Understanding Pneumonia: Key Prognosis and Treatment Strategies
Pneumonia is a common lung infection requiring timely diagnosis and effective treatment. This article explores prognosis methods, symptoms, and therapy options, emphasizing prevention through vaccination and healthy habits. Early detection and care are vital to prevent severe complications and fatalities.
Sponsored
Pneumonia is an infection that causes inflammation in the lungs, affecting one or both air sacs with pus or fluid accumulation. It is prevalent across the United States, impacting individuals from infants to adults. Annually, over a million hospital admissions are due to pneumonia, with approximately eight to ten million cases overall. Common symptoms include difficulty breathing, chills, fever, and productive cough. Early diagnosis typically results in milder outcomes, whereas delayed treatment can be life-threatening.
Pneumonia prognosis - As one of the most widespread respiratory infections, pneumonia claims many lives each year. Accurate prognosis helps in early intervention and reduces fatal risks. Diagnosing pneumonia generally involves specific medical tests based on symptoms.
Blood tests - Routine blood examinations aid in confirming infections by identifying the causative organisms.
Pulse oximetry - Besides blood tests, pulse oximetry measures blood oxygen levels, revealing any impairments in oxygen exchange.
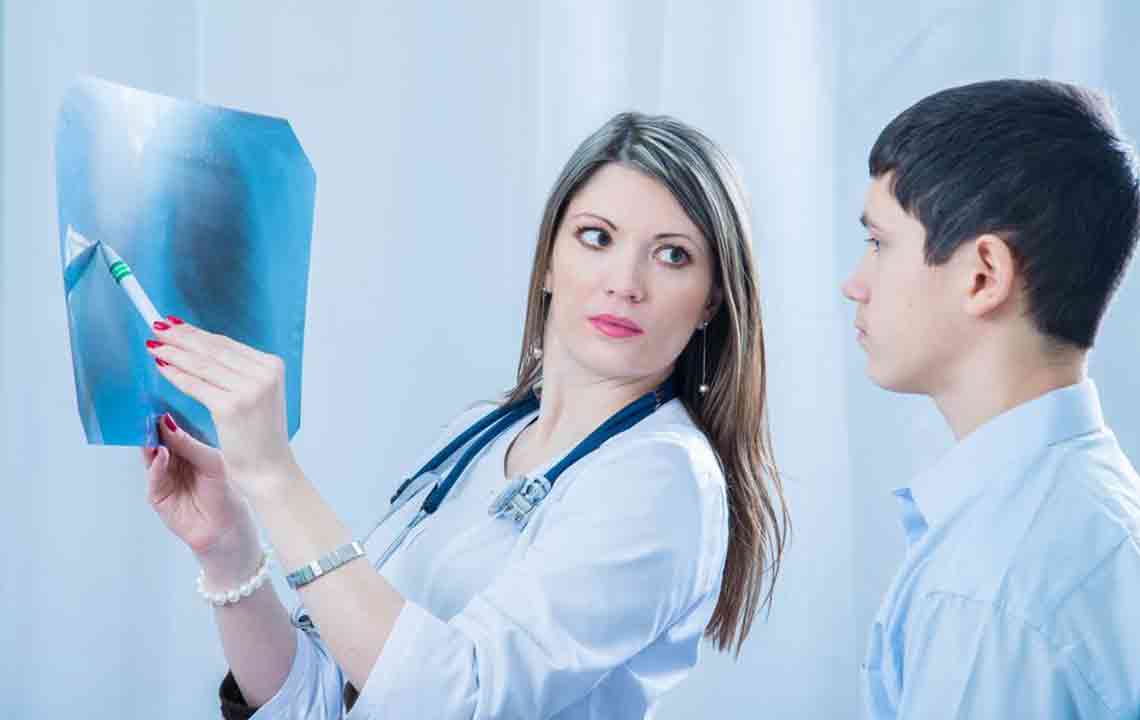
