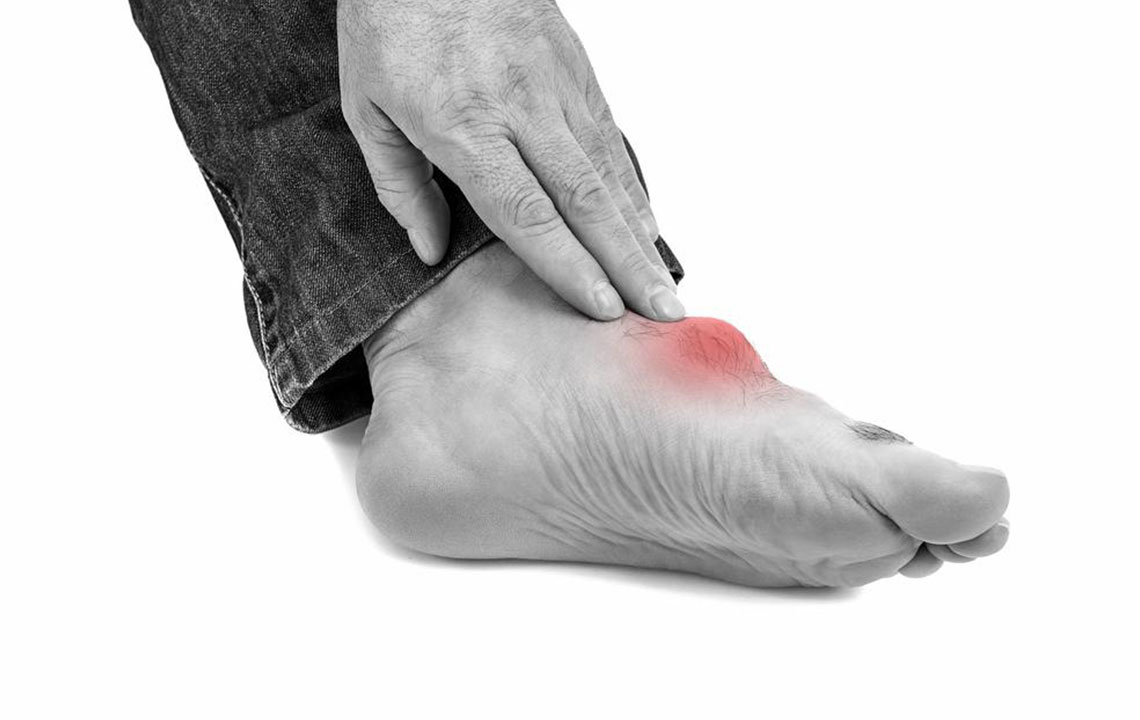
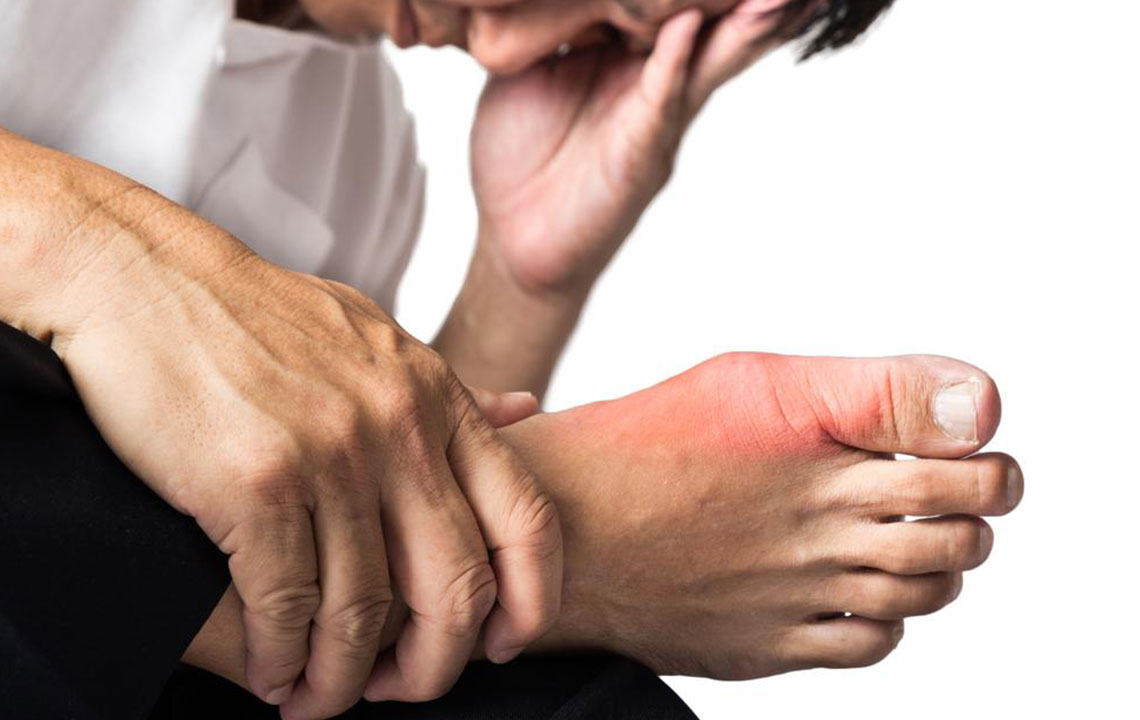
Gout is a joint disorder caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals, leading to sudden and intense pain, swelling, and redness. It predominantly affects the feet, especially the big toe, but can occur in other joints as well. Recognizing its causes is vital for prevention and treatment. High levels of uric acid, resulting from purine breakdown in foods, are the main trigger. Factors such as genetics, obesity, kidney issues, and diet play significant roles. Managing gout involves lifestyle modifications and medication to reduce uric acid levels and mitigate symptoms.
