Understanding the Differences Between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Gout: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
Discover the key differences between rheumatoid arthritis and gout, including their symptoms, causes, and treatment options. This comprehensive guide helps identify each condition, enabling timely diagnosis and effective management of foot joint pain and inflammation.
Sponsored

Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis and Gout: Key Differences in Symptoms, Causes, and Management
Comparing Rheumatoid Arthritis and Gout - Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Approaches
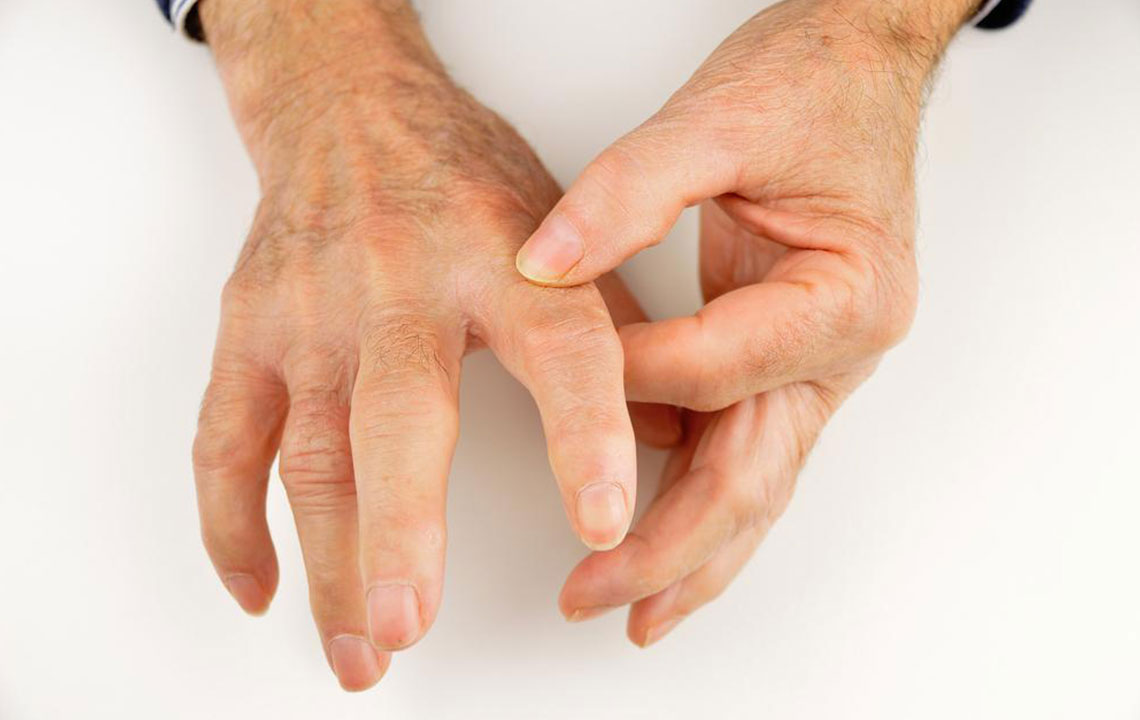
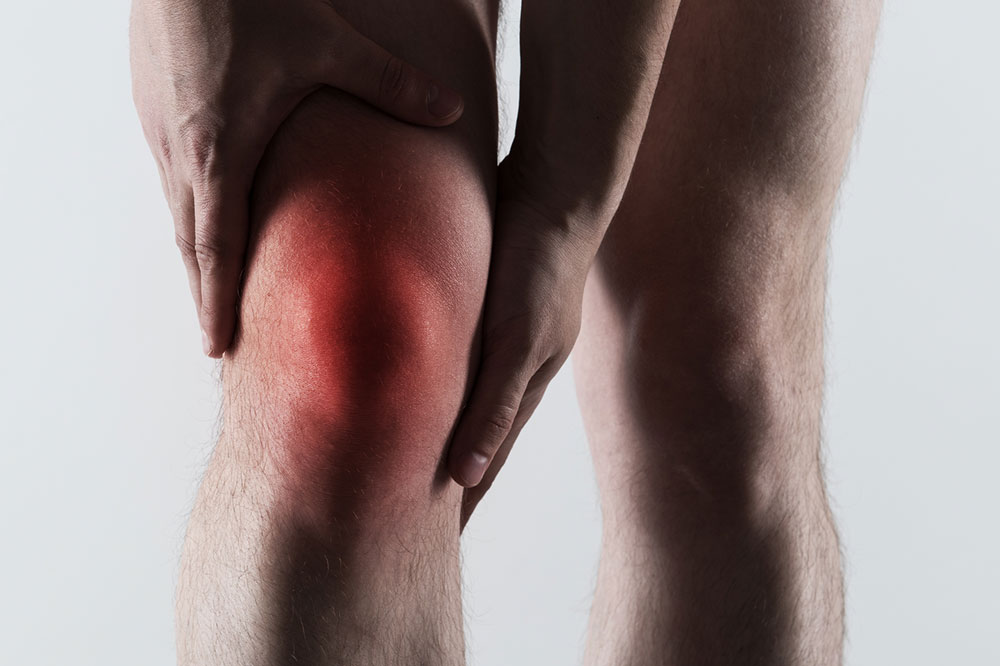
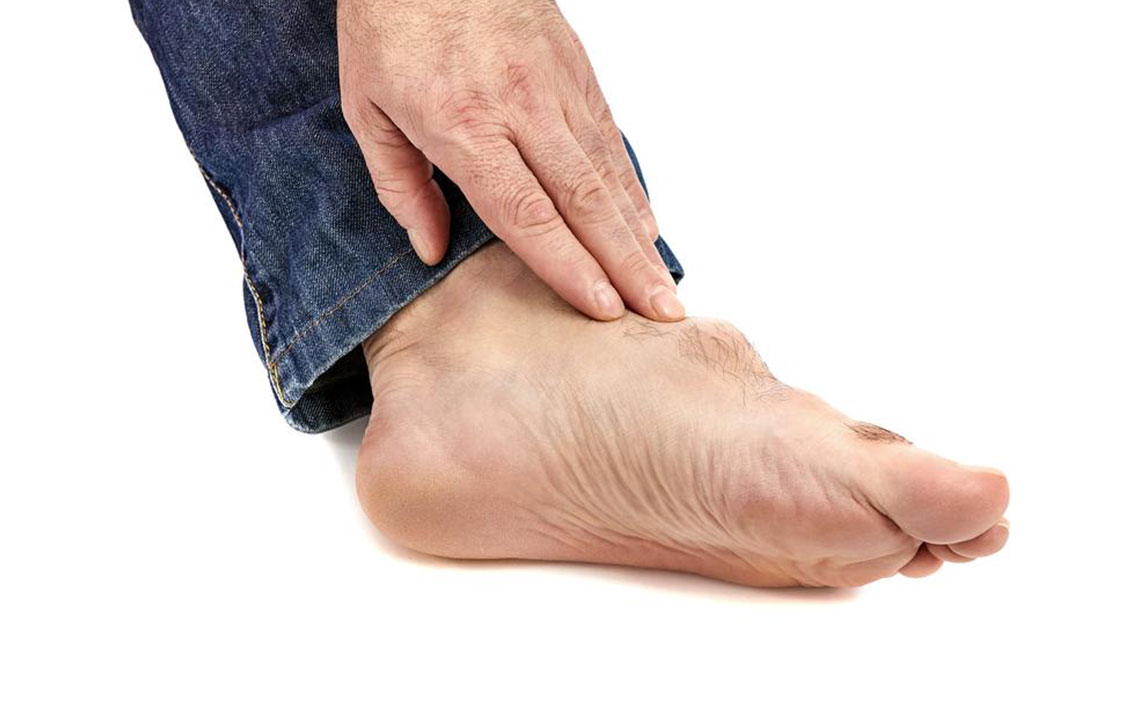
Arthritis affects over 54 million people nationwide, making it a leading cause of disability. Among its many types, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and gout are often mistaken for each other because they both involve painful joint inflammation. Typically targeting foot joints, their similar early symptoms can complicate diagnosis. Recognizing the unique features of each condition is crucial for timely and effective treatment. Keep reading to explore the distinctions and management options for rheumatoid arthritis and gout foot pain.
