Essential Insights into Blood Clots and Their Prevention
Learn vital facts about blood clots, including causes, symptoms, and treatments. Recognize early warning signs like chest pain and leg swelling to seek prompt medical help. Preventive steps such as staying active and avoiding long periods of inactivity are essential for reducing risk. Understanding blood clot risks and management is crucial for maintaining overall health and avoiding severe complications.
Sponsored
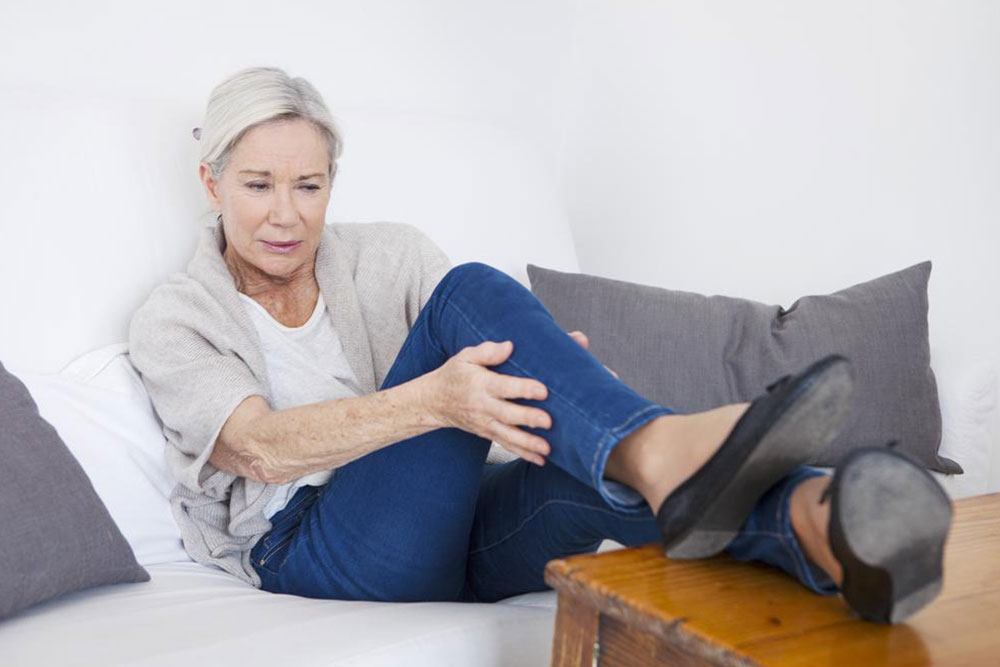
Blood clots, or thrombi, are semi-solid masses that form when blood solidifies to prevent excessive bleeding. While clotting is a natural protective response, abnormal clot formation or movement can cause serious health issues. Mobile clots may travel through the bloodstream and block vital organs, posing life-threatening risks. Clots in the veins, like deep vein thrombosis (DVT), often resist breakdown and require prompt treatment. Recognizing symptoms such as chest pain, stroke signs, or leg swelling is crucial for timely intervention.
Reasons Behind Blood Clot Formation
The primary trigger for blood clots involves alterations in blood components, often due to vessel injury or health conditions that impair normal flow. Factors like inactivity, surgeries, vascular damage, infections, cancer treatments, and lifestyle choices contribute to clot development.
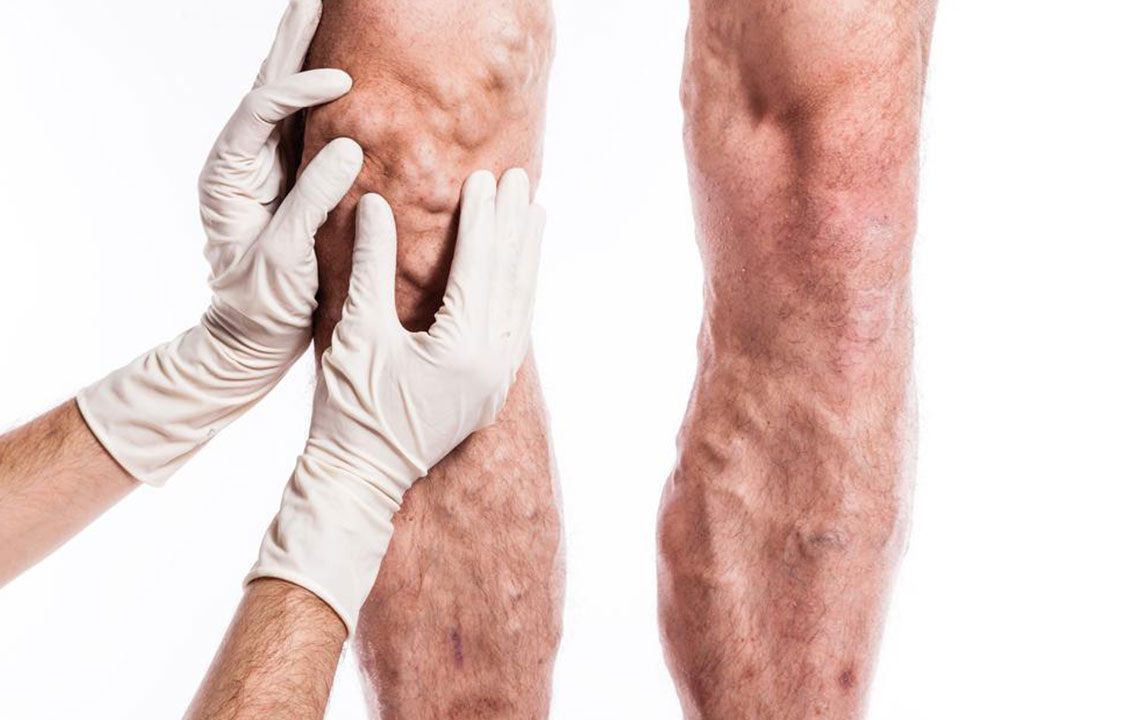
Symptoms of blood clots include chest pain, which could signal a heart attack, and neurological deficits indicating stroke, such as numbness, speech difficulties, or paralysis. DVT manifests through leg swelling, tenderness, redness, and warmth. If a clot travels to the lungs, it can cause a pulmonary embolism, presenting with breathlessness, chest pain, and blood-tinged sputum. Medical treatment involves anticoagulants and blood thinners to prevent clot progression and embolism. Preventative measures include staying active, avoiding prolonged immobility, and exercising regularly.