What causes gout?
Gout occurs when excess uric acid in the blood crystallizes and accumulates in joints. Normally, uric acid dissolves and is eliminated via the kidneys, but in some cases, it builds up due to inefficient excretion or overproduction. Consuming purine-rich foods like red meat, organ meats, and alcohol can increase uric acid levels. Other factors include genetic predisposition, obesity, and impaired kidney function.
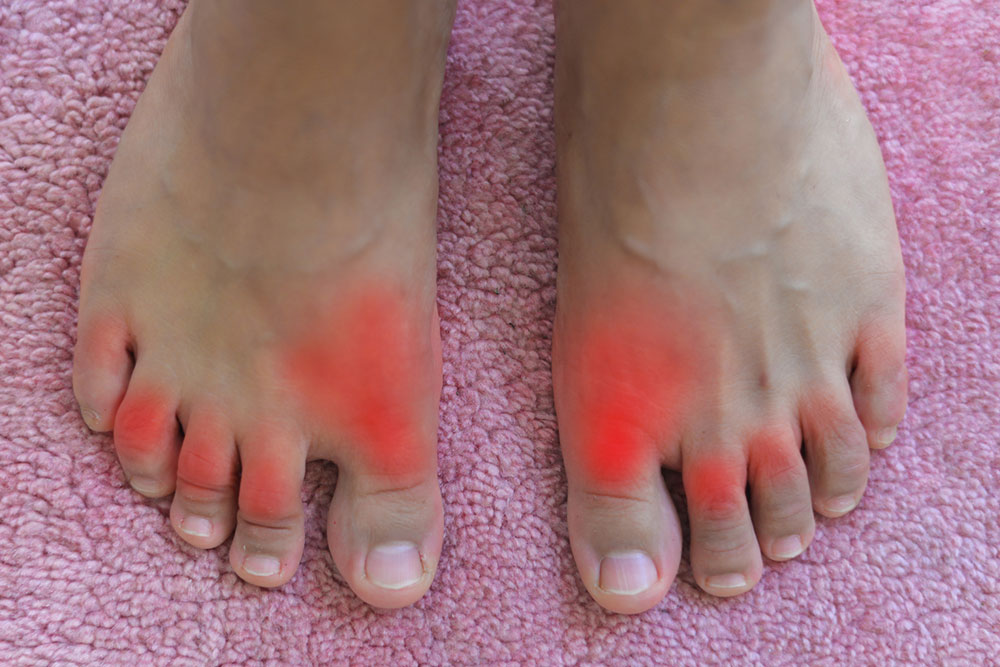
Symptoms of gout often manifest as sudden, severe pain in affected joints, commonly the big toe. The joint becomes swollen, red, and tender, with skin stretching tight and movement restricted. Recurrent episodes can involve multiple joints over time. The formation of tophi—visible, chalky nodules under the skin—is another sign of chronic gout.
How is gout treated?
Gout treatment depends on severity. Minor cases may be managed through dietary changes, such as reducing intake of alcohol, red meats, and organ foods. Persistent or severe attacks require medications like uric acid-lowering drugs, anti-inflammatory agents, and prophylactics. Common drugs include allopurinol, probenecid, and febuxostat. Alongside medication, a healthy diet and weight management are essential for preventing future episodes.