Understanding Lupus: Key Symptoms and Dietary Strategies for Management
This article offers insights into early lupus symptoms such as skin rashes, fever, hair loss, and fatigue. It emphasizes the importance of a diet rich in omega-3s, calcium, and antioxidants to help manage the condition. Additionally, it highlights foods to avoid like high-fat dairy and processed meats to reduce inflammation and organ damage. Recognizing symptoms early and adopting a health-conscious diet can significantly improve quality of life for those with lupus.
Sponsored

Understanding Lupus: Recognizing Symptoms and Dietary Tips for Care
Lupus is an autoimmune disorder where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, leading to inflammation and discomfort. It can affect vital organs including kidneys, brain, heart, lungs, joints, and skin. Identifying early symptoms and following an appropriate diet can help manage the condition effectively.
Common early signs of lupus include:
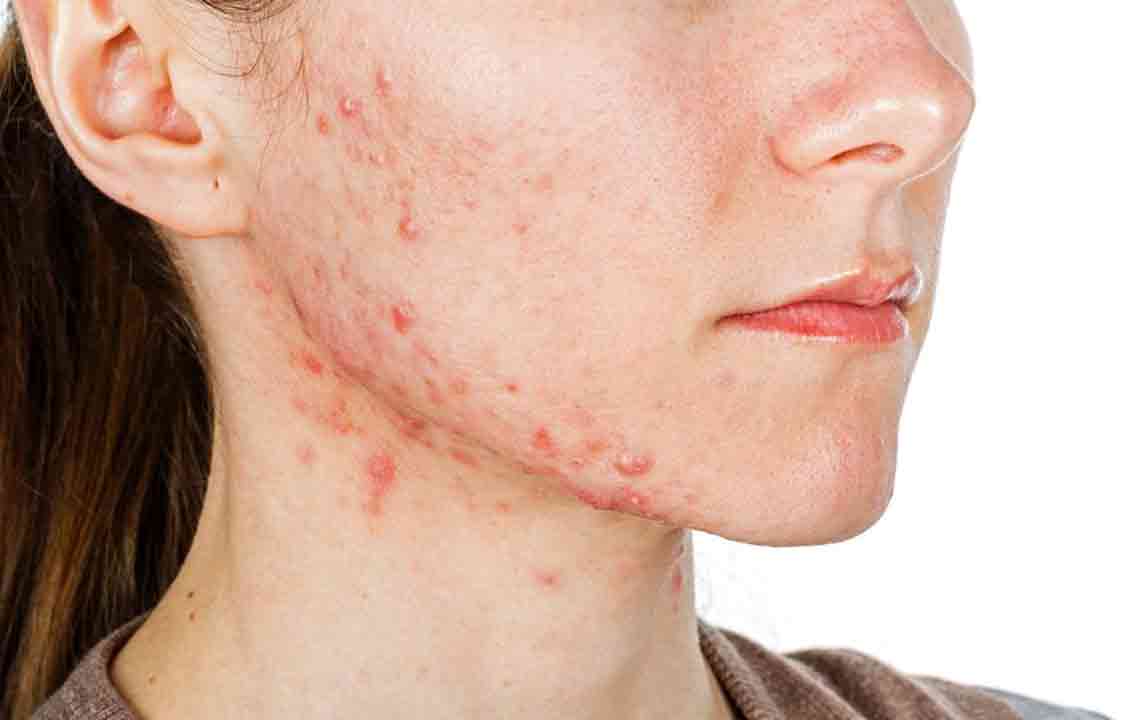
Skin Rashes
Facial rashes are typical, appearing gradually or suddenly covering the face.
While symptoms vary among individuals, some shared indicators include:
Fever
Persistent fever above 100°F is common due to inflammation and immune response.
Hair Loss
Hair thinning is a frequent sign, though it doesn't directly reveal the root cause.
Fatigue
Lupus attacks red blood cells, leading to chronic tiredness.
To manage lupus symptoms and reduce organ damage, certain foods can be beneficial:
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Rich in walnuts, seeds, and fatty fish, omega-3s help combat inflammation and decrease flare-ups.
Calcium-Rich Foods
Yogurt, tofu, and leafy greens strengthen bones and joints, slowing potential damage.
Incorporating antioxidants helps neutralize free radicals associated with lupus symptoms.
Foods to avoid include:
High-Fat Dairy Products
Whole milk, cheese, and cream contain saturated fats that promote inflammation.
Red Meat and Processed Foods
These items contain saturated fats and sodium, which can worsen inflammation and overall health.