Essential Insights into Managing Diabetes Effectively
This article offers a comprehensive overview of diabetes, covering its symptoms, causes, and risk factors. It emphasizes the importance of awareness to manage and prevent complications related to high blood sugar levels. Understanding the different types of diabetes helps individuals take proactive steps towards health. The piece also discusses the critical role of insulin and the factors influencing its effectiveness. Whether for individuals at risk or those diagnosed, the insights provided serve as valuable guidance for effective disease management and prevention.
Sponsored
Understanding Key Aspects of Diabetes
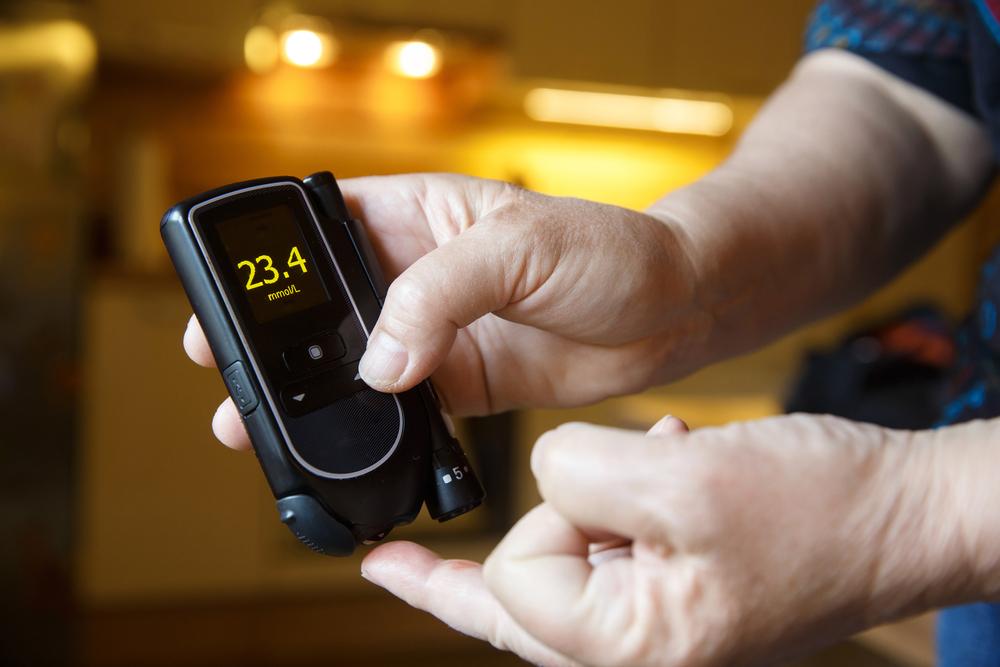
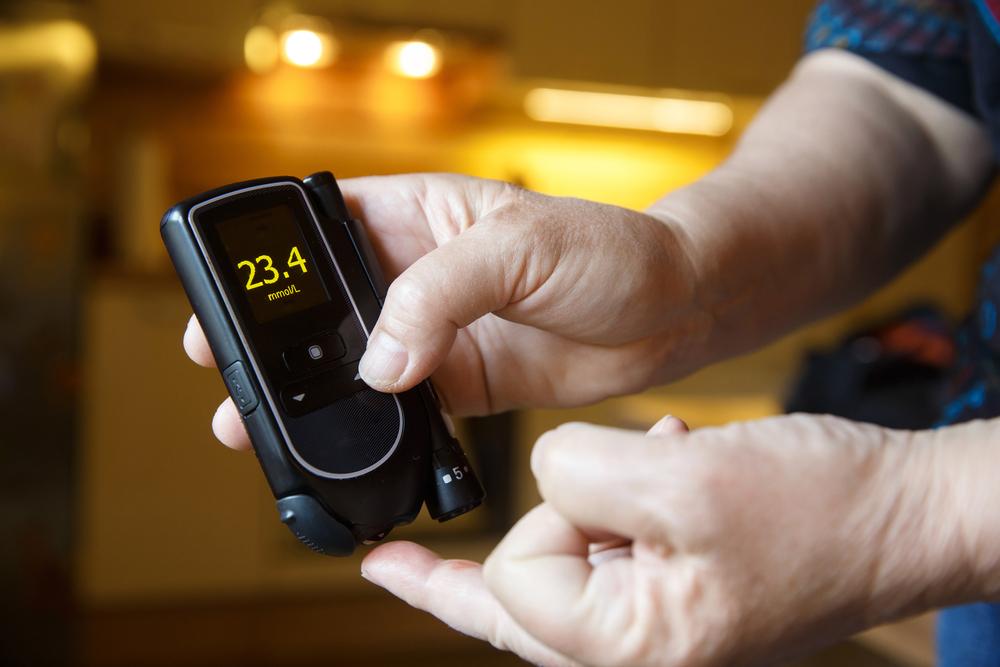
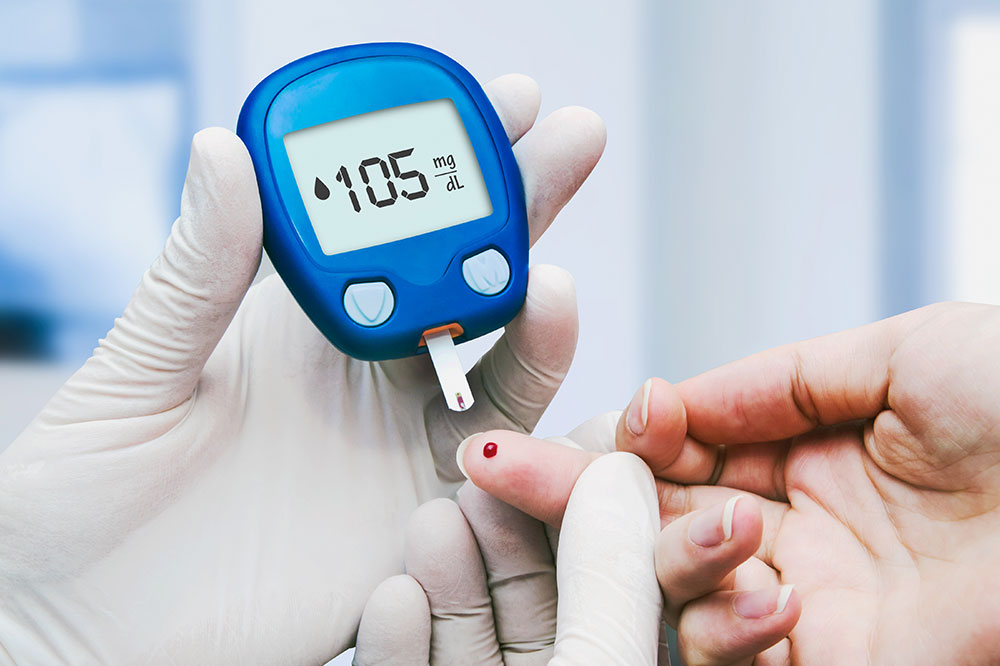
Diabetes is a health condition characterized by elevated levels of blood sugar, also known as blood glucose. This sugar is vital for providing energy to the body, primarily sourced from the foods we eat.
The pancreas produces insulin, a hormone responsible for transporting glucose into cells for energy utilization. In some people, the body doesn't produce enough insulin, leading to a buildup of glucose in the bloodstream.
Prolonged high blood sugar levels can result in various health issues. While a complete cure for diabetes remains elusive, understanding its symptoms, causes, and risk factors helps in effective management.
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms vary based on blood sugar levels. Early stages of pre-diabetes or type 2 diabetes may not show noticeable symptoms. However, type 1 diabetes often manifests symptoms quickly and more severely.
Common symptoms for both types include:
Increased thirst
Frequent urination
Unexplained weight loss
Persistent fatigue
Blurred vision
Frequent infections on skin and gums
Underlying Causes
Insulin's role is to regulate blood sugar by helping glucose enter cells for energy. When blood sugar drops, insulin secretion decreases. The causes of diabetes depend on its type.
Type 1 Diabetes
The exact cause isn't fully understood. Evidence suggests that an autoimmune response malfunctions, causing the immune system to attack insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, thus impairing insulin production.
Type 2 and Prediabetes
These forms involve the body's cells resisting insulin's effects, while the pancreas struggles to produce enough insulin to compensate. This imbalance leads to high blood sugar levels.
Risk Factors
Risk factors vary between types. For type 1, genetic factors and viral exposures play a role. Prediabetes and type 2 risks include:
Overweight
Physical inactivity
Genetics
Advanced age
High blood pressure