Understanding Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management
Gout is a painful arthritis condition caused by high uric acid levels, influenced by genetics, lifestyle, and diet. Symptoms include severe joint pain, swelling, and redness, often affecting the big toe. Treatment involves medications, dietary changes, and healthy habits to manage and prevent attacks. Early diagnosis and lifestyle modifications are key to controlling this condition and avoiding joint damage.
Sponsored
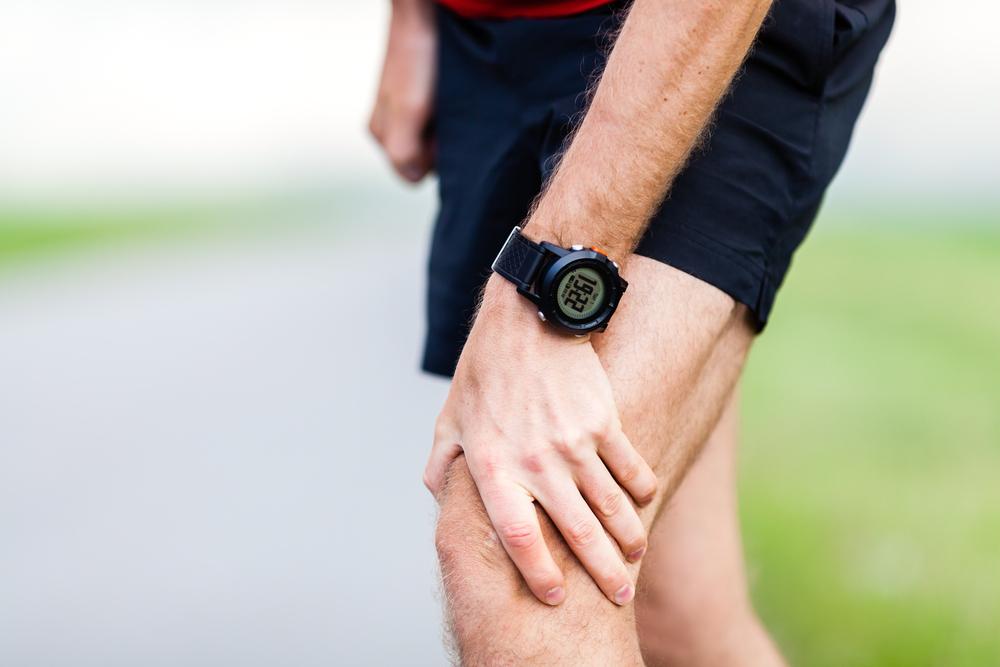

Gout is a debilitating form of arthritis characterized by sudden, intense joint pain and swelling. It affects both men and women, with higher prevalence in men over 40. Women often experience symptoms post-menopause. Attacks typically last a few days or weeks, with pain gradually diminishing. If symptoms worsen or don't respond to treatment, medical consultation is essential. Gout arises from multiple factors, including genetic predisposition, high blood pressure, and lifestyle habits like excessive alcohol intake and red meat consumption. Managing gout involves medications, lifestyle adjustments, and dietary changes to control uric acid levels.
Causes Certain genetic factors increase susceptibility to gout. Other contributors include hypertension, elevated cholesterol, type-2 diabetes, obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, and high-purine diets. Medications and weight gain can also trigger attacks.
