Managing Gout Pain: Symptoms and Effective Remedies
Learn about the symptoms of gout and discover effective treatments, including medications, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies to manage pain and prevent future attacks.
Sponsored

Managing Gout Discomfort: Recognizing Symptoms and Treatment Options
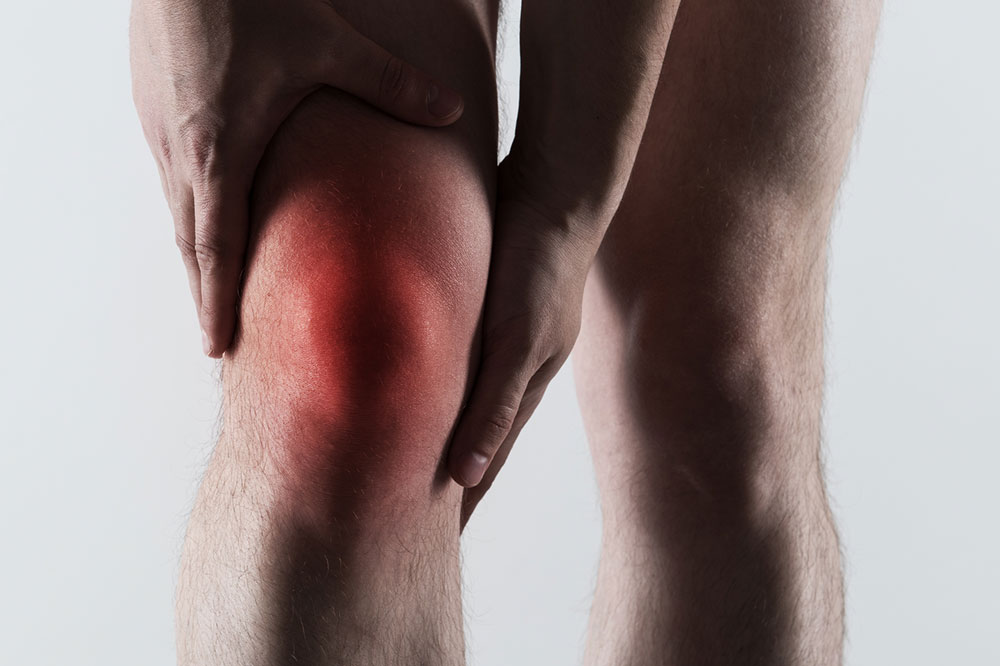
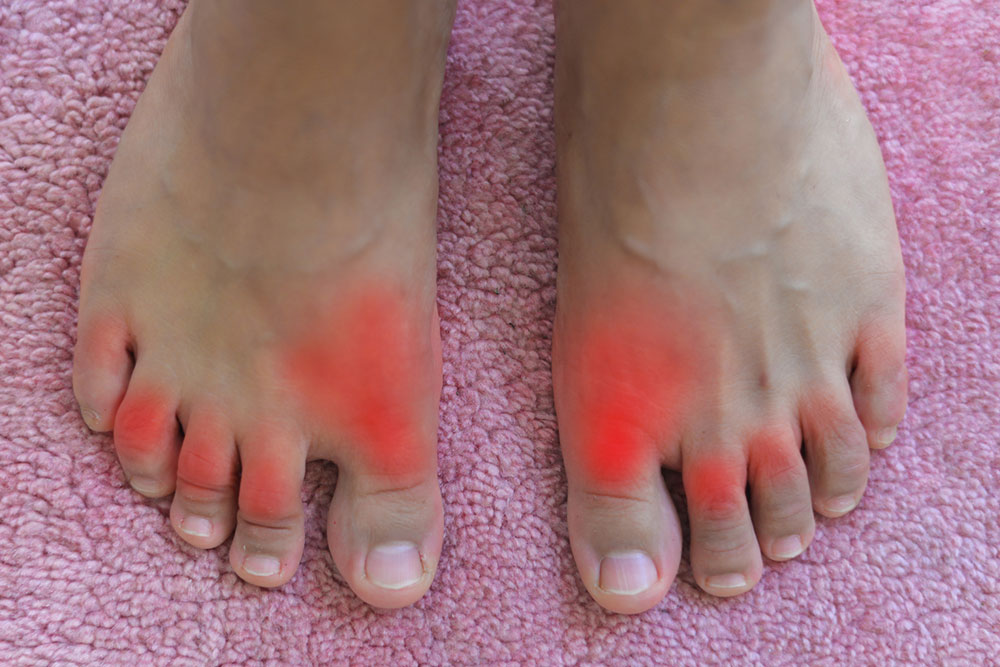
Sudden intense pain often strikes the big toe or other joints, causing significant discomfort that can occur unexpectedly anytime. These symptoms are characteristic of gout, a type of arthritis caused by excess uric acid crystals forming in joints. Gout commonly affects the big toe and can impact anyone. An attack typically lasts around 10 days, with the worst pain happening within the first three days.
