Key Insights into Managing and Preventing Diabetes
This article explores essential aspects of diabetes, including its causes, potential complications, symptoms, and preventative measures. It emphasizes lifestyle changes like regular exercise and healthy eating to reduce risk, highlighting the importance of early detection and management for better health outcomes.
Sponsored

Understanding Critical Aspects of Diabetes
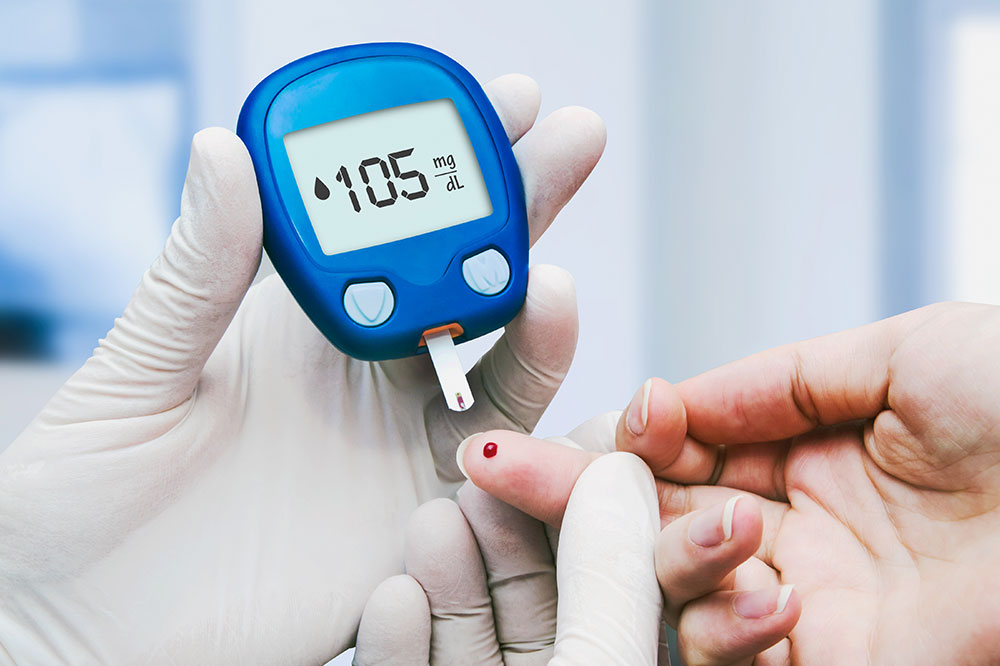
Diabetes is a widespread condition affecting millions globally. It encompasses a group of metabolic disorders characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. While glucose is vital for energy production, excess blood glucose can lead to severe health issues. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, regulates blood sugar by helping cells absorb glucose. When pancreatic function falters, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream, potentially resulting in diabetes. Though often linked to high sugar intake, genetics also play a significant role in its development. Newborns can also inherit the condition through genetic factors.
The main cause of elevated blood sugar is inadequate insulin production or usage. The risk factors for diabetes include family history, ethnicity, genetics, and environmental influences. Causes vary based on the type of diabetes and individual circumstances, with triggers such as infections, obesity, sedentary lifestyles, poor diets, autoimmune responses, toxins in food, pregnancy complications, and certain syndromes like Cushing's. Understanding these elements can help in early detection and management.
Potential Health Risks from Diabetes
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to complications including eye problems like cataracts, diabetic retinopathy, and glaucoma. It increases susceptibility to skin infections and disorders. High blood sugar levels can impact mental health, contributing to stress, anxiety, and depression. Diabetes may impair hearing and cause hearing loss, and it's often associated with gum diseases. Wound healing can also be delayed, posing further health risks.
Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes
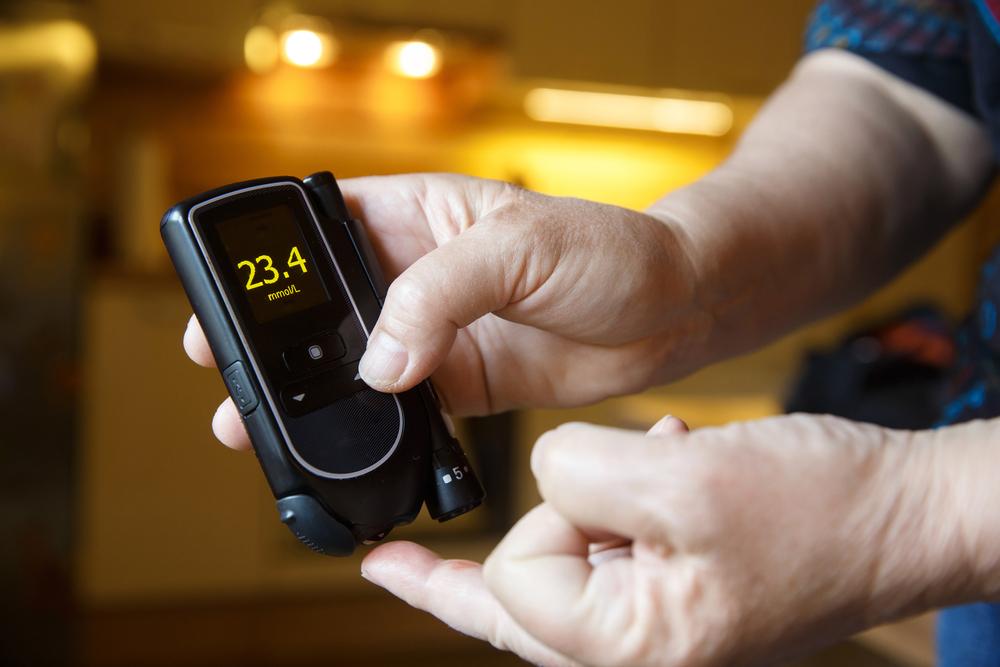
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes often develop gradually and may be subtle or absent, while type 1 symptoms appear rapidly within weeks. Common indicators include blurred vision, sudden weight loss, fatigue, unexplained hunger, slow-healing wounds, and increased urination. Recognizing these signs early is crucial for effective management.
