Understanding Osteoarthritis: Symptoms and Treatment Options
This article provides comprehensive insights into osteoarthritis, highlighting key symptoms such as joint stiffness, pain, tenderness, and bone spurs. It discusses various treatment options including medications, physical therapy, and surgical procedures. Early diagnosis and intervention are emphasized for better outcomes, with advice on lifestyle modifications to manage and alleviate symptoms effectively. Understanding these aspects can help individuals seek timely medical help and improve joint health.
Sponsored

Osteoarthritis: Key Symptoms and Effective Treatments
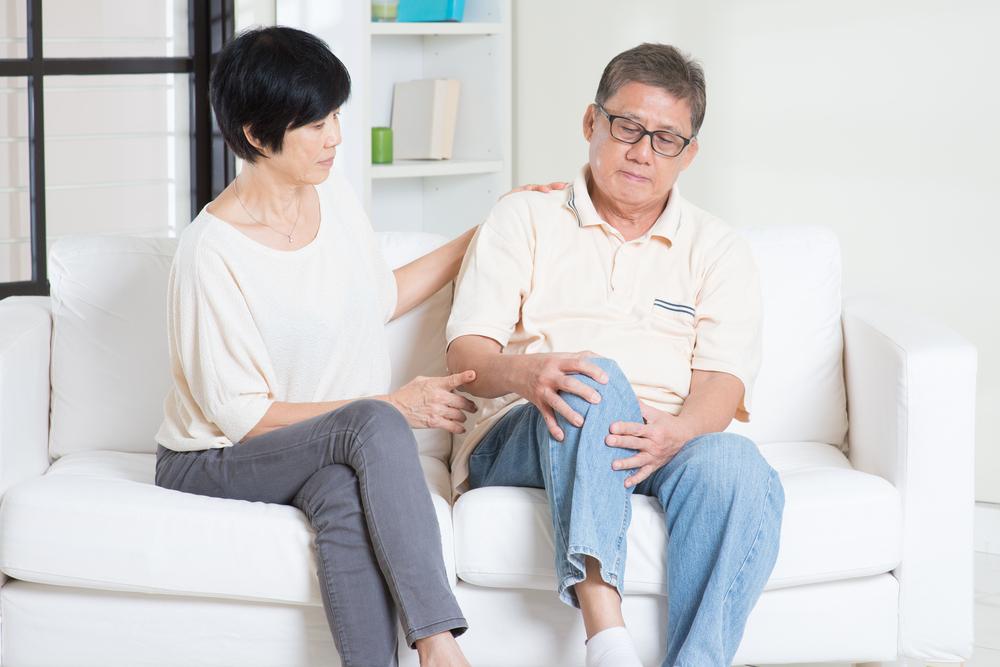
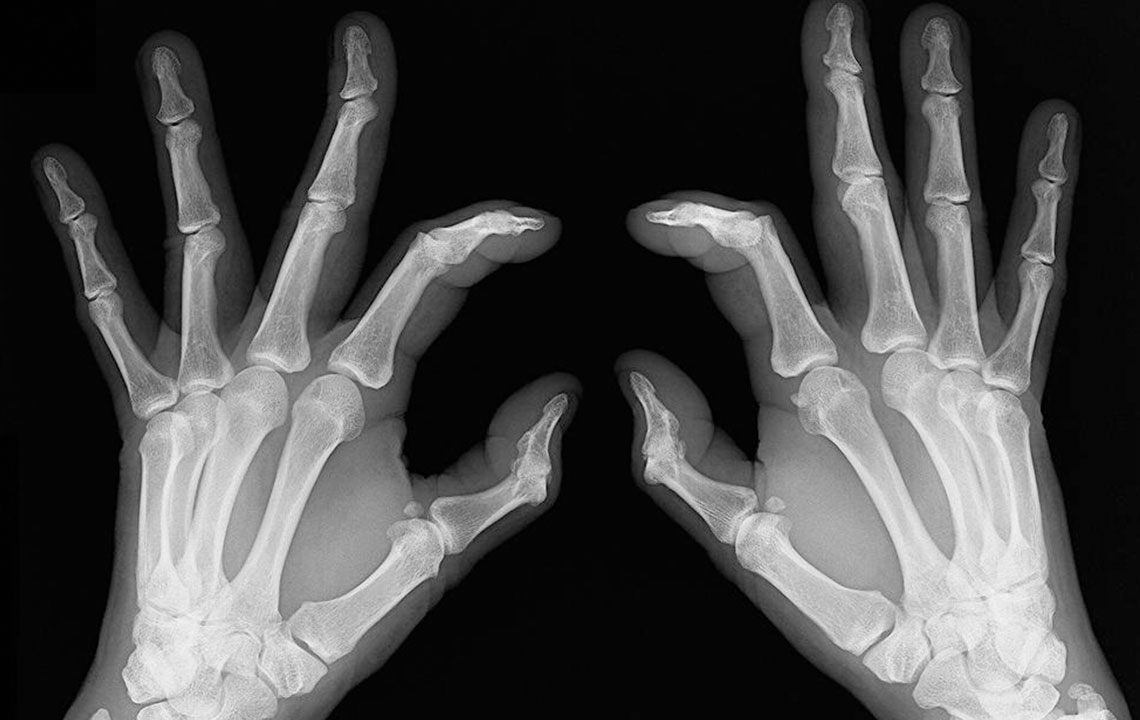
Osteoarthritis is the most prevalent form of arthritis, commonly affecting seniors and individuals with obesity. It is a degenerative joint disease that impacts areas such as the knees and hips. The condition occurs when cartilage deteriorates, losing its ability to cushion bones during movement. Over time, this wear and tear lead to increased friction, resulting in pain, restricted mobility, swelling, and other discomforts.
If left untreated, osteoarthritis can worsen, causing permanent joint damage and chronic pain. Recognizing early symptoms is crucial for prompt intervention. Below are common signs to watch for.
Joint Stiffness: Feeling stiffness after inactivity is typical. Reduced flexibility may hinder daily tasks.
Persistent Pain: Ongoing joint pain during movement signifies the need for medical attention—early treatment prevents deterioration.
Joint Tenderness: Tenderness upon touch and difficulty bearing weight indicate progressive damage. Bone tenderness or rubbing sensation may occur.
Bone Spurs: Extra bone growths, known as spurs, develop around affected joints and can cause discomfort.
Once diagnosis confirms osteoarthritis, various treatment options are available. Medications, physical therapy, and in advanced cases, surgery, can manage symptoms effectively.
Medication Approaches: NSAIDs, acetaminophen, and duloxetine help reduce pain and inflammation. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized prescriptions.
Therapeutic Interventions: Physical therapy, yoga, and regular exercise strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and alleviate joint stress. Active lifestyles and strength training yield positive outcomes.
Surgical Options: Surgery is considered when conservative treatments fail. Procedures like joint replacement or realignment repair severe joint damage.
Osteoarthritis often coexists with osteoporosis, a condition causing decreased bone density. Modern treatments include new medications and dietary supplements to enhance bone strength. Early symptom recognition