Understanding Pneumonia: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Pneumonia is a challenging lung infection with symptoms like cough, chest pain, and fever. Diagnosis involves physical exams, X-rays, and lab tests to identify the cause. Treatment varies from antibiotics for bacterial types to supportive care for viral pneumonia. Early detection and proper management can lead to successful recovery, reducing risks of complications. This article covers symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options for pneumonia, emphasizing the importance of timely medical intervention across different settings.
Sponsored
Pneumonia can be contracted from various sources, with the origin influencing the diagnosis since certain pathogens are linked to specific environments. Healthcare facilities, especially those providing long-term care for illness or elderly patients, often harbor resistant bacterial strains.
Typical symptoms of pneumonia include
– Chest pain during breathing or coughing
– Persistent cough often with phlegm
– Fever, sweating, chills
– Fatigue and weakness
– Lowered temperature in older adults or immune-compromised individuals
– Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
– Shortness of breath
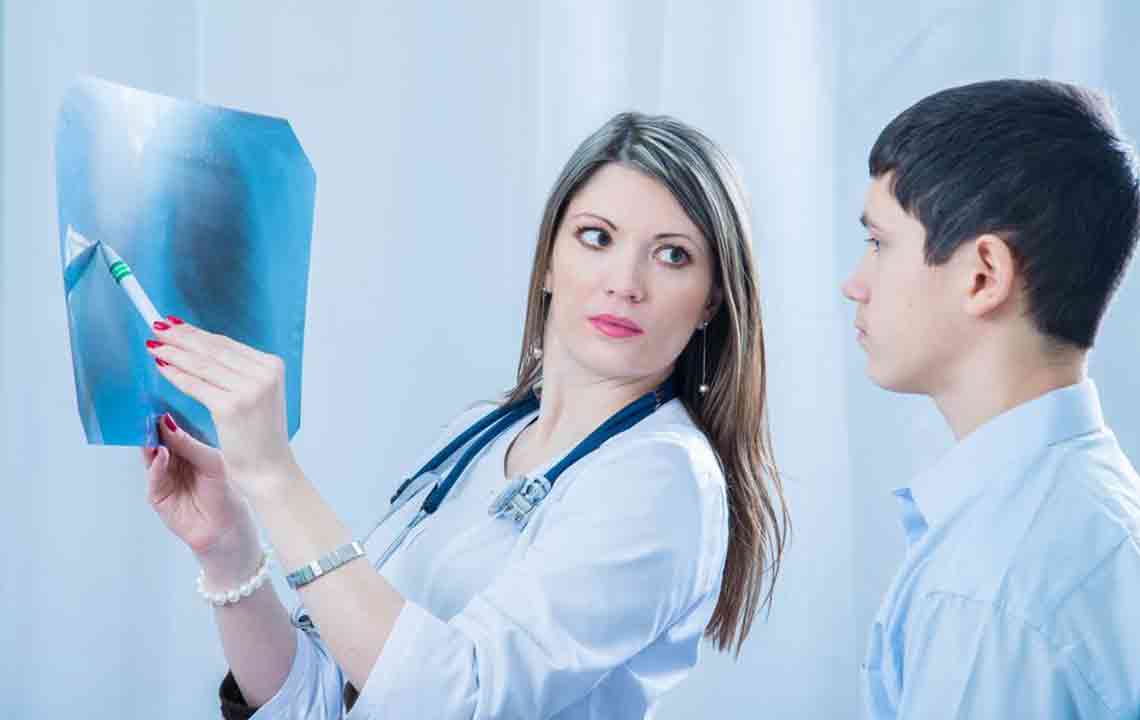
Diagnosis involves a thorough medical history and physical exam, notably listening to the lungs with a stethoscope to pinpoint infection locations. Chest X-rays reveal infection extent, while blood and sputum tests help identify the causative agent. Oxygen levels are monitored via pulse oximetry, and additional imaging like a CT scan may be necessary if the infection persists or worsens. Tests such as pleural fluid cultures provide further detail on the pathogen.
Treatment depends on the infectious origin. Community-acquired pneumonia usually responds well to antibiotics, whereas hospital-acquired strains are often resistant, requiring more aggressive therapy. Antipyretics, cough suppressants, and pain relievers help manage symptoms. Fungal infections require specific antifungal drugs, whereas viral pneumonia typically improves with supportive care as the illness runs its course. Most cases of community-acquired pneumonia can be treated at home unless complications arise, necessitating hospitalization.






