Understanding Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
This article explores the essentials of diabetes, including its causes, symptoms, and management strategies. With a focus on different types of diabetes and their impact, it emphasizes lifestyle changes and medical interventions to control blood sugar levels effectively. Understanding these aspects is vital for prevention and proper treatment of this widespread condition.
Sponsored

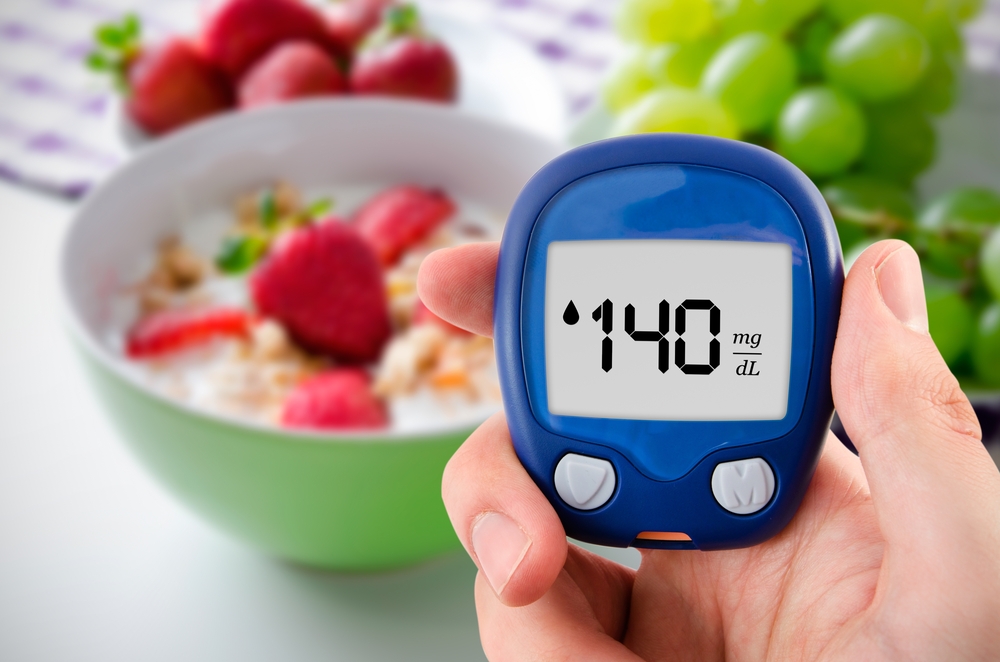
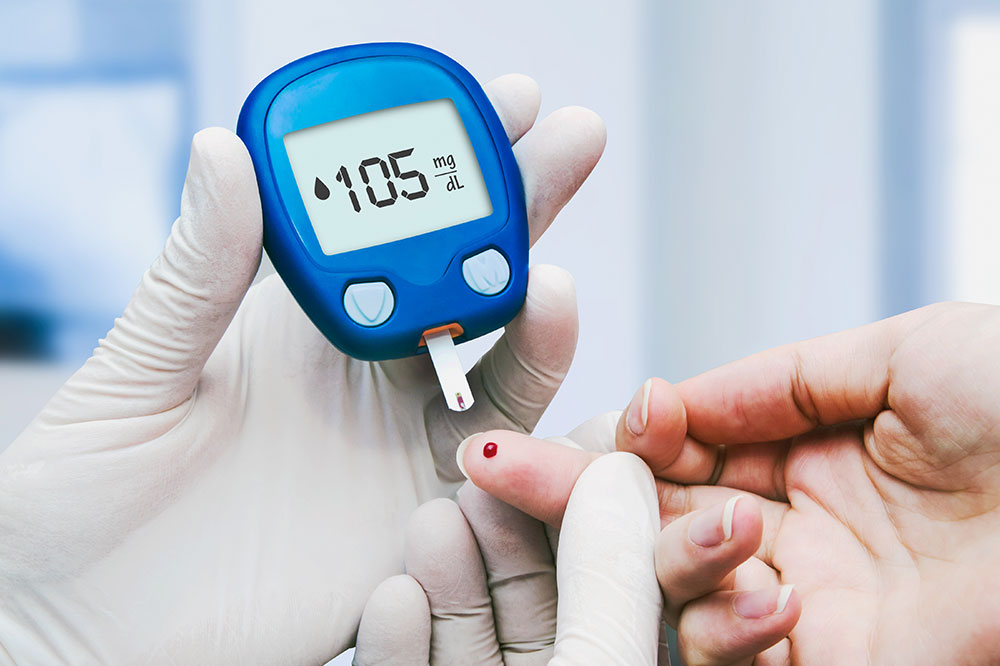
Diabetes occurs when the pancreas either does not produce enough insulin or the body becomes resistant to insulin's effects. This disrupts the body's ability to efficiently utilize food energy, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels.
After eating, food is broken down into glucose, which travels through the bloodstream to feed cells. Insulin, produced by the pancreas, helps transport this glucose into cells for energy use.
The issue arises when blood sugar remains high due to insufficient insulin production or insulin resistance. Persistent high blood glucose can lead to diabetes if dietary habits are not managed.
There are three primary types: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes, with pre-diabetes being a warning stage.
In the country, about 30.3 million individuals suffer from diabetes, while approximately 84 million are unaware they are pre-diabetic.
Causes of Diabetes
Pre-diabetes, or impaired glucose tolerance, is a condition where blood sugar is elevated but not yet at diabetes levels. Without intervention, it could develop into type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the pancreas produces little or no insulin, typically affecting those under 20 years of age.
Type 2 diabetes primarily affects overweight adults but is increasingly diagnosed in children and young adults due to inactivity and poor lifestyle choices.
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and resolves post-delivery, affecting about 4% of women in the second trimester.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Extreme thirst
Frequent urination
Persistent fatigue
Unexpected weight loss
Slow-healing sores
Dry, itchy skin
Blurred vision
Tingling in extremities
Diabetic ketoacidosis
If symptoms are noticed, consulting a healthcare provider is essential for proper diagnosis and management.
Managing Diabetes
While there is no cure, effective management helps keep blood sugar levels in check.
A balanced diet and regular exercise are crucial for improving insulin effectiveness.
Type 1 diabetics and some with type 2 require insulin injections, whereas others may use oral medications to enhance insulin use.