Effective Strategies for Managing Deep Vein Thrombosis
This article explores the key methods for treating deep vein thrombosis (DVT), including medication options, compression therapy, filters, and advanced procedures like thrombolysis. Early diagnosis and tailored treatment are essential to prevent serious complications such as pulmonary embolism. Understanding these approaches can help patients and clinicians manage DVT effectively and reduce risks associated with this condition.
Sponsored
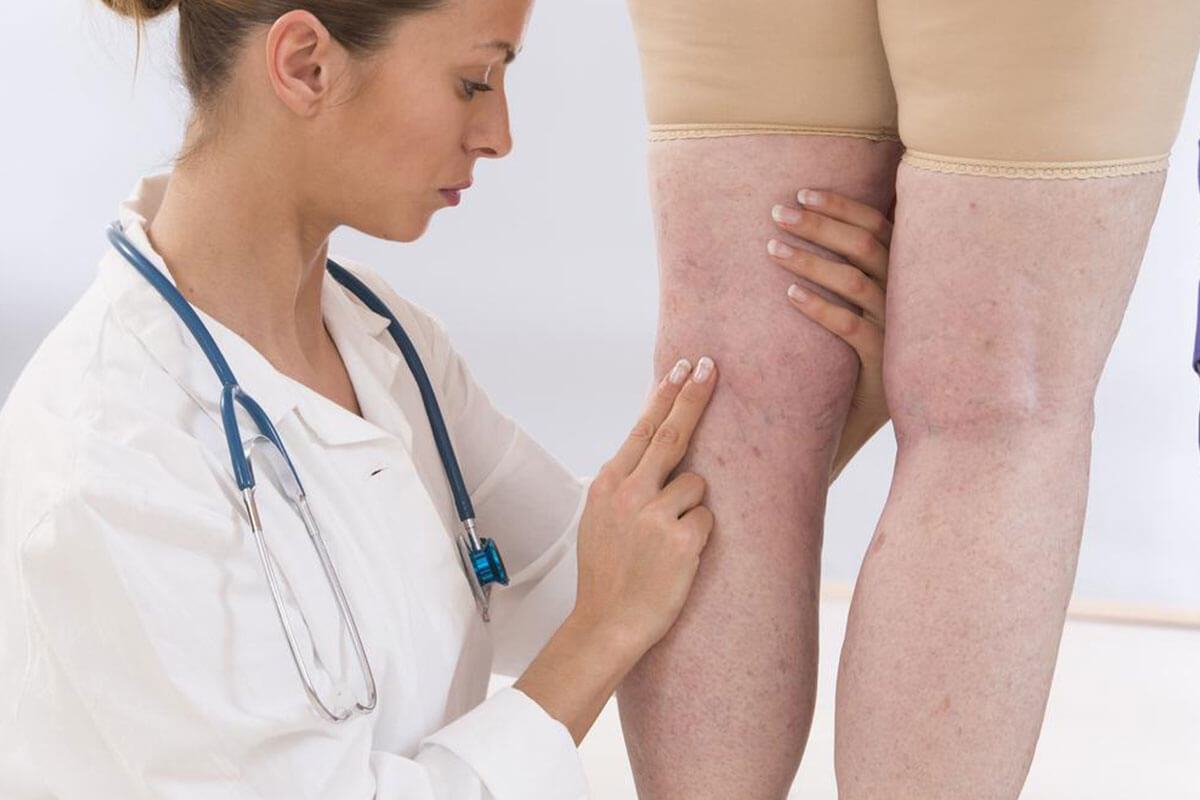
