Complete Guide to Understanding and Managing Psoriasis
This article offers an in-depth overview of psoriasis, including its symptoms, causes, and available treatments. It emphasizes the importance of professional diagnosis and management strategies to effectively control this autoimmune skin disorder, which affects millions. Understanding the condition can help sufferers seek proper care and improve their quality of life.
Sponsored

Comprehensive Insights into Psoriasis
All you need to know about psoriasis
Skin conditions can be both physically painful and emotionally distressing, often accompanied by social stigma. Many misconceptions exist, such as the false belief that all skin diseases are contagious, which can hinder proper understanding and treatment. Attempting self-treatment without medical guidance can worsen the situation. Awareness and professional consultation are crucial for effective management of psoriasis, a common skin disorder.
Psoriasis is a long-term autoimmune condition affecting about 7.5 million individuals nationwide. It leads to skin abnormalities, pain, and significant lifestyle disruptions. Understanding its causes and treatment options is essential for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
What is psoriasis?
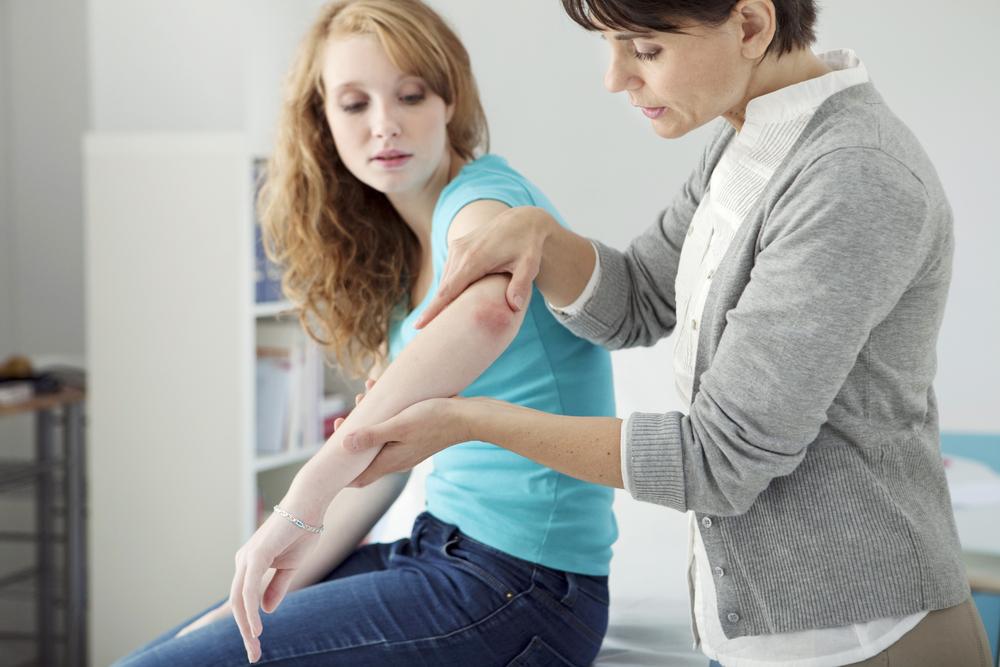
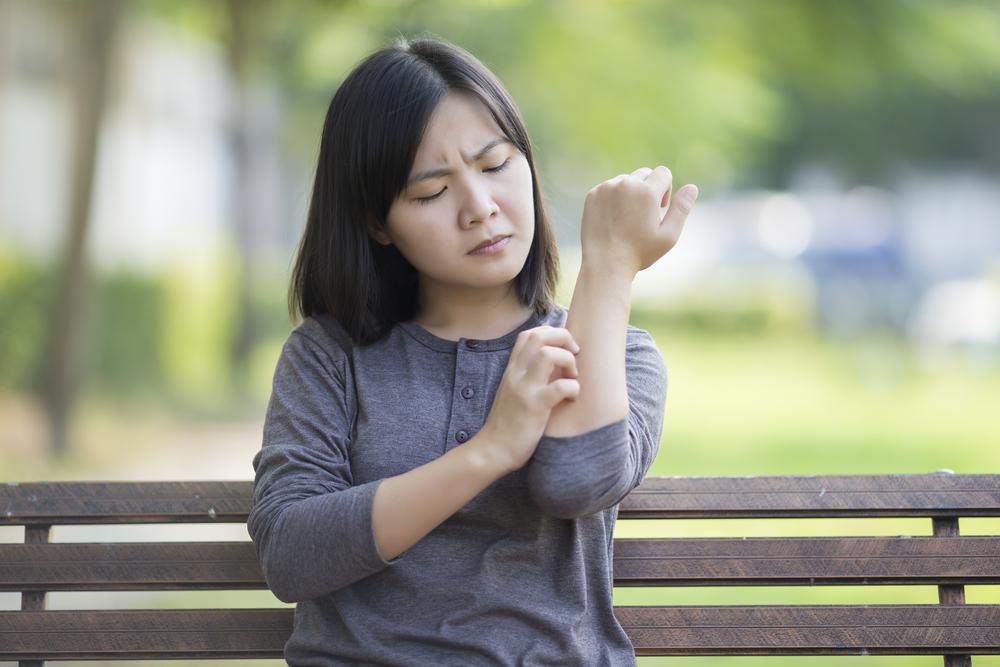
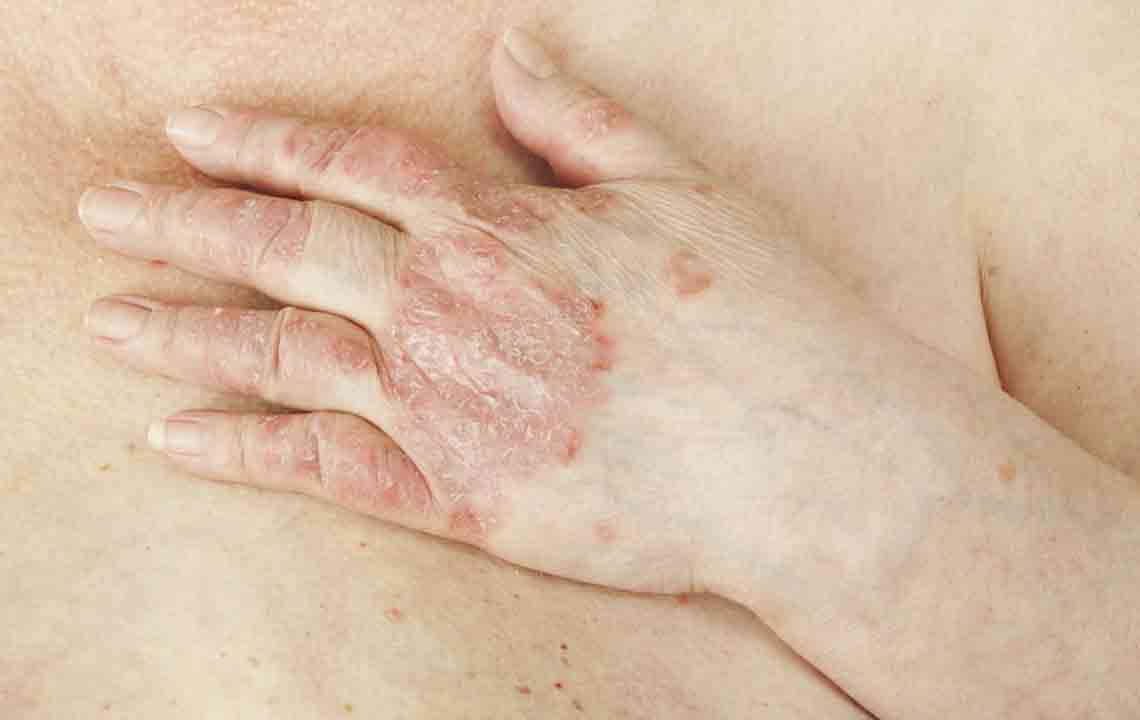
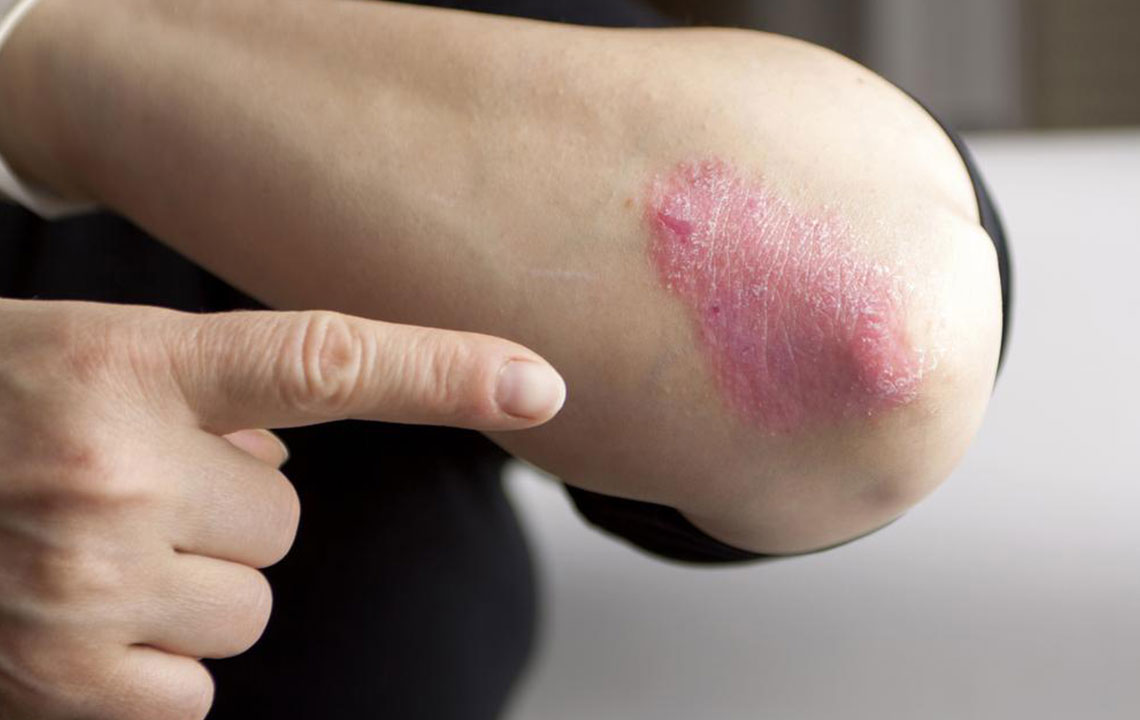
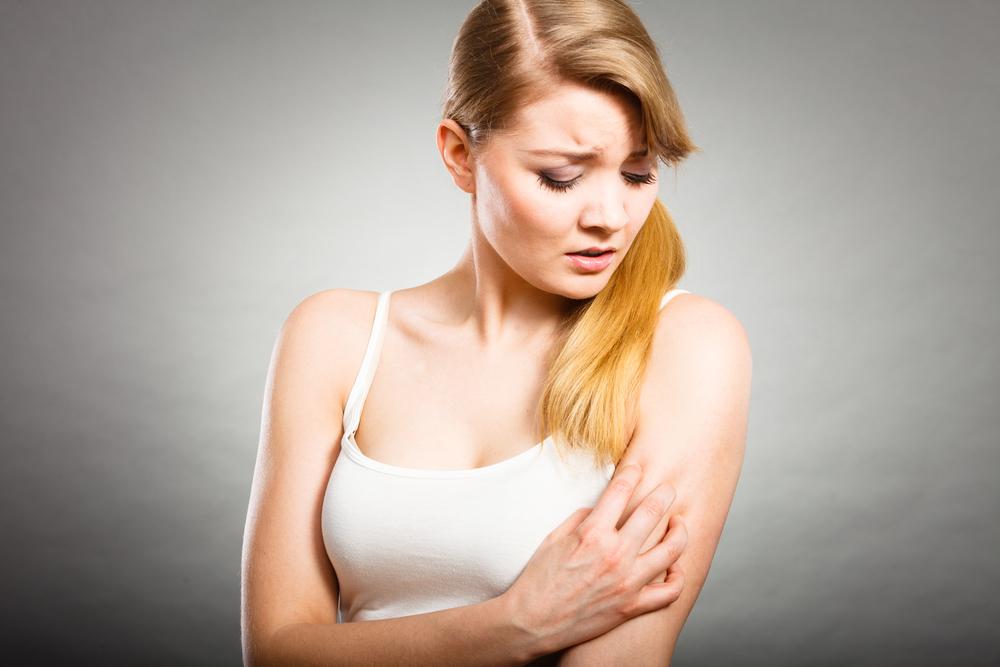
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system causes excessive skin cell production, resulting in scaly patches, redness, and inflammation on the skin.
Commonly presenting as silvery-white scales on red patches, psoriasis can impact the hands, feet, scalp, face, and other areas including nails, mouth, or genitals. It results from rapid skin cell turnover, occurring in days instead of the usual month, causing buildup and visible lesions.
Key symptoms of psoriasis
Symptoms vary by individual and psoriasis type, but commonly include red, raised patches; soreness; dry, cracking skin; itching; burning sensations; joint pain; and nail abnormalities.
Causes of psoriasis
While the exact cause remains unclear, research highlights genetics and immune system dysfunction as main factors.
Genetics: Family history increases susceptibility, with 2-3% of affected individuals inheriting the condition.
Immune response: Psoriasis triggers when immune cells mistakenly attack healthy skin, causing inflammation and rapid cell production, leading to plaques.
Available treatment options for psoriasis
Although there is no cure, various therapies can help control symptoms.
Topical treatments: Steroid creams, salicylic acid, moisturizers, and other ointments can reduce inflammation in mild to moderate cases.
Systemic medications: Severe cases may require oral or injectable drugs like methotrexate, cyclosporine, retinoids, or biologics.
Light therapy: Exposing skin to natural or ultraviolet light can diminish immune activity and slow cell growth.
Tags- psoriasis, skin disorders, autoimmune diseases