Understanding Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Symptoms and Causes
This article explores the key symptoms and causes of squamous cell carcinoma, a common skin cancer. It emphasizes the importance of recognizing early signs such as sores, bumps, and patches, especially on sun-exposed skin areas. The piece highlights how genetic mutations influenced by ultraviolet rays contribute to its development and underscores prompt medical intervention for effective treatment. Although usually not life-threatening initially, untreated cases can lead to serious health issues, making awareness vital for prevention and early diagnosis.
Sponsored
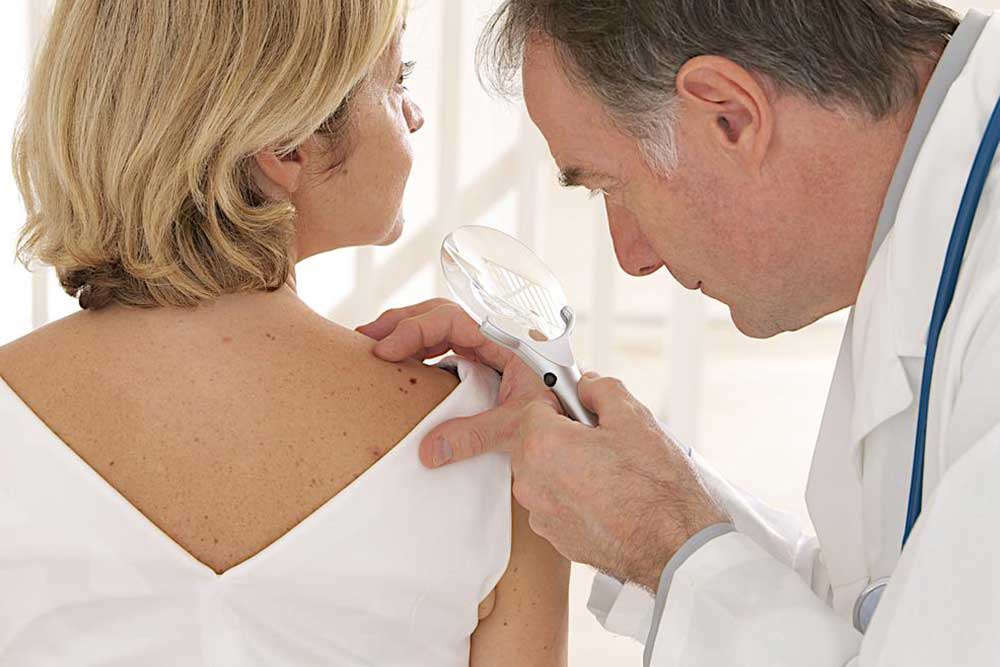
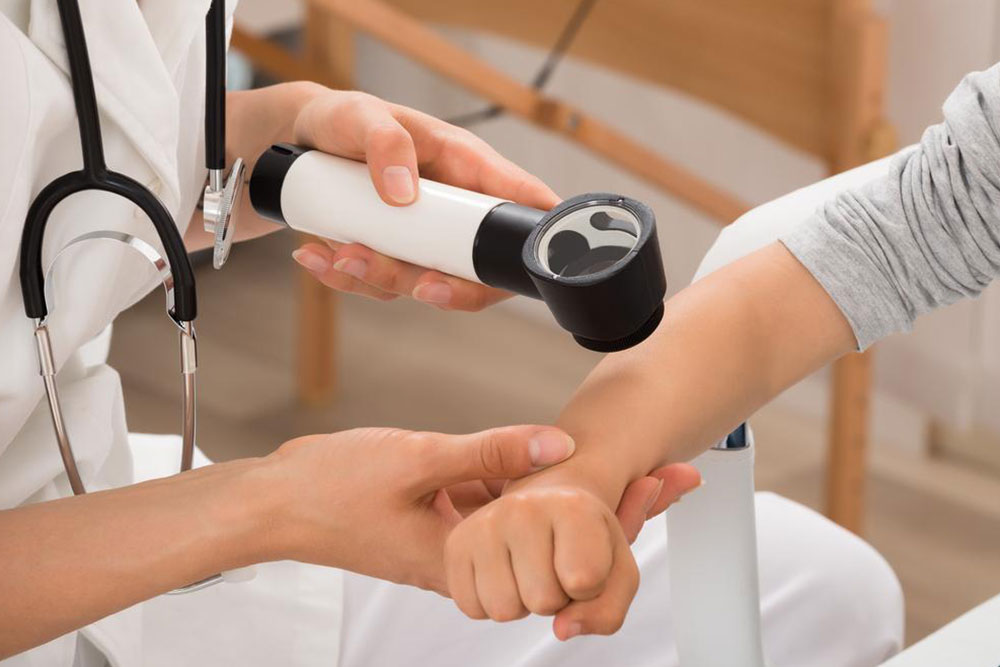
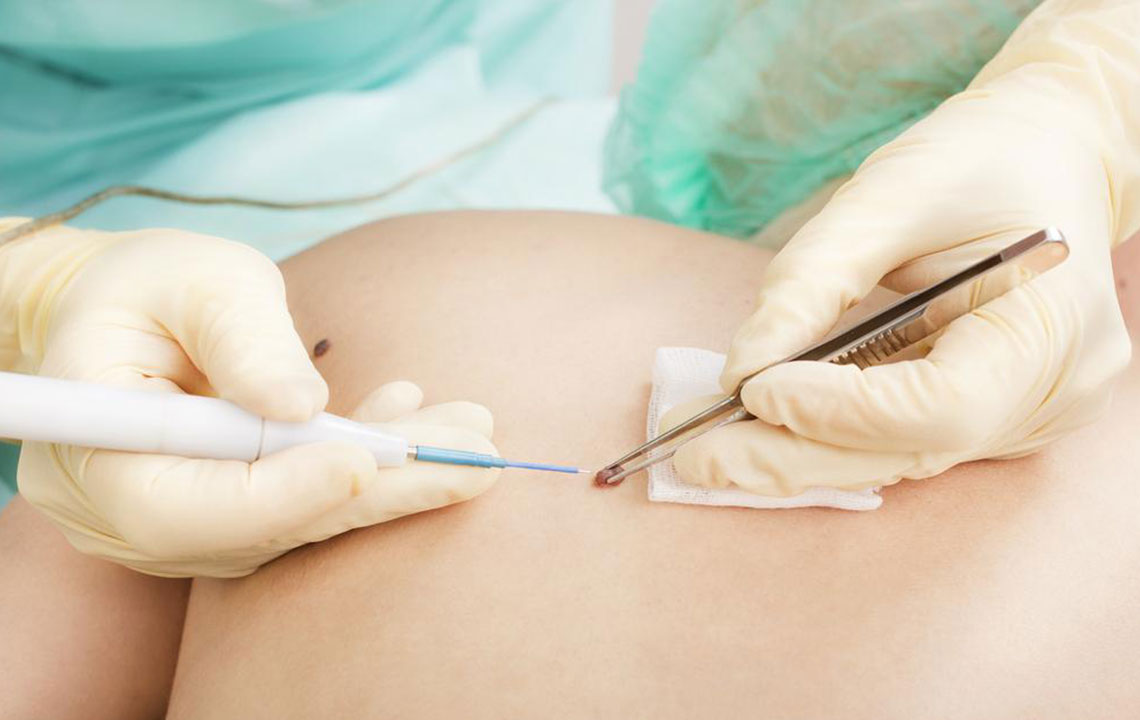
Squamous cell carcinoma ranks among the prevalent skin cancers, originating from the squamous cells of the skin's middle and outer layers. While often not considered life-threatening initially, neglecting treatment can lead to tumor growth or metastasis, posing serious health risks.
Signs of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
This form of skin cancer commonly appears on sun-exposed areas, presenting various symptoms:
A firm, red bump
A persistent sore with a scaly surface
A new ulcer or recurring sore on the skin or scar
A rough, scaly patch around the lips that may turn into an open sore
A red lesion or patch inside the mouth that may cause itching
What Causes Squamous Cell Carcinoma?
The condition arises when skin cells experience genetic mutations disrupting normal cell growth. Typically, new cells replace older ones, but DNA errors cause uncontrolled proliferation, resulting in cancer.
Primary Factors Contributing to Risk
Ultraviolet radiation from sunlight and tanning devices causes significant DNA damage in skin cells. Interestingly, cancers can also develop on less sun-exposed skin, suggesting other influencing factors. Although less aggressive than other cancers, early detection and treatment are essential. Seek medical advice if symptoms appear to prevent severe complications, as squamous cell carcinoma remains a serious health concern if ignored.