Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Severe Psoriasis
Explore comprehensive treatment options for severe psoriasis, including topical therapies, phototherapy, and systemic medications. Effectively managing symptoms can improve quality of life. Consult with healthcare providers to determine the best approach tailored to your needs.
Sponsored

Effective Approaches to Managing Severe Psoriasis
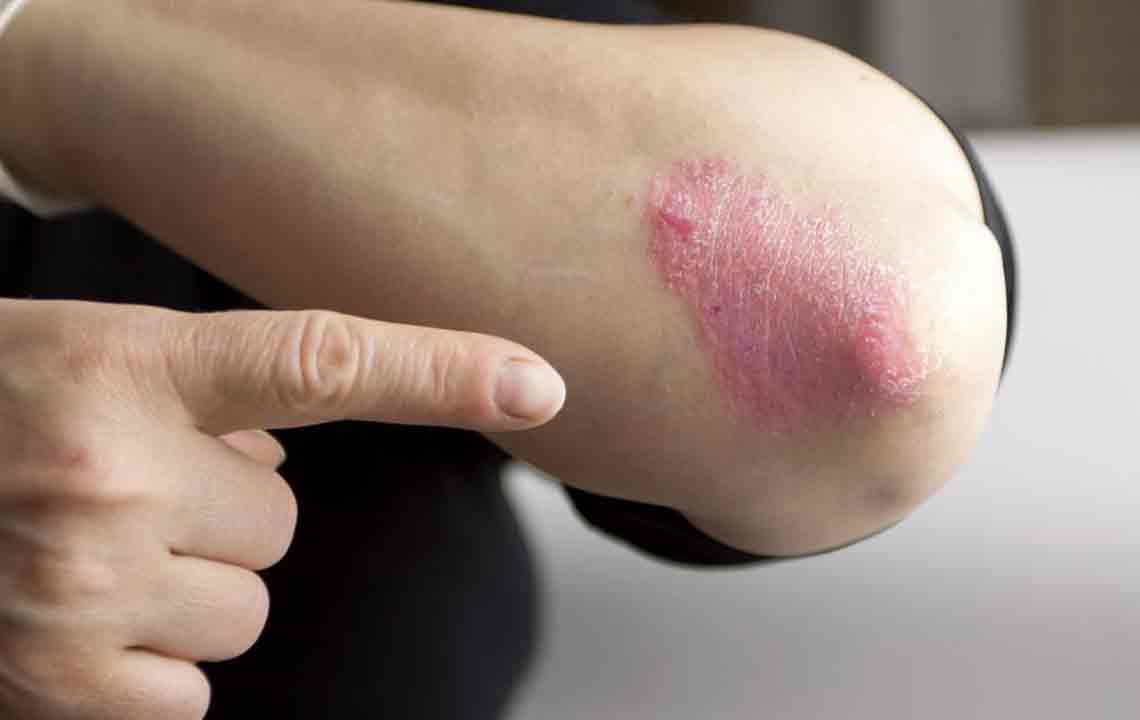
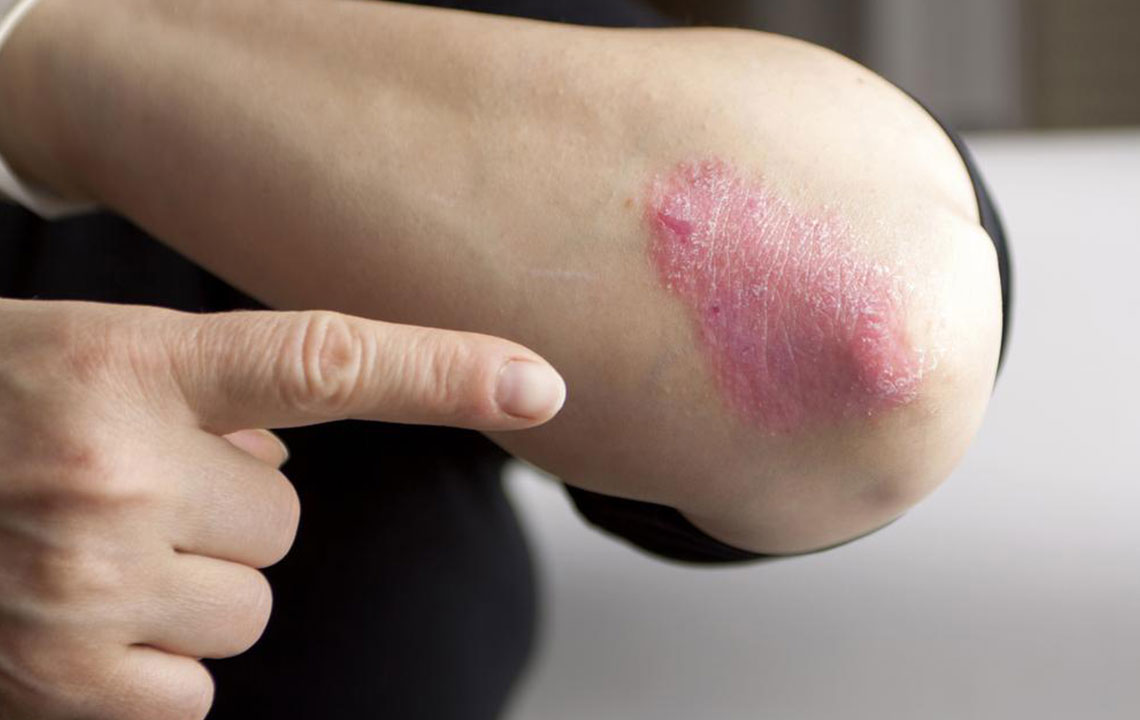
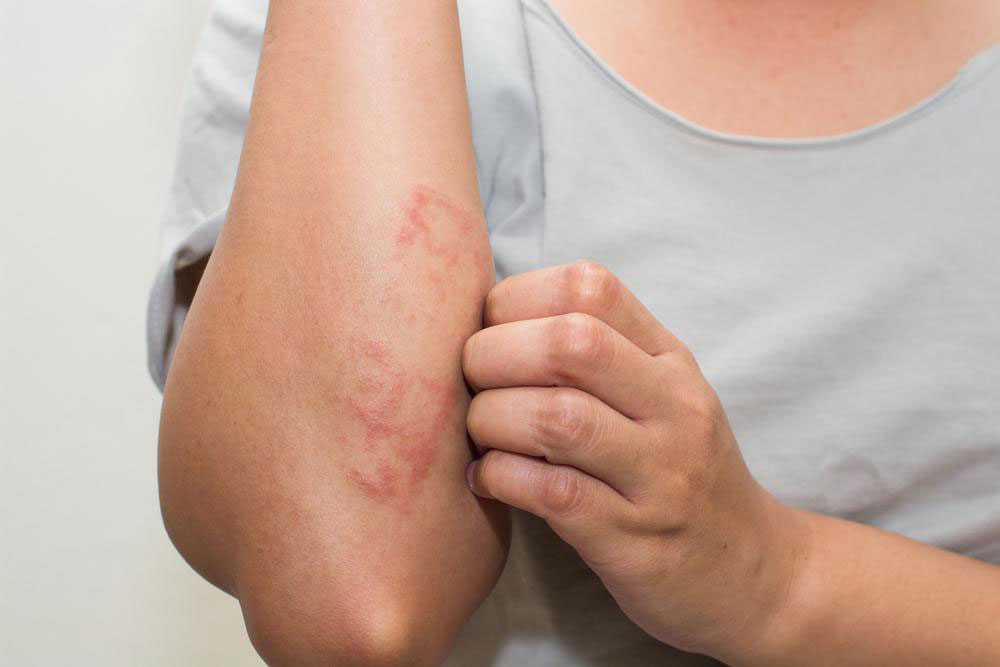
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by dry, itchy, and scaly skin patches. It results from accelerated skin cell growth, leading to abnormal skin appearance. While a permanent cure remains elusive, various treatment options can help manage symptoms effectively.
Treatment methods for psoriasis include:
Topical therapies
Low-dose corticosteroids – Help reduce inflammation and soothe itching, especially in sensitive areas like the face or skin folds.
Vitamin D analogs – Such as Calcipotriene, which slow down skin cell proliferation and are suitable for mild to moderate cases.
Additional topical treatments
Moisturizers – Applying emollients like petroleum jelly can diminish plaque formation.
Anthralin – Promotes slow skin renewal and scales removal but should be used cautiously due to potential irritation.
Salicylic acid – Removes dead skin layers, decreasing scaling, often used in medicated shampoos and scalp solutions.
Coal tar – Reduces inflammation and scaling, available as creams, shampoos, or oils but has a distinctive odor.
Topical retinoids – Derived from Vitamin A, they help lessen inflammation but should be used with sun protection.
Phototherapy options
Sunlight exposure – Controlled sunlight can slow skin cell production but excessive exposure may be harmful.
UVB therapy – Uses specialized lamps to deliver UVB light, effective for localized plaques, with broadband and narrow-band options.
Goeckerman therapy – Combines UVB with coal tar for enhanced effectiveness.
PUVA therapy – Uses photoactive medication with UVA light to penetrate deeper, suitable for resistant patches.
Systemic medications
Methotrexate – Suppresses immune response and slows skin cell growth.
Cyclosporine – Temporarily dampens immune activity but is not recommended for long-term use.
Biologic drugs – Such as Etanercept, Infliximab, Adalimumab, Ustekinumab, Golimumab, along with Apremilast, Secukinumab, and Ixekizumab, especially for treatment-resistant cases.