Understanding Gout: Causes, Symptoms, Management, and Dietary Recommendations
Discover comprehensive insights into gout, including its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and dietary tips. Learn how lifestyle changes and medications can help manage this painful condition effectively and prevent future attacks. Embrace a gout-friendly diet emphasizing low purine foods, hydration, and weight management for healthier joints and improved quality of life.
Sponsored
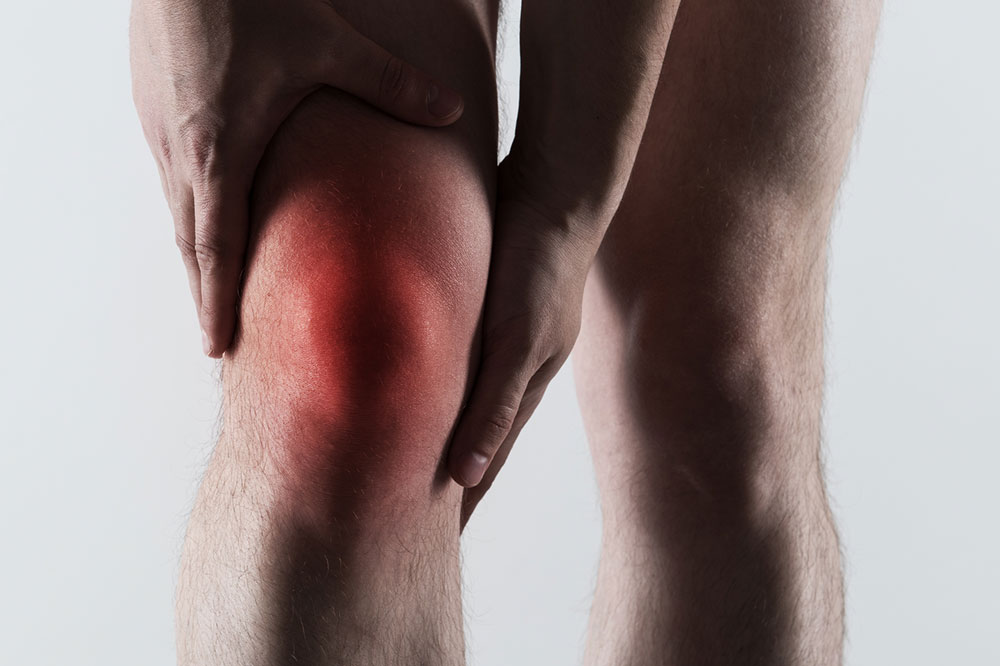
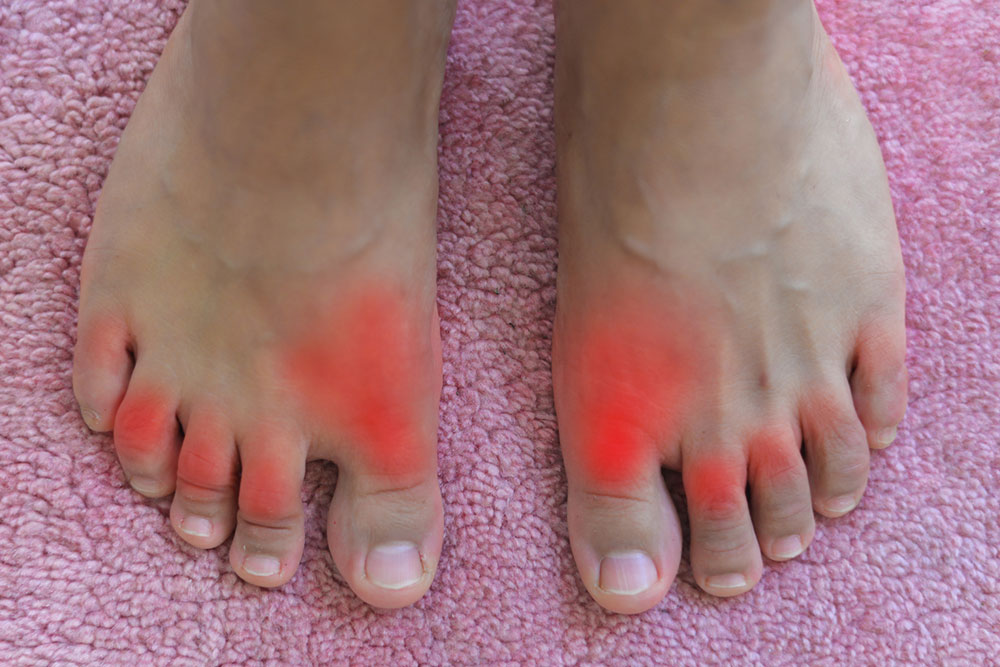
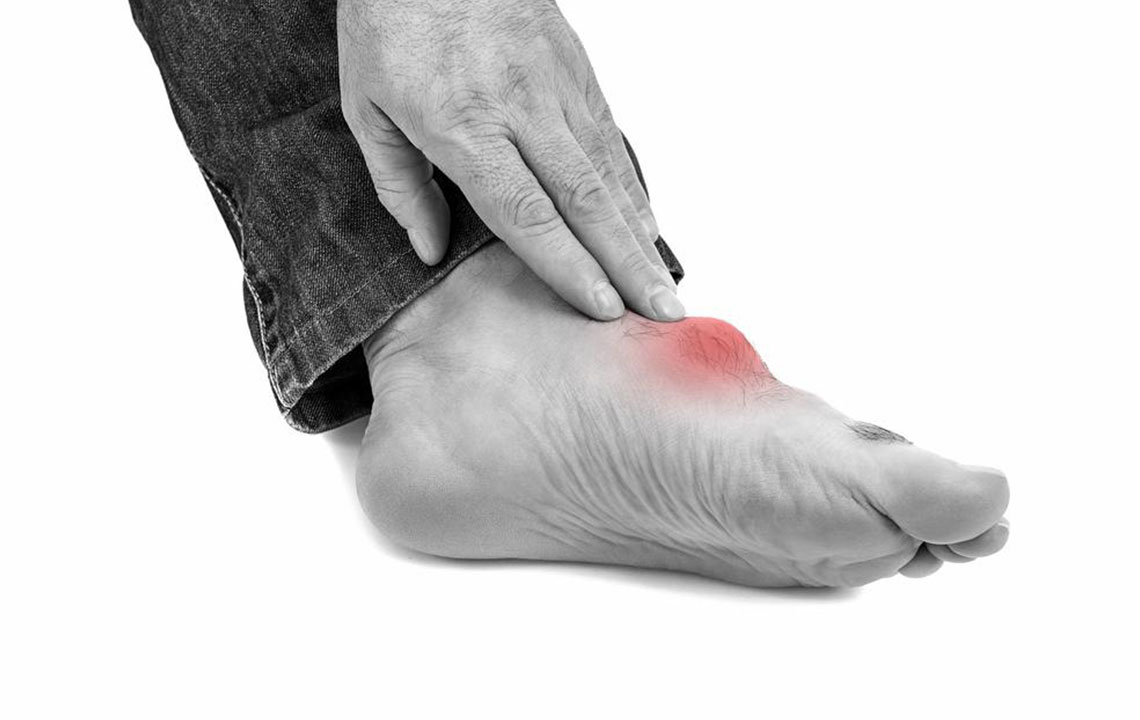
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis that causes sudden and severe joint pain. It arises when uric acid crystals deposit around joints, leading to episodes of intense inflammation. Commonly impacting the big toe, gout can also affect knees, ankles, wrists, and fingers. The condition tends to recur, with each attack bringing swelling, redness, heat, and tenderness. Elevated uric acid levels in the blood, often due to genetic factors or diet, are the primary cause. Lifestyle, diet, and weight management play a crucial role in controlling gout symptoms.
Historically called “the disease of kings,” gout was linked to rich diets and excess alcohol. Nowadays, factors like obesity, excessive meat and alcohol consumption, and processed foods increase risk. A gout-friendly diet emphasizes vitamin C, dairy, and moderation in high-purine foods, along with regular exercise. Symptoms include sudden joint pain, swelling, and sometimes fever or fatigue. To prevent chronic damage, treatment combines medication to reduce inflammation and lower uric acid, along with dietary adjustments. Medications such as NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and uric acid reducers like allopurinol are common. Limiting purine-rich foods—shellfish, red meat, organ meats, certain fish—and staying well-hydrated are key strategies. Lifestyle modifications, including weight loss and exercise, complement medical treatment for effective gout management.