Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis: Causes and Prevention Strategies
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) forms when blood clots develop in deep leg veins, potentially leading to serious health issues. Understanding its causes—like prolonged immobility, pregnancy, obesity, and vein damage—is vital. Preventive measures include changing sitting positions regularly, early post-surgery movement, and staying hydrated. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking medical help can prevent complications like pulmonary embolism. Incorporating these strategies can significantly lower DVT risks and promote overall vascular health.
Sponsored

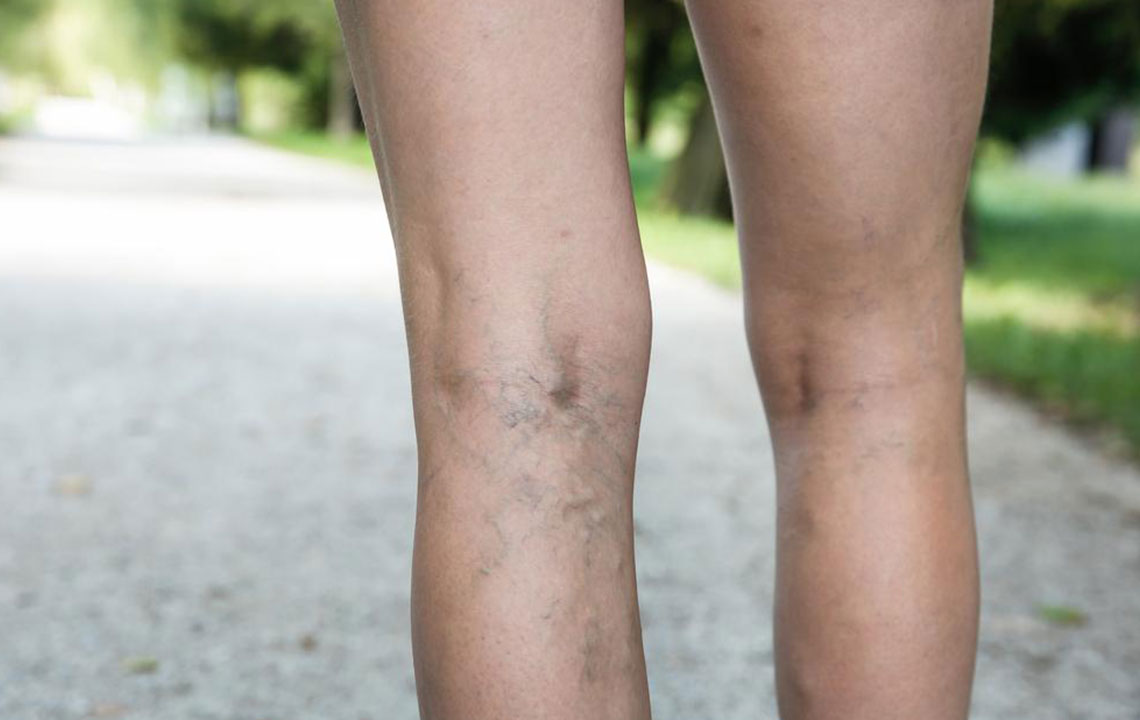
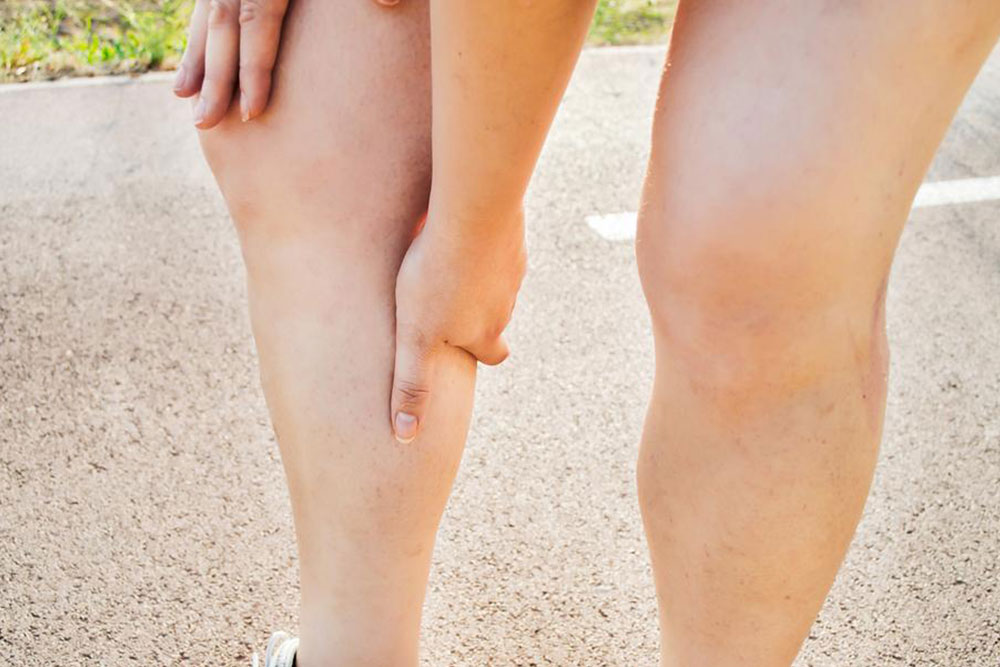
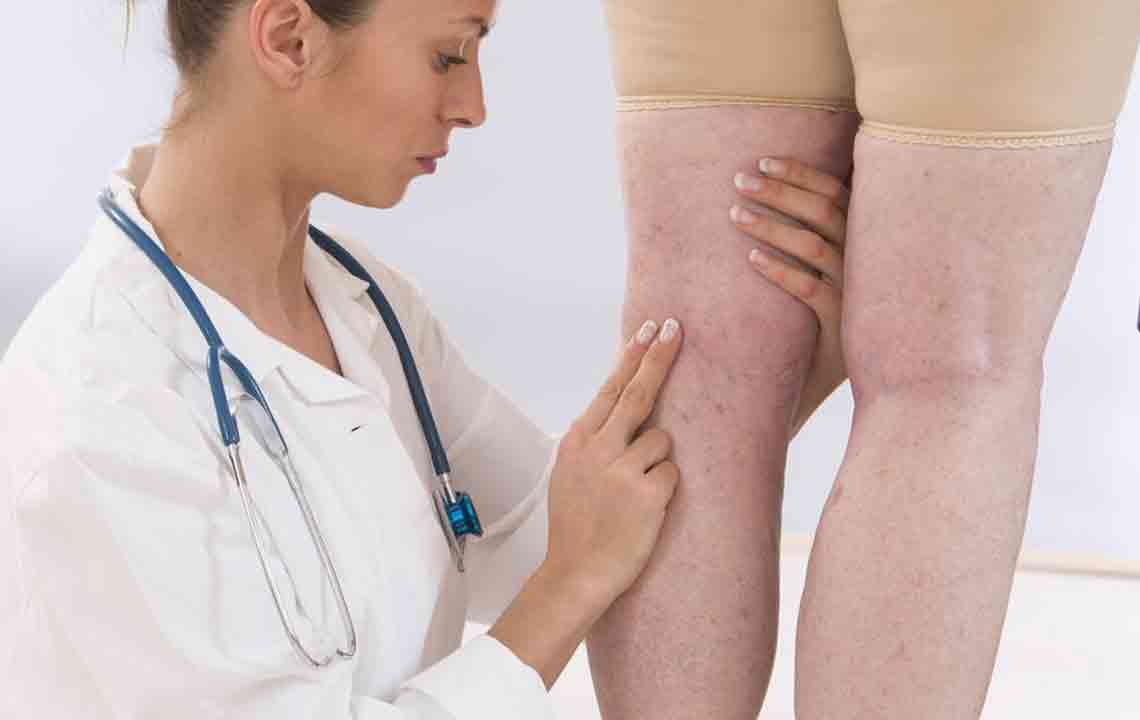
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) happens when blood clots form in deep veins, commonly in the legs. It may cause swelling in the affected limb and can sometimes occur without noticeable symptoms. Recognizing the causes and taking preventive measures are key to reducing risk.
What factors contribute to DVT?
Extended bed rest can promote blood clotting in deep leg veins. Since these veins circulate blood to the lungs and heart, immobility hampers proper flow, leading to clot formation.
Pregnancy increases DVT risk due to elevated estrogen levels, which encourage blood clotting. Use of birth control pills or hormone therapy can further heighten this risk.
Obesity is a significant factor, as excess body weight increases the likelihood of clot development. Maintaining a healthy weight can help lower this risk.
Damage to the inner lining of veins can also trigger clot formation, leading to DVT.
Effective strategies to minimize DVT risk
Change your sitting posture:
Avoid staying in one position for long durations. Regularly stand, stretch, or walk to promote healthy blood circulation and prevent clot formation.
Begin mobilization promptly after surgery:
Early movement after surgical procedures helps prevent blood stasis and reduces the chance of clots.
Plan your daily activities:
If you need to sit for extended periods, take frequent breaks, stretch your legs, wear loose clothing, and stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water to enhance circulation. Avoid alcohol to further support healthy blood flow.
Remember, untreated DVT can cause serious complications like pulmonary embolism. Seek medical attention if you experience symptoms such as dizziness, excessive sweating, or rapid heartbeat.