Understanding Herpes: Causes, Transmission, and Management
Herpes is a common STI caused by the herpes simplex virus, presenting with sores around the mouth or genitals. Transmission occurs through contact, often without visible symptoms. While incurable, antiviral treatments help manage outbreaks and symptoms, emphasizing importance of prevention and protection during sexual activity.
Sponsored
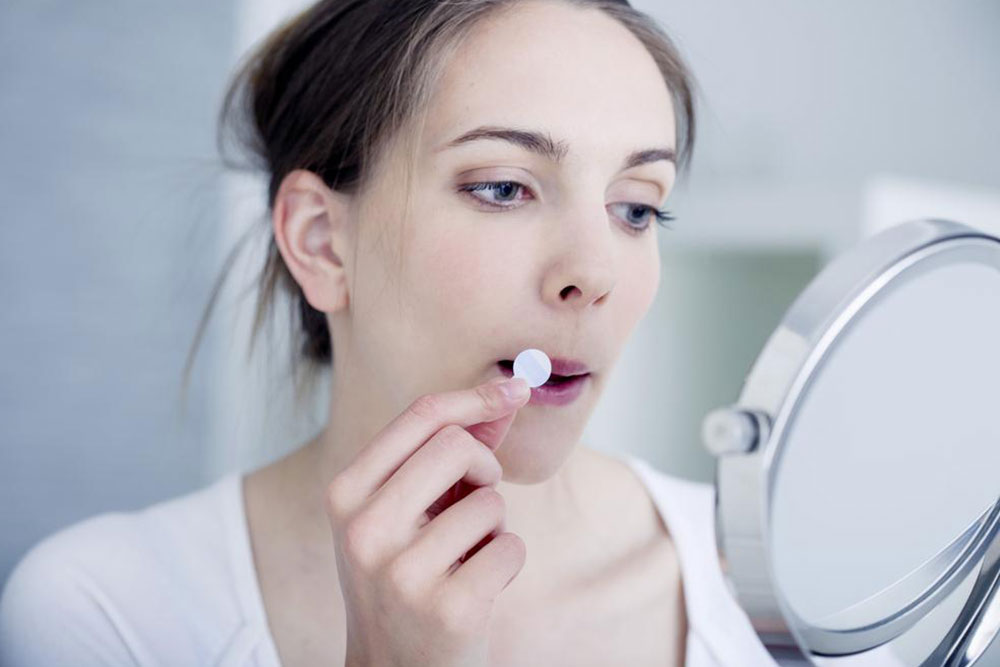

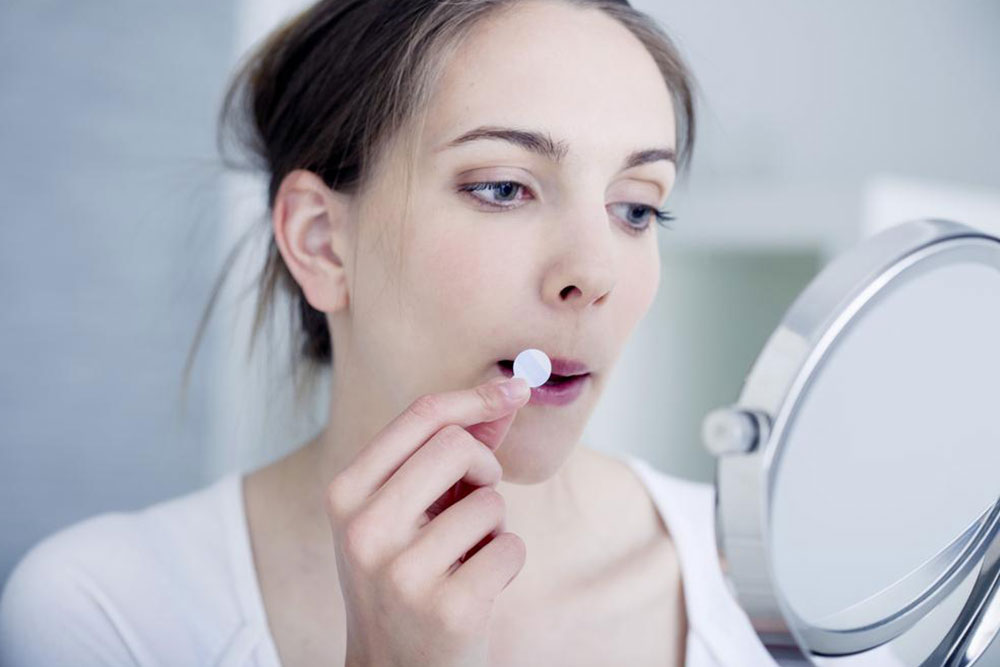
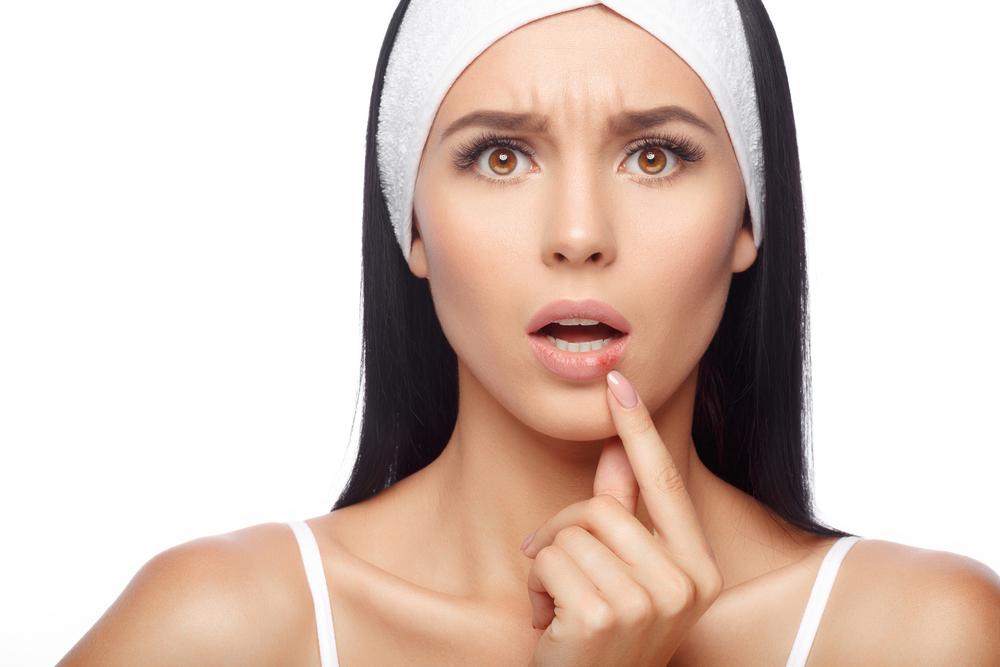
Herpes is a widespread sexually transmitted infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. It manifests primarily as oral herpes (type 1) and genital herpes (type 2). The hallmark symptoms include sores, which typically appear around the mouth or genitals. Type 2 herpes can also affect other areas, such as the soles of the feet. The virus transmits through saliva, skin contact, or sexual activity, even without visible sores. It can also pass from mother to child during childbirth. Many individuals carry the virus without symptoms, and outbreaks can be triggered by factors like stress, fatigue, or immune suppression.
The initial outbreak is often the most severe, characterized by pain, burning, and discomfort around the affected area. Urination may be painful, and some may notice discharges. Oral herpes causes tingling and burning sensations around the lips and mouth. Though there is no cure for herpes, antiviral medications can help manage symptoms and reduce outbreaks. Over time, episodes tend to become less frequent and less severe. Prevention through consistent condom use and avoiding contact during outbreaks is essential to reduce transmission risks.