Approaches to Treating Deep Vein Thrombosis
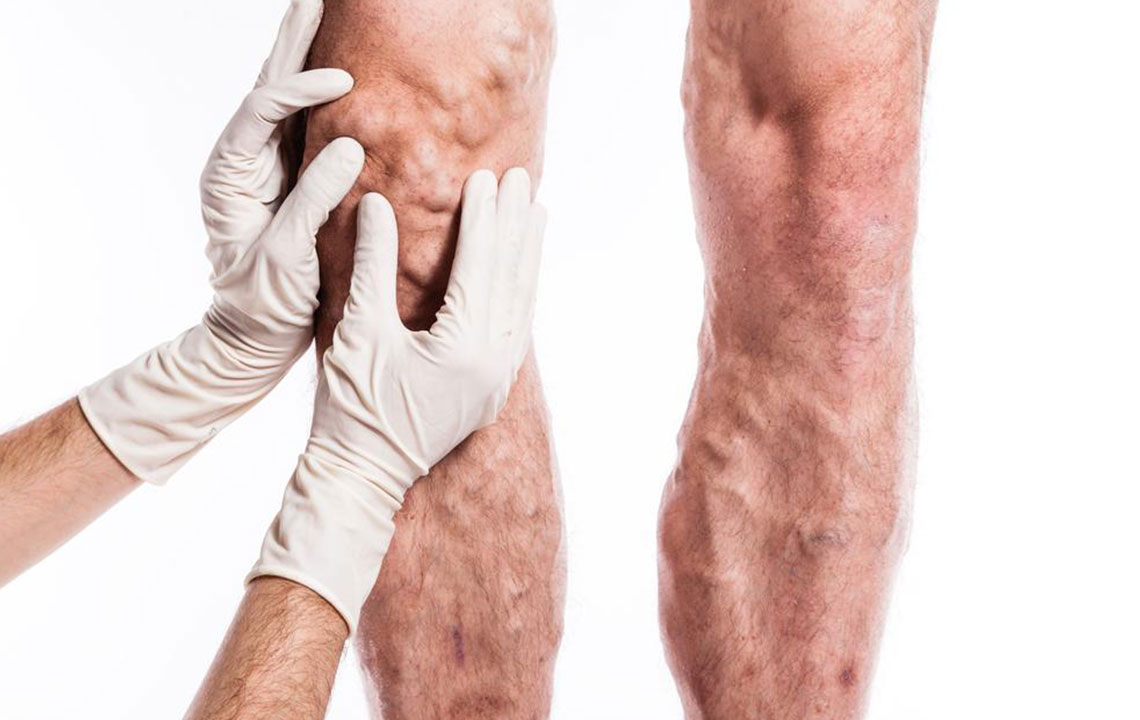
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot develops within deep veins, often in the legs. Here’s an overview of common treatment options for DVT.
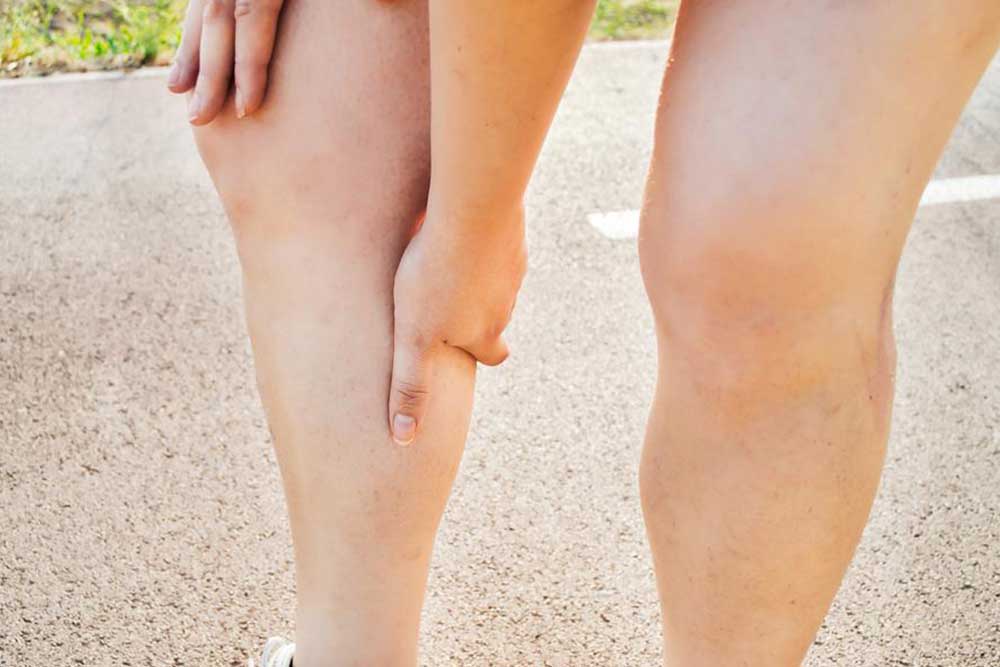
If you experience a clot in a deep vein, especially in your legs, you may notice swelling and discomfort without other symptoms. Risk factors include smoking, obesity, sedentary habits, and being over 60. Recognizing early signs is vital to prevent complications.
