Understanding Psoriasis: Signs, Causes, and Effective Treatments
Explore comprehensive insights into psoriasis, including its symptoms, causes, and various treatment options. Learn how to identify the condition and manage its symptoms effectively with medical guidance. This article offers valuable information for individuals seeking to understand or cope with psoriasis, emphasizing the importance of professional treatment plans.
Sponsored

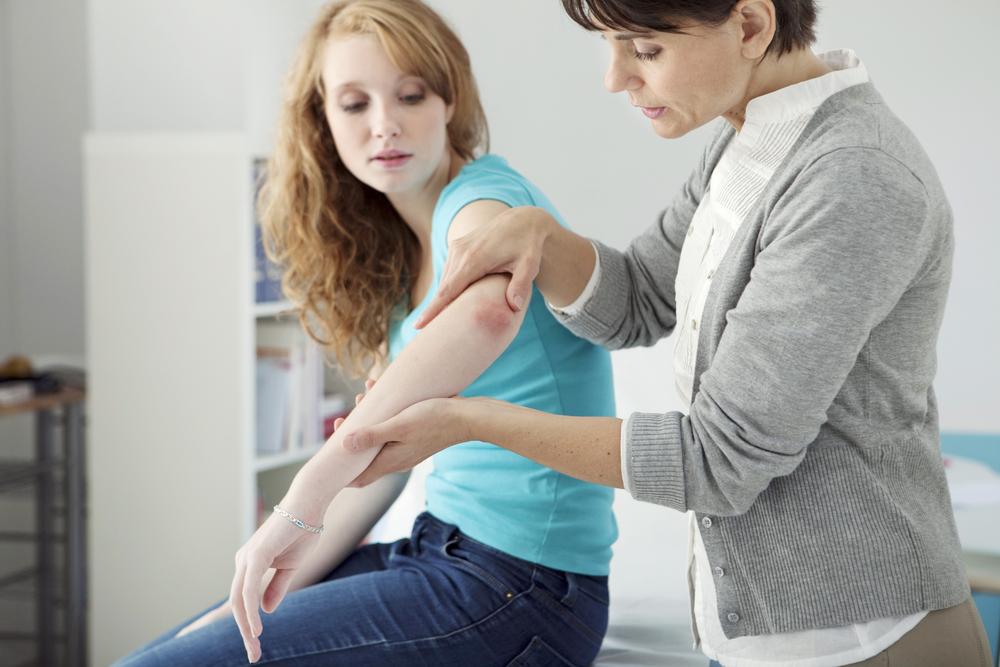
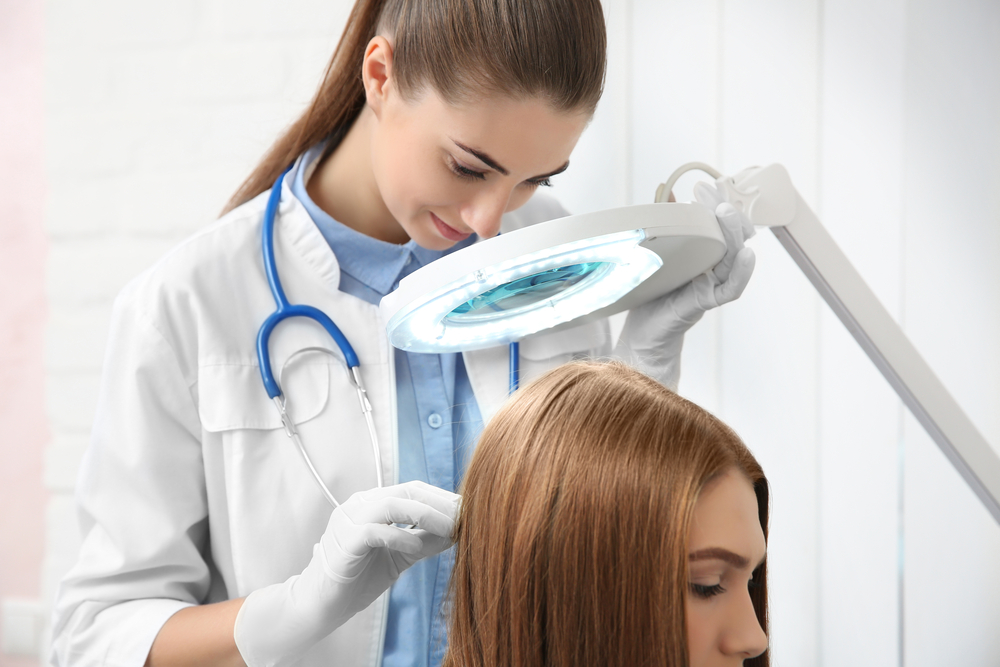
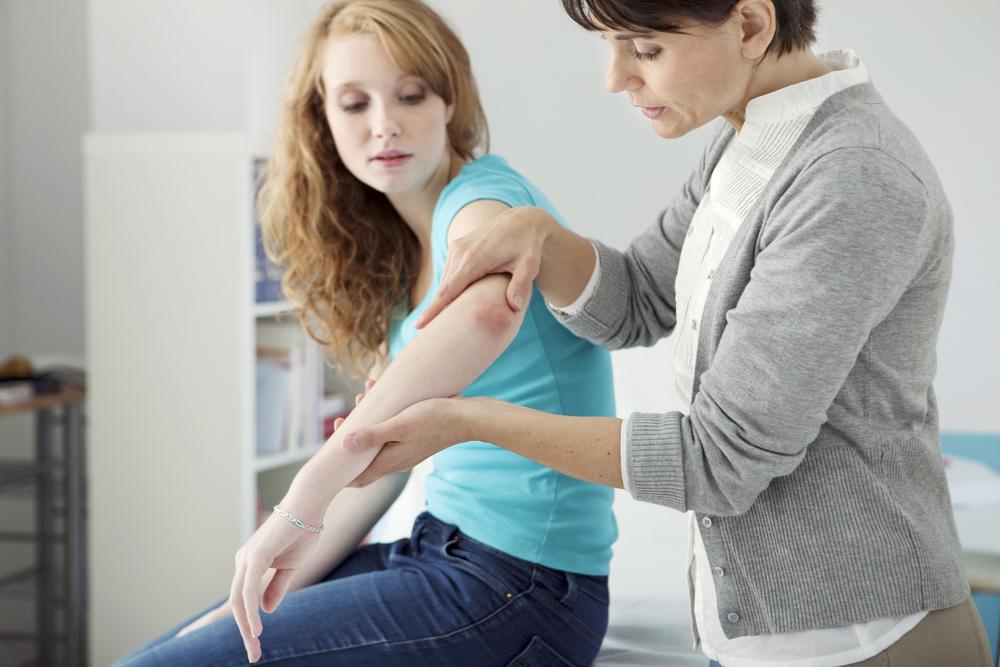
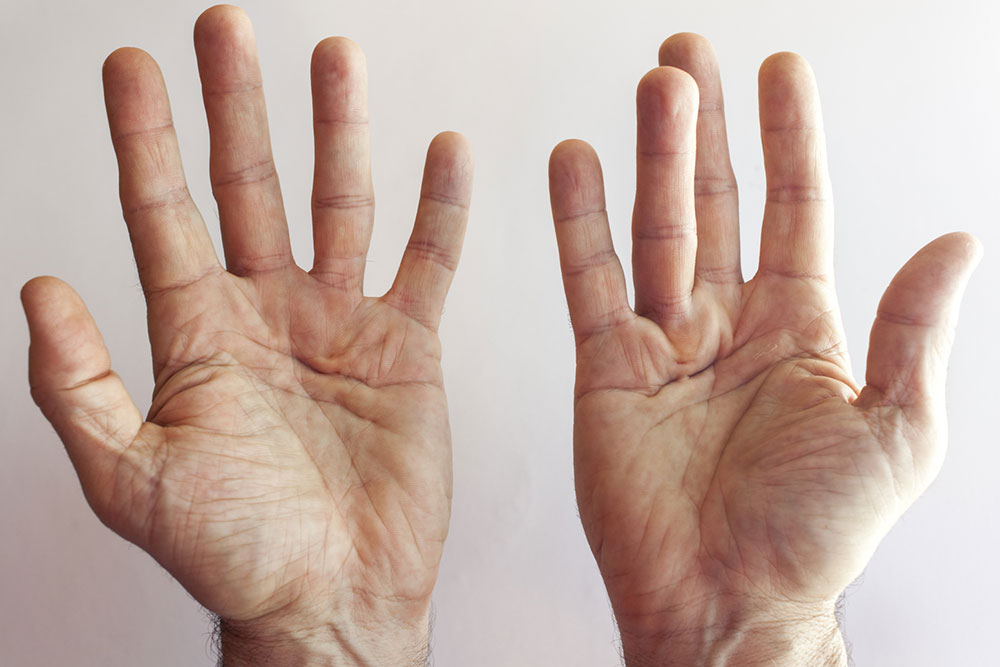
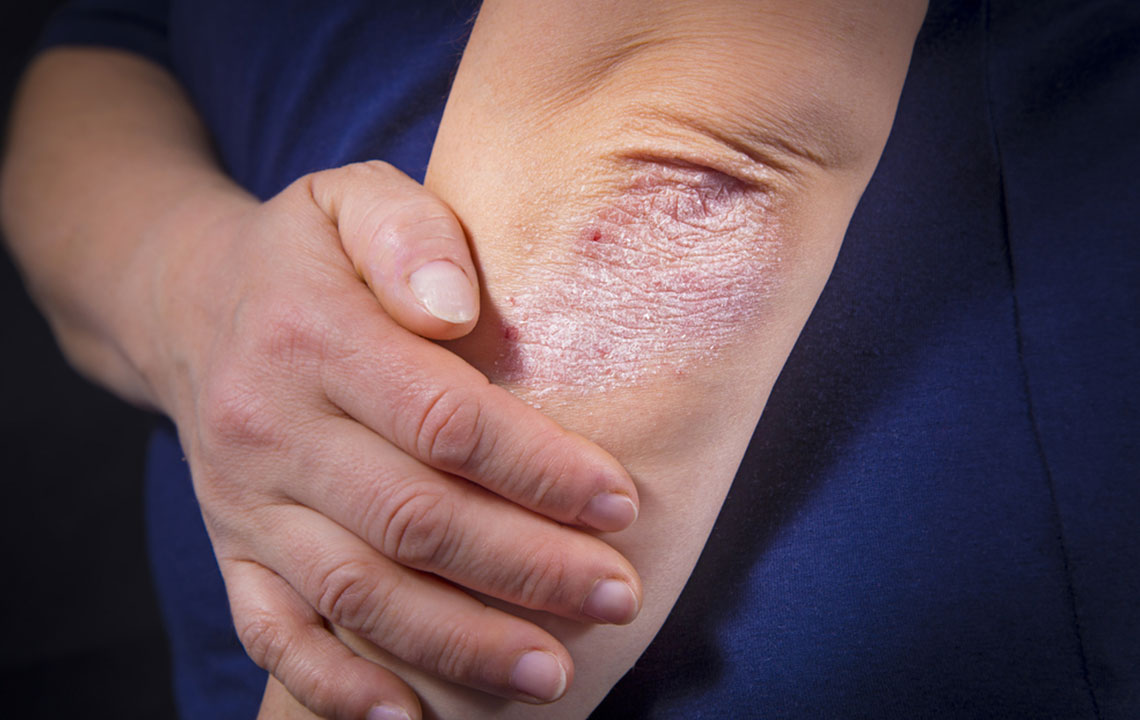
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disorder characterized by rapid skin cell growth, resulting in red, scaly patches. Typically developing in early adulthood, it can affect small or large areas of the body. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes are crucial for managing this condition. While no cure exists, various treatment options are available to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
Common Symptoms
Symptoms vary but often include:
Small, flaky skin lesions
Thickened nails with ridges or pitting
Itching, soreness, or burning sensations
Joint swelling and stiffness (psoriatic arthritis)
Dry, cracked skin that may bleed and cause discomfort
Underlying Causes
The exact cause remains unclear, but genetics and environmental factors play significant roles. Psoriasis may run in families and can be triggered by various external influences such as:
Infections like strep throat or skin infections
Cold or very dry weather
Stress of physical, mental, or emotional nature
Heavy alcohol use
Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke
Skin injuries, cuts, bug bites, or burns
Medications including beta-blockers
Available Treatments
Though psoriasis has no cure, treatment can control symptoms effectively. These options include:
Corticosteroid creams and ointments: Used for mild to moderate cases, available as topical applications, sprays, or shampoos.
Vitamin D analogs: Synthetic forms like calcipotriene and calcitriol slow skin cell proliferation and can be used alone or with corticosteroids.
Coal tar: Over-the-counter formulations that reduce scaling, itching, and inflammation.
Additional therapies include retinoids, calcineurin inhibitors, salicylic acid, and Goeckerman treatment. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any therapy.