Symptoms of gout often begin abruptly, typically at night, and can include:
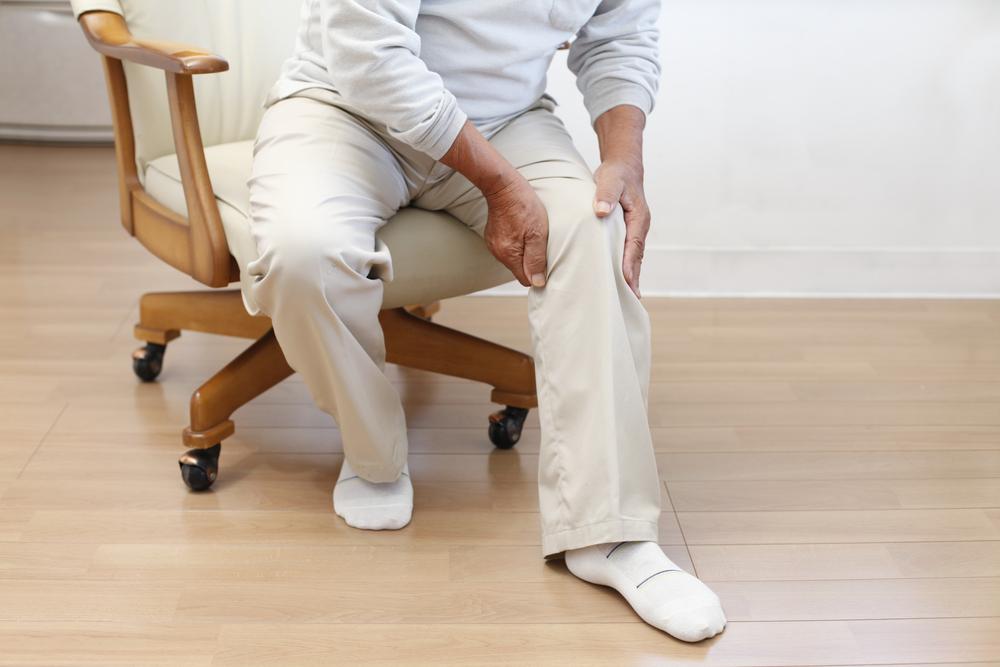
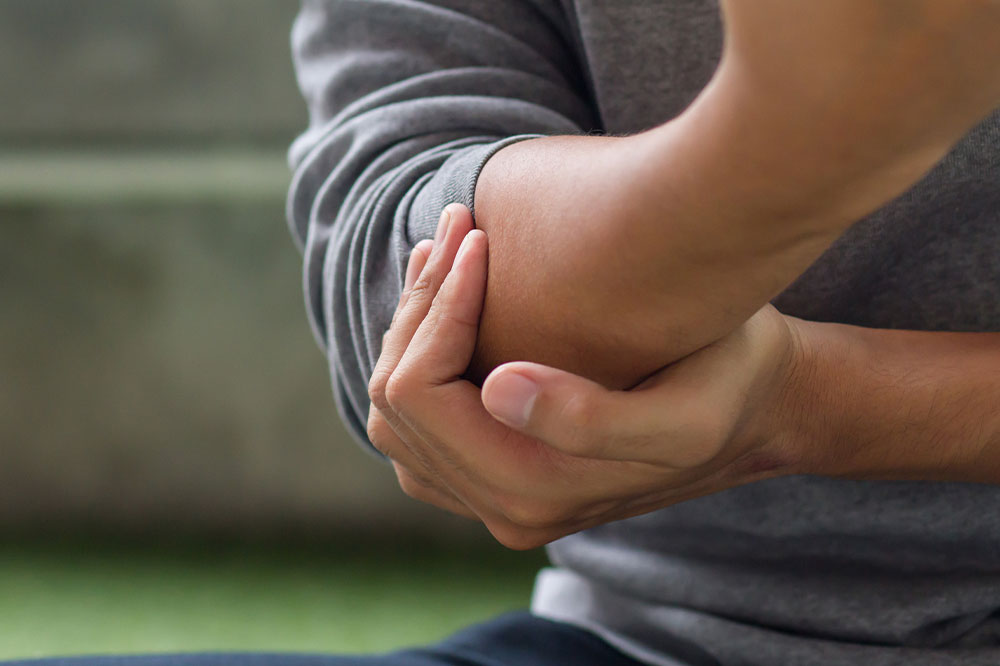
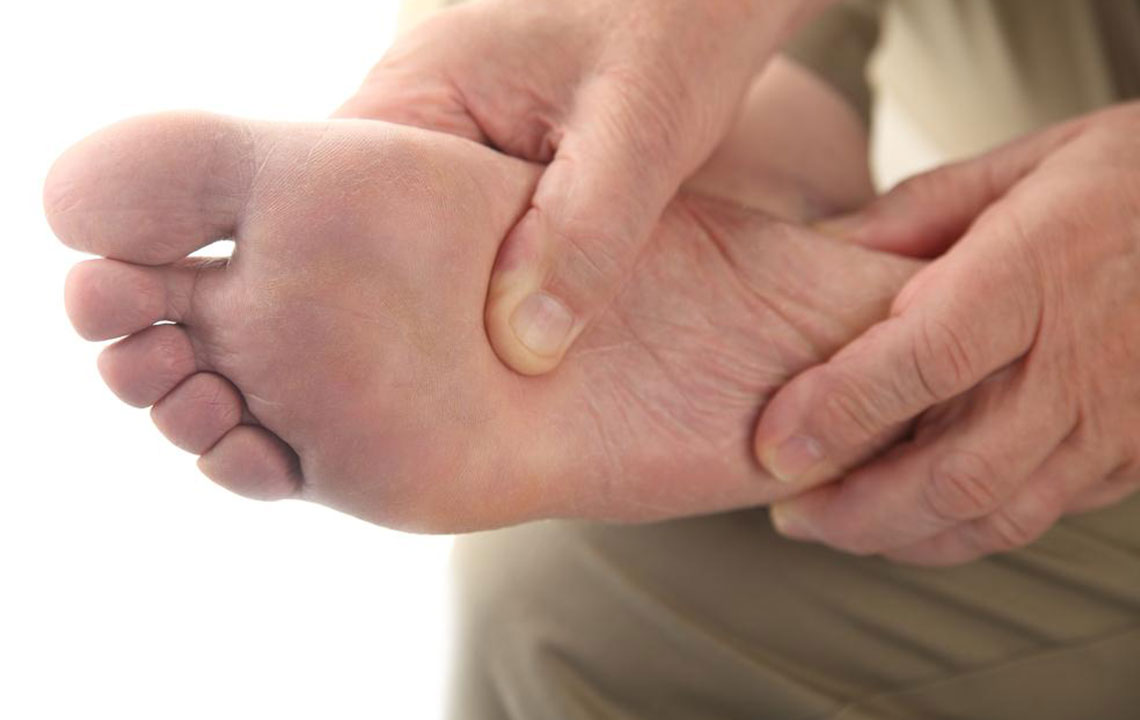
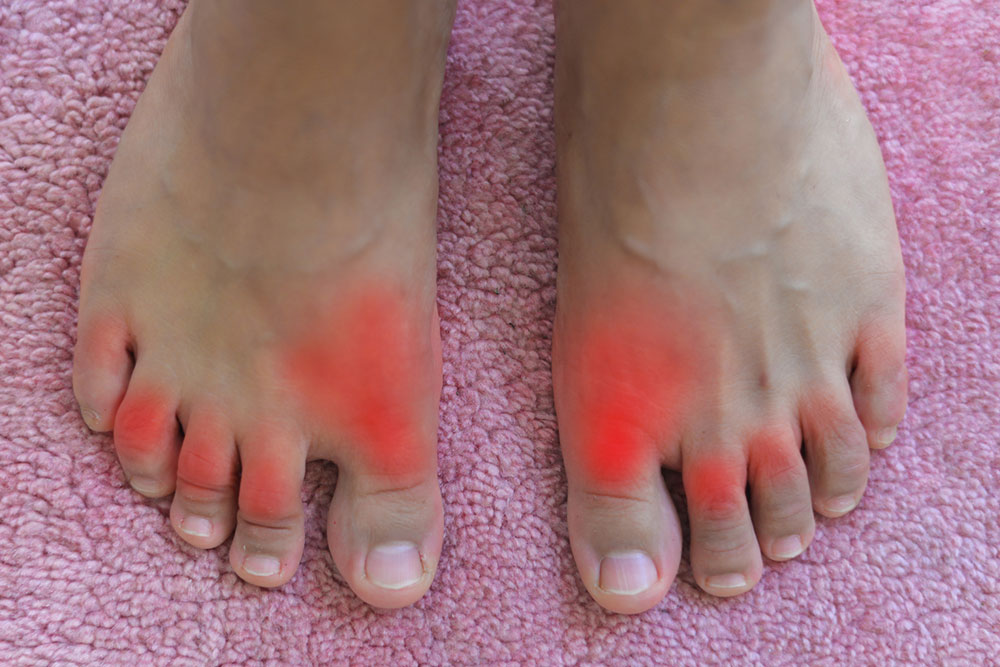
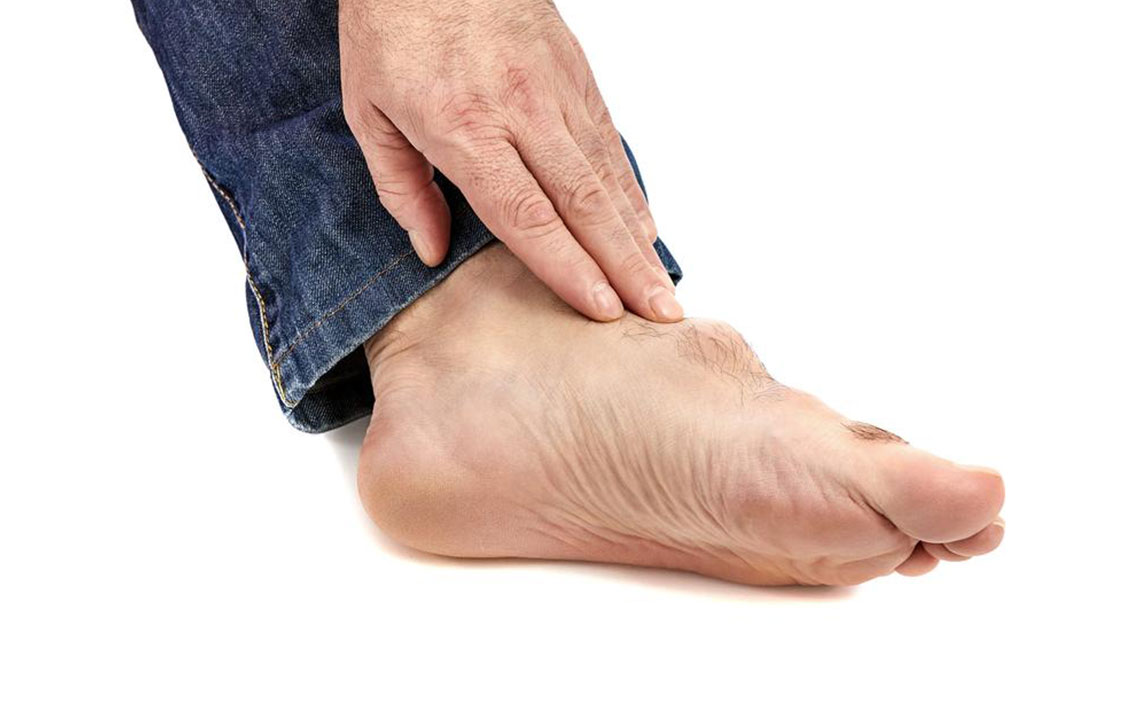
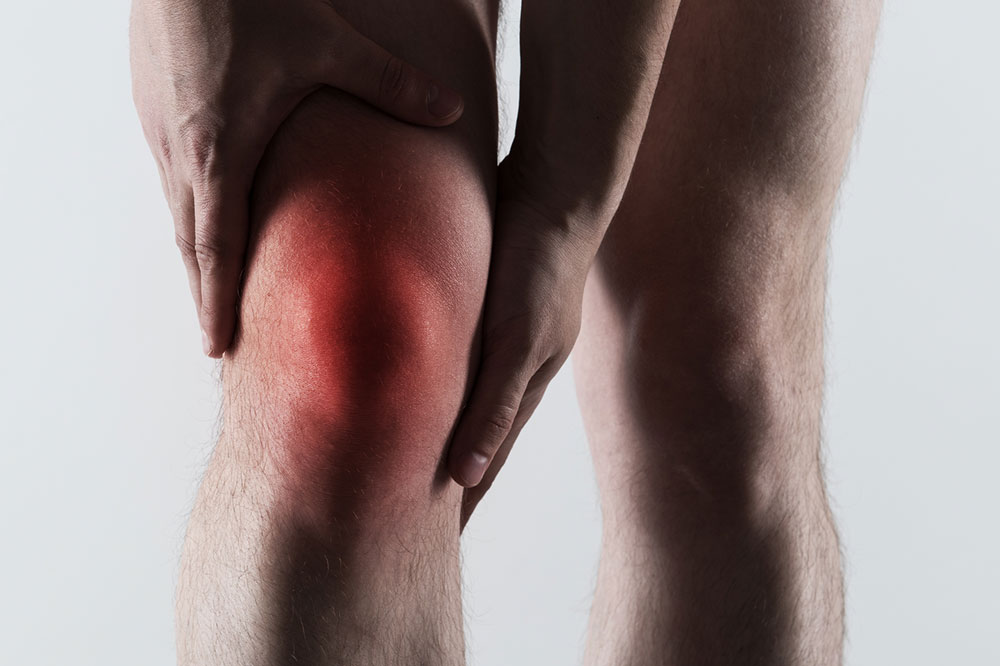
Excruciating joint pain: Usually affects the big toe but can involve ankles, wrists, elbows, or knees. Pain intensifies within hours.
Lasting discomfort: Pain diminishes, but residual pain or swelling can persist for days or weeks, with subsequent attacks involving more joints and lasting longer.
Limited mobility: Swelling and pain restrict joint movement, making even simple tasks painful.
Redness and swelling: Affected joints become tender, red, and warm.
Formation of tophi: Chronic untreated gout can lead to nodules under the skin called tophi, causing joint damage.
Effective treatment includes medications to reduce inflammation and uric acid levels, along with lifestyle changes. Doctors may prescribe NSAIDs, pain relievers, uric acid-lowering drugs, and recommend dietary modifications such as reducing purine-rich foods, quitting alcohol and smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight. Adequate hydration and vitamin C intake can also help lower uric acid levels, preventing future flares and joint damage.