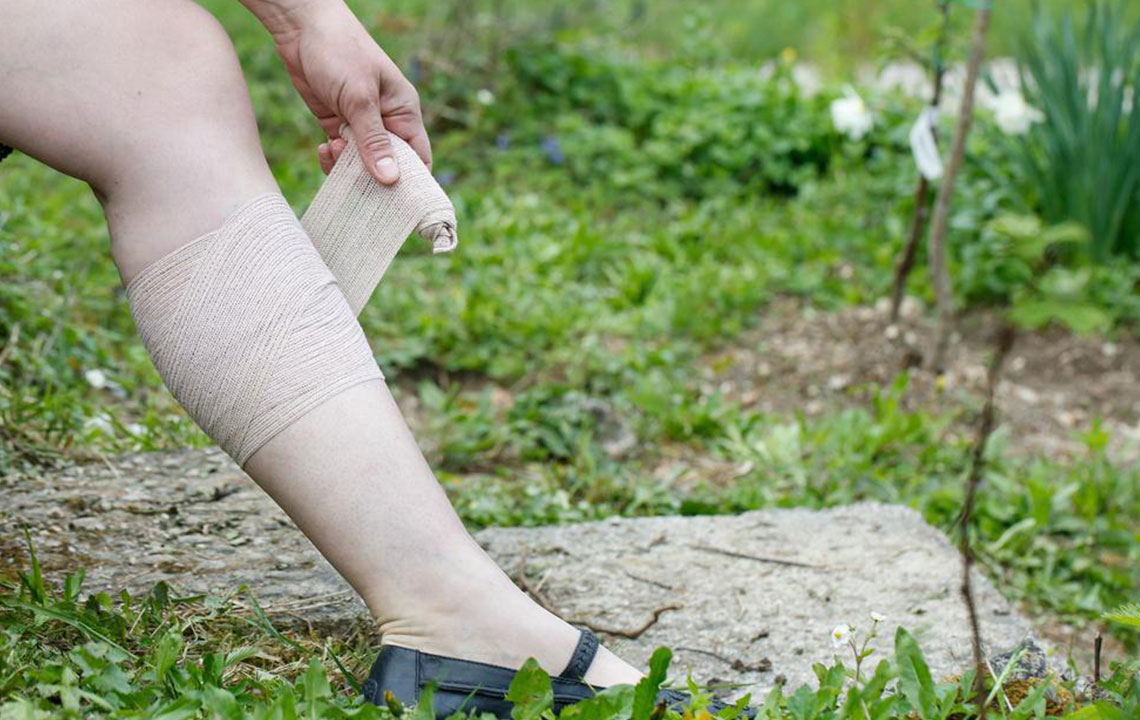
Monitoring for symptoms like leg pain and swelling is crucial, especially if you belong to a high-risk group. DVT is serious because clots can dislodge and travel to the lungs, causing pulmonary embolism. Diagnosis often involves ultrasound, MRI, or venography to confirm the presence of clots. Treatment aims to prevent clot expansion, reduce risk of embolism, and manage symptoms. Common approaches include anticoagulant medications such as heparin, warfarin, and rivaroxaban, which thin the blood to prevent clot growth. Compression stockings can also help reduce swelling and improve blood flow. In cases where medications cannot be used, filters implanted in the vena cava prevent clots from reaching the lungs. For high-risk cases, catheter-directed thrombolysis uses agents to dissolve clots rapidly, though it carries higher risks like bleeding. The best treatment plan depends on individual health and DVT severity, determined by your healthcare provider.