Recognizing the Top Signs of Pneumonia
This article highlights the key symptoms of pneumonia, including fever, cough, rapid breathing, chest pain, nausea, and changes in skin color. Prompt recognition of these signs can lead to early medical intervention, reducing risks of severe complications, especially for vulnerable groups like children and the elderly. Understanding the differences between hospital-acquired and community pneumonia helps tailor appropriate treatment. Recognizing symptoms early ensures better health outcomes and saves lives.
Sponsored

Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs, known as alveoli, in one or both lungs. These sacs fill with fluid or pus, hindering oxygen transfer to the bloodstream and potentially causing severe health issues. There are different forms, including lobar pneumonia affecting one lobe, and multilobar impacting several. It can also be unilateral or bilateral, posing serious risks especially for children and seniors over 65. Pneumonia often results from bacterial or viral infections, with symptoms varying accordingly.
It can lead to complications and weakened immune defenses.
Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) typically develops during hospital stays, especially in ICU or ventilated patients, and tends to be more severe. Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), common outside healthcare settings, is usually caused by bacteria in adults and viruses in children. Recognizing these types helps in prompt treatment and management.
Common symptoms of pneumonia include:
High fever with chills
Fever often appears suddenly with chills, indicating severe infection. Chills may be more intense than the fever itself, with teeth chattering and temperatures soaring to 105°F. Persistent high fever and chills are key indicators.
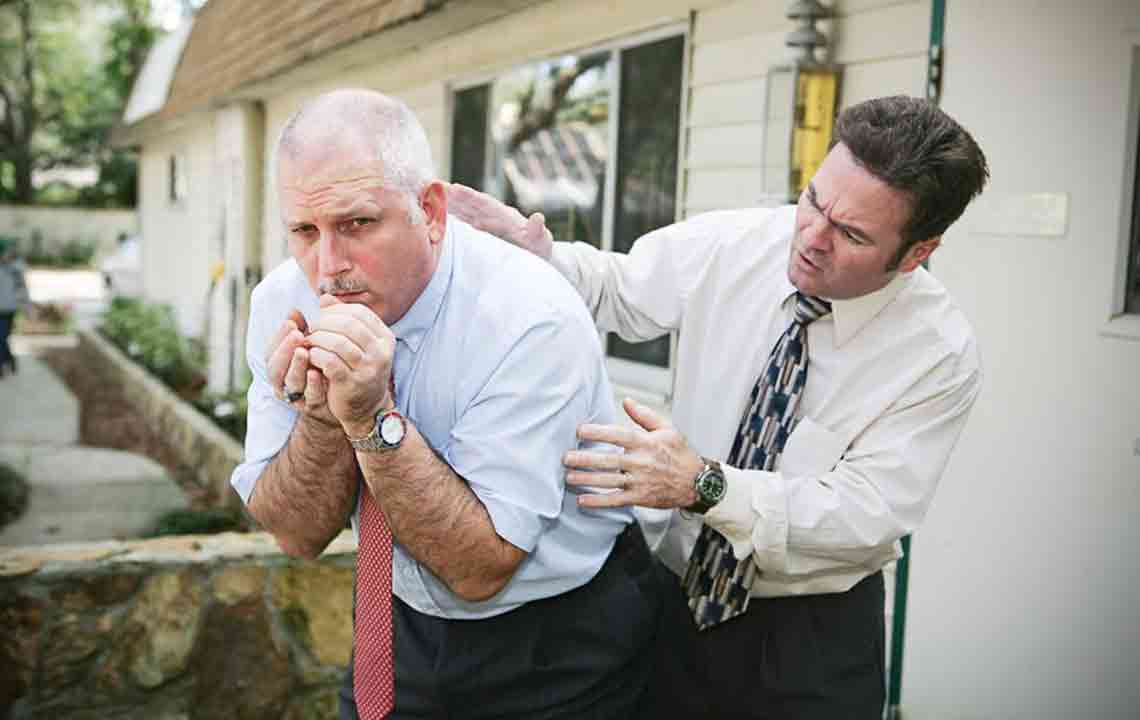
Persistent cough
A severe, dry cough accompanied by mucus or blood is typical. Patients often feel throat irritation and chest tightness, with mucus streaked with green or rust-colored blood, and worsening symptoms after initial hours.
Rapid breathing
Shortness of breath and increased respiratory rate are crucial signs. Patients may wheeze or grunt, and a rapid pulse often accompanies this symptom, indicating respiratory distress.
Pleuritic chest or abdominal pain
Sharp chest pain, especially during deep breaths, and localized pain are common. If the infection affects the lower lungs, abdominal discomfort may also occur.
Nausea and vomiting
Children may refuse food and show signs of stomach unease, with nausea and vomiting. Such symptoms can cause confusion and delirium if untreated.
Color change in lips and nails
Severe cases may turn lips and nails bluish or grayish, reflecting oxygen deprivation and breathing difficulties.
If you experience these symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional immediately is vital. Pneumonia can weaken your health rapidly and become life-threatening if ignored. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential, so spreading awareness can help others seek timely care and prevent complications.