Comprehensive Guide to Pneumonia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Strategies
This article provides a detailed overview of pneumonia, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis, proper medication, and preventive vaccination. Recognizing symptoms such as persistent cough, fever, and breathing difficulties can help in timely intervention, which is crucial for effective recovery. Combining medical treatment with home remedies like hydration and rest can significantly speed up healing and reduce complications associated with pneumonia.
Sponsored

Pneumonia is a respiratory infection that inflames the air sacs in the lungs. It is frequently caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, with Streptococcus pneumoniae being a common bacterial culprit. Mild symptoms like a persistent cough and cold can develop into pneumonia if left untreated, especially when the immune system is weakened. A strong immune response helps in fighting the infection effectively.
Main Causes of Pneumonia Pneumonia occurs due to inflammation in the lungs' air spaces, primarily caused by infectious agents like bacteria, viruses, fungi, or prolonged dust exposure. Depending on the cause, pneumonia is classified into four types:
Bacterial pneumonia
Viral pneumonia
Mycoplasma pneumonia
Other variants
Identifying Symptoms of Pneumonia Although often mild, pneumonia can become severe if not diagnosed early. Symptoms include:
A persistent dry cough producing mucus
Fatigue and weakness
High fever with chills lasting several days
Shortness of breath in children
Loss of appetite
Chest pain and breathing discomfort
Blue tinged fingertips indicating oxygen deficiency
Sleep disturbances and recurring headaches
Blood in cough from prolonged coughing
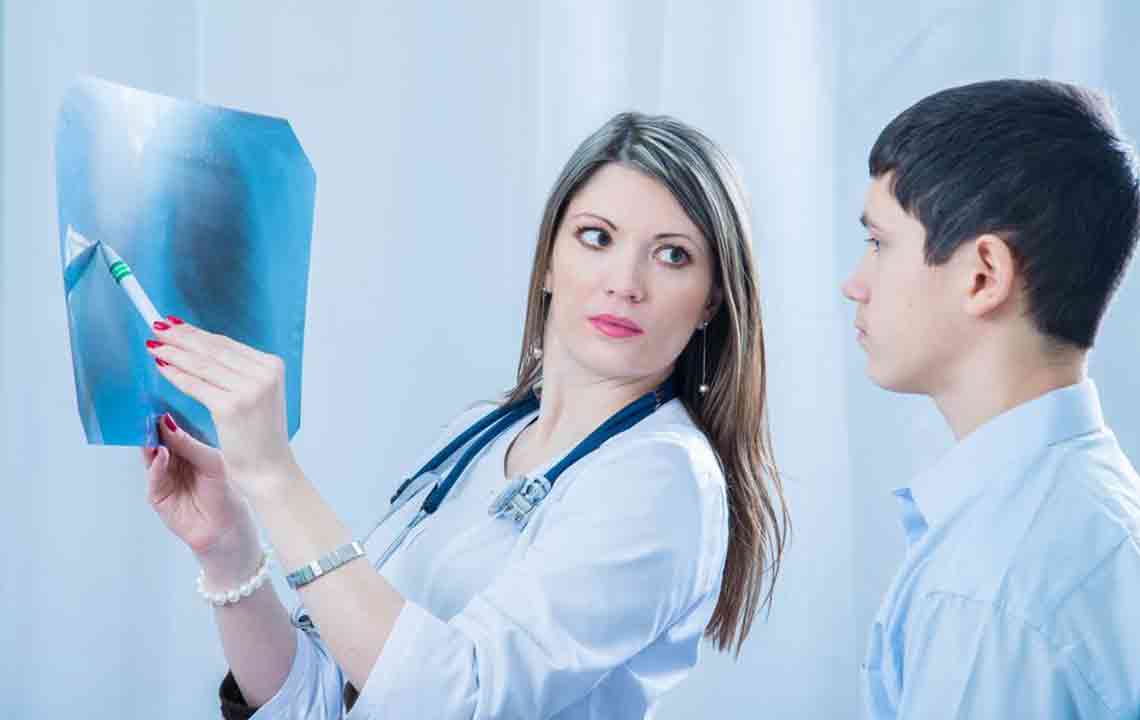
Approaches to Treating Pneumonia Treatment typically involves antibiotics, with vaccination playing a preventive role against bacterial infections. Early diagnosis through tests like blood analysis, chest X-rays, and sputum tests is crucial. Managing symptoms and eliminating infection are primary goals. Recovery can take time, with fatigue lingering up to a month.
Depending on the type and severity, treatment may include:
Maintaining adequate hydration by drinking plenty of water
Completing the full course of prescribed antibiotics
Resting sufficiently until symptoms subside
Consult your healthcare provider immediately if you notice symptoms to initiate prompt treatment and prevent complications.