Both conditions impact joint health but differ significantly in cause, progression, and treatment. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease resulting in long-term joint swelling and stiffness, often affecting fingers, toes, and later other joints and organs. Its cause remains unclear but is linked to genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Gout, on the other hand, is characterized by sudden, intense attacks caused by urate crystal buildup in joints due to high uric acid levels, commonly impacting the big toe. Gout primarily affects men and tends to be episodic. Differentiating these conditions allows for targeted treatment to alleviate pain and prevent progression.
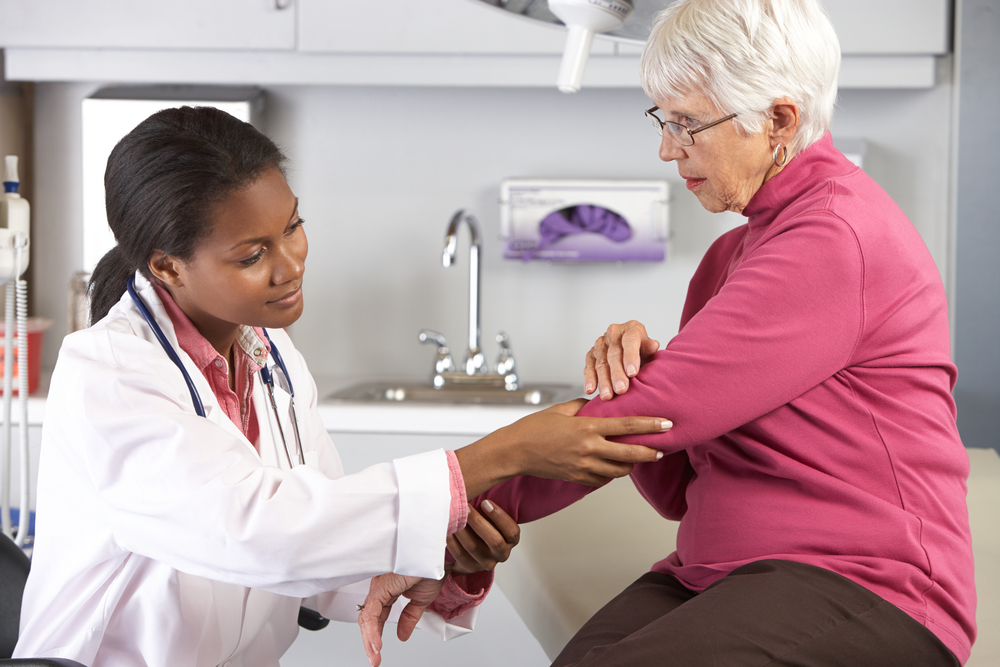
Accurate diagnosis involves blood tests measuring inflammation markers like ESR and CRP and uric acid levels. Imaging techniques such as X-rays and ultrasounds help detect joint changes and crystal deposits. Treatment varies: RA management includes NSAIDs, corticosteroids, DMARDs, and sometimes surgery to repair joints. Gout treatment focuses on controlling uric acid with medications like XO inhibitors and uricosurics, along with anti-inflammatory drugs during attacks. Recognizing symptoms early ensures better management and improved quality of life.