If untreated, gout can spread to neighboring joints. Prompt treatment reduces inflammation, alleviates pain, and prevents joint involvement.
Early intervention is key to controlling gout attacks. Symptoms vary depending on uric acid buildup, with crystals forming in joints. Key signs include:
Severe joint pain: Most commonly in the big toe, but it can extend to ankles, elbows, wrists, and fingers.
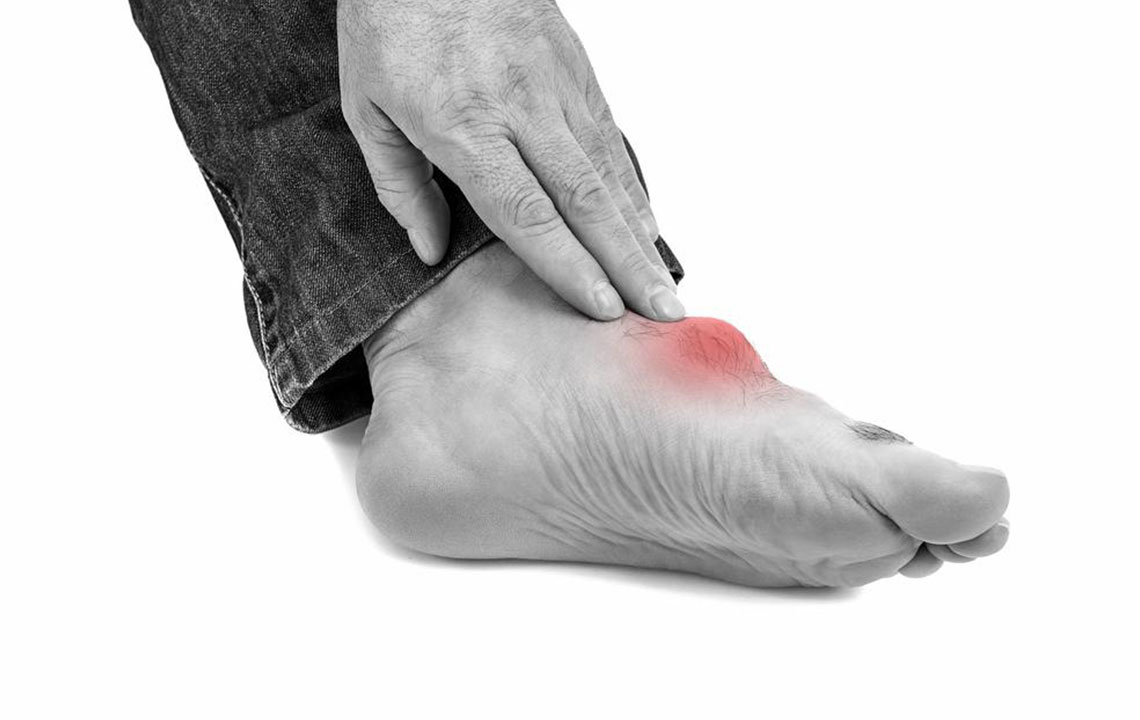
Swelling: Uric acid deposits cause noticeable swelling and nodules under the skin at affected joints.
Persistent discomfort: Post-attack, mild pain can linger for weeks, with future episodes potentially lasting longer and becoming more intense.
Inflammation: Joints appear red, tender, and warm due to uric acid accumulation.
Limited mobility: Swelling and pain restrict movement, especially in the big toe.
Balance issues: Pain and swelling can cause difficulty walking, leading to balance problems.
Fever: Severe attacks may be accompanied by fever, indicating possible joint infection.
Gout Management Strategies
Early treatment usually reduces symptoms within ten days, even without intervention. Severe cases involving fever require immediate medical care. Depending on severity, treatments include medications and lifestyle changes.
Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids help relieve pain. Uric acid-lowering drugs prevent future attacks by reducing crystal formation.
Home Care: Using cold packs, resting, and wearing comfortable footwear help ease symptoms. Limiting joint use promotes faster recovery.
Diet and Lifestyle: Lowering purine-rich foods, increasing fluid intake, and avoiding alcohol and caffeine help prevent gout flare-ups. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces attack frequency.
Alternative Therapies: Herbal supplements like turmeric and bromelain, acupuncture, and hot-cold compresses may offer additional relief when traditional treatments don’t suffice.
Gout management involves medication, physical adjustments, and lifestyle modifications. Untreated gout can lead to recurrent attacks, joint damage, and kidney issues.