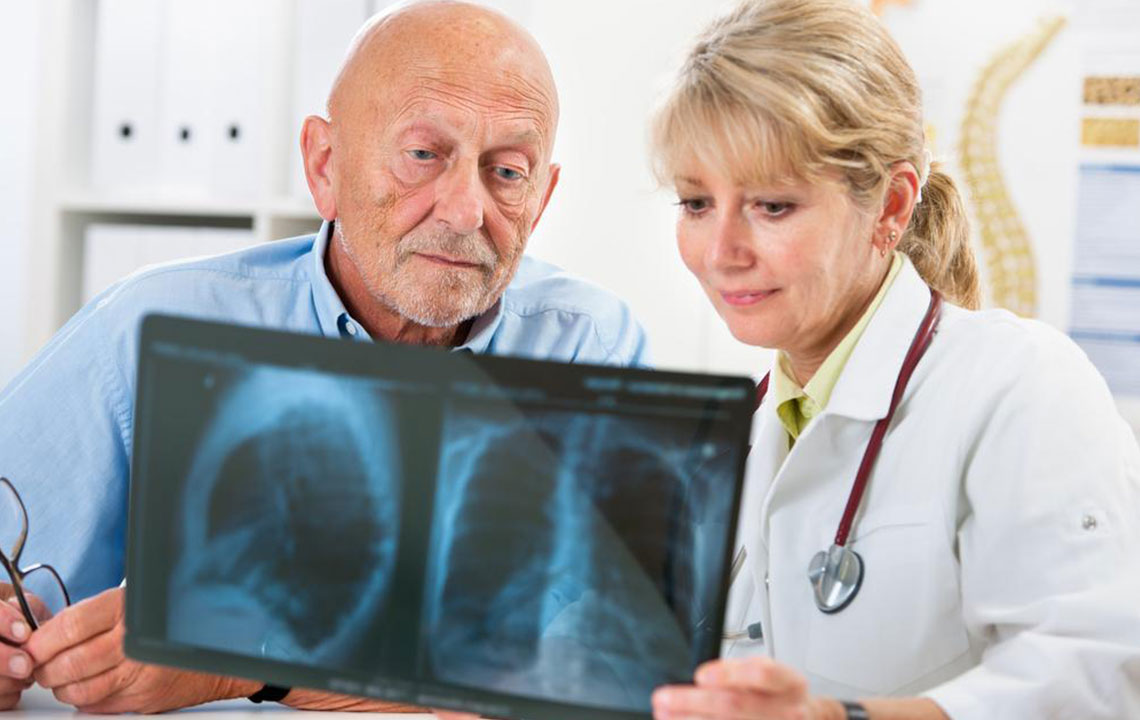
Chest X-ray - If blood tests suggest pneumonia, a chest X-ray is performed to assess the infection's severity. However, it doesn't specify the pathogen.
Sputum analysis - To determine the infection source, sputum samples from lungs are examined before initiating treatment.
Additional tests like chest CT scans or pleural fluid cultures may be necessary for elderly patients or cases unresponsive to initial treatment, to pinpoint the cause and prognosis.
Symptoms of pneumonia - Recognizing symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis. Key signs include breathing difficulty, nausea, chills, fever, fatigue, confusion (especially in seniors), and persistent chest pain during cough or breath.
Infants may exhibit restlessness, excessive tiredness, fever, cough, or vomiting, requiring prompt medical attention.
Management and treatment - Accurate diagnosis must be followed by appropriate therapy. Self-medicating with over-the-counter drugs is not advised. Medical professionals often prescribe antibiotics targeting bacterial causes, tailored to patient age and severity.
Supportive treatments include cough suppressants, fever reducers, and pain relievers. In severe or hospitalized cases, intensive care might be necessary. Preventing pneumonia through vaccination and a healthy lifestyle is highly recommended. Early medical intervention and preventive measures can significantly reduce risks and promote quicker recovery.