Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis: Essential Lifestyle Tips to Avoid Flare-Ups
This article provides practical lifestyle advice for managing rheumatoid arthritis, focusing on habits to avoid such as sedentary behavior, poor posture, and high-impact exercises. It emphasizes the importance of a balanced diet low in refined carbs and processed foods, and highlights emerging treatments like Otezla® that target inflammation. Implementing these tips can help reduce symptoms, prevent joint damage, and improve quality of life for individuals with RA.
Sponsored

Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis: Key Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Symptoms
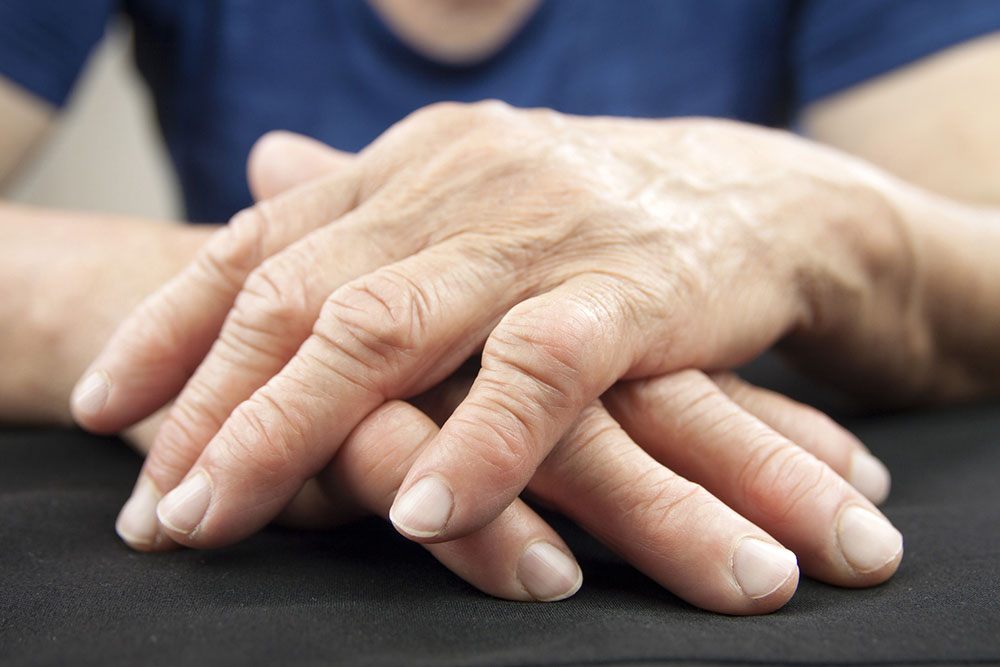
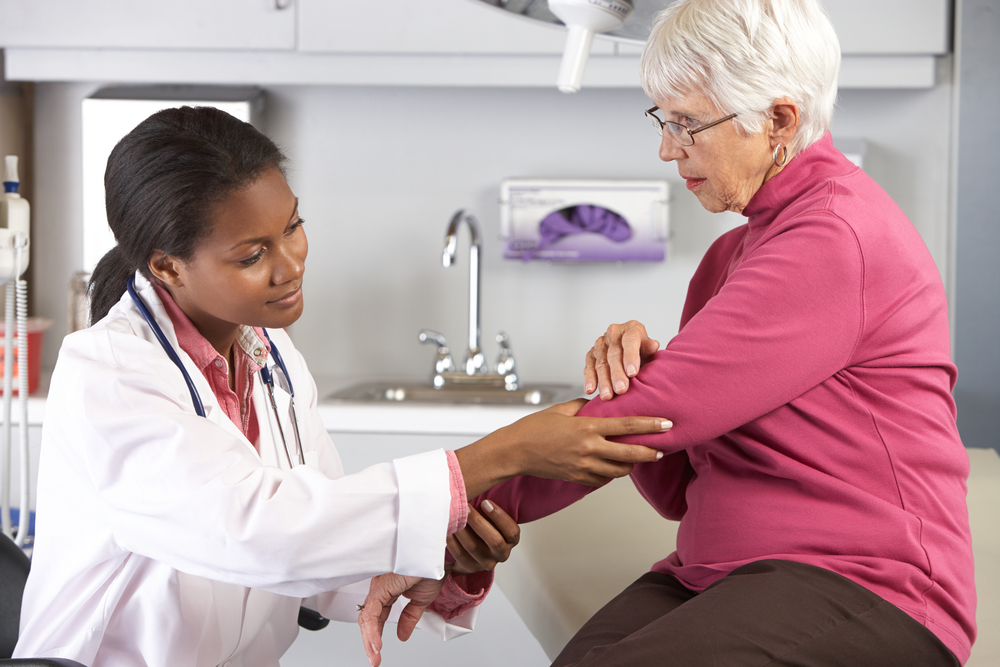
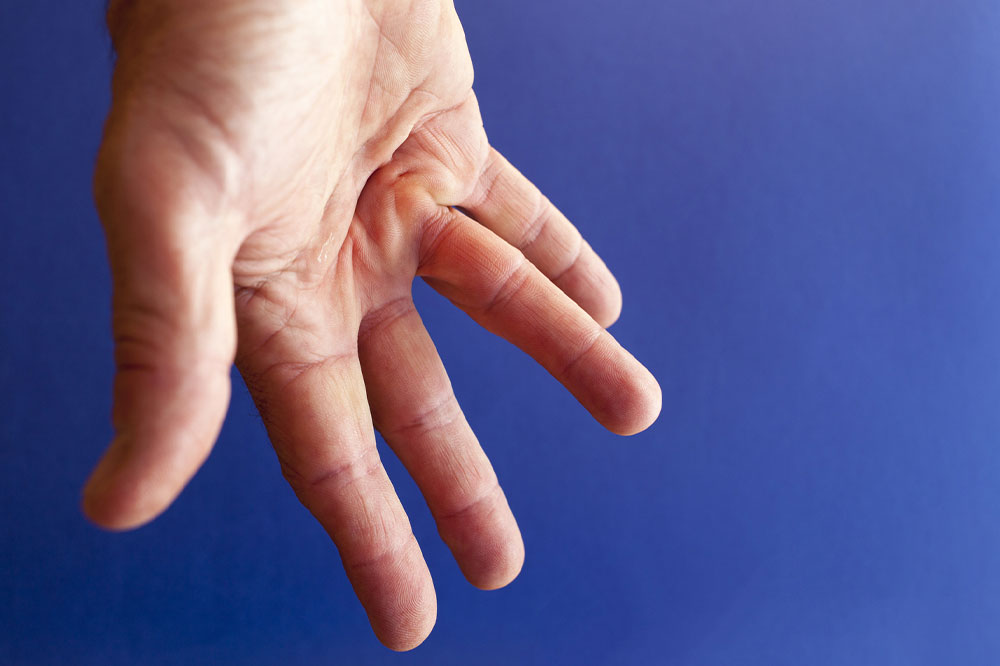
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by joint inflammation and cartilage deterioration. It results from the immune system attacking the body's tissues, often exacerbated by joint wear and tear. Over 50 million individuals worldwide, approximately 20% of the population, live with rheumatic conditions like RA. To better manage this condition, certain daily habits should be avoided to minimize flare-ups and joint damage.
Sedentary behavior
Staying inactive contributes significantly to RA progression. Lack of movement weakens joints and hampers symptom management. Incorporating gentle exercises can alleviate pain and strengthen joints.
Poor posture
Incorrect body positioning adds strain to weakened joints, worsening RA symptoms. Maintaining proper posture can reduce joint pain and support mobility.
Wearing high-heeled shoes
High heels place undue pressure on knees and hips, potentially aggravating cartilage damage and inflammation. Opting for comfortable footwear helps protect joints.
Engaging in high-impact workouts
Intense physical activity can harm sensitive joints, especially in RA patients. Low-impact exercises are preferable to avoid inflammation and tissue stress.
Eating refined carbs
Foods made from white flour, rice, pasta, and pastries lack essential nutrients and may increase inflammation. Reducing intake helps lessen symptoms.
Consuming processed foods
Packaged foods high in preservatives and additives like MSG can elevate sodium and uric acid levels, which might cause joint pain and swelling.
Drinking sugary carbonated drinks
Sodas and fizzy drinks are rich in sugar and can lead to weight gain, reduced calcium absorption, and increased risk of osteoarthritis and RA, especially in women with low calcium levels.
Otezla® (apremilast), a medication that inhibits an enzyme linked to inflammation, shows promise in early RA treatment, offering additional therapeutic options for managing symptoms.