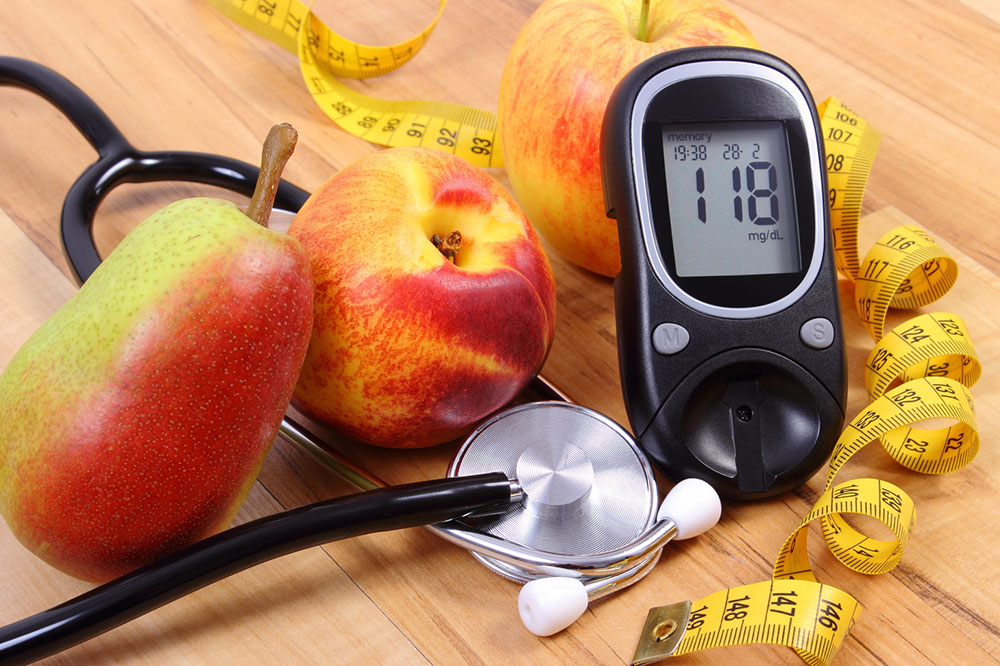
Preventive Strategies Against Diabetes
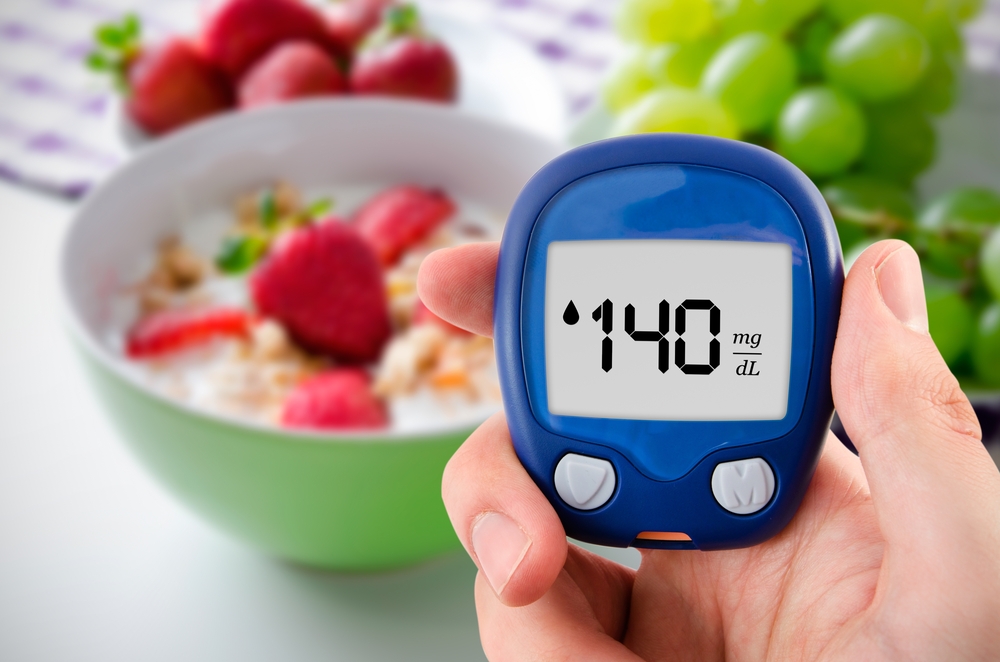
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is essential for prevention. Regular exercise, including resistance training, helps maintain optimal blood sugar levels. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced diet choices and limiting processed foods is vital. Routine medical checkups enable early detection, improving management outcomes. Since there is no cure for diabetes, avoiding risk factors through lifestyle modifications is the best approach to safeguarding health.