Effective Treatments for Neutropenia: A Comprehensive Guide
This article offers an in-depth overview of common treatments for neutropenia, including medications like G-CSF and GM-CSF that stimulate white blood cell production. It emphasizes the importance of medical supervision to manage this condition effectively and prevent infections. Learn about symptoms, causes, and treatment options to better understand how to handle neutropenia and stay protected against infections.
Sponsored

Common Therapies for Neutropenia
Effective therapies for neutropenia
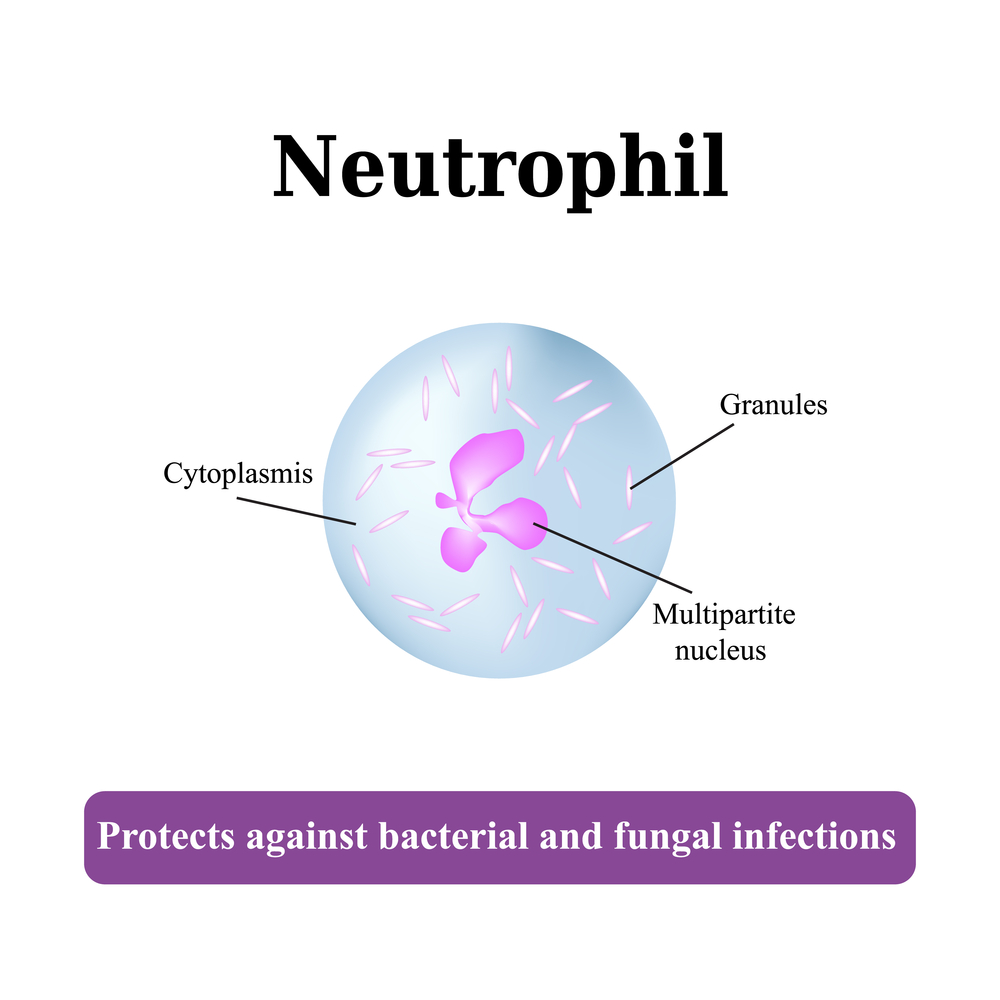
Neutropenia is a condition characterized by a shortage of neutrophils, a vital type of white blood cell responsible for combating infections. These cells play a crucial role in destroying bacteria and fungi, protecting the body from illnesses.
Role of Neutrophils
Maintaining an adequate level of neutrophils is essential for immune defense. A deficiency increases susceptibility to infections, making hygiene practices, like regular handwashing, critical for affected individuals.
Signs and Symptoms
While neutropenia itself is symptomless, infections resulting from low neutrophil levels can cause symptoms such as:
Sore throat
Ulcers in the mouth or dental pain
Pain during urination
Abdominal discomfort
Anal soreness
Unusual vaginal discharge
Redness or swelling around cuts or wounds
Diarrhea or anal sores
Cough or difficulty breathing
Causes
Neutrophil production occurs in the bone marrow, and any disruption in this process can lead to neutropenia. A common cause is chemotherapy, affecting nearly half of cancer patients undergoing treatment.
Treatment Approaches
The primary treatment involves stimulating neutrophil production using specific medications.
Colony-Stimulating Factors (CSFs)
These glycoproteins, such as G-CSF (filgrastim), encourage the bone marrow to produce more neutrophils and release them into circulation. Other options include GM-CSF (sargramostim), a naturally occurring glycoprotein that works similarly. Antibiotics may also be prescribed to combat infections that occur due to low white blood cell counts.
Medications like pegfilgrastim (Neulasta, Udenyca, Fulphila), a synthetic version of natural growth factors, help increase neutrophil levels. Leukine (sargramastim) and filgrastim (Granix, Zarxio) are other drugs used in managing neutropenia, especially in chemotherapy or radiation exposure cases. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any treatment, as proper diagnosis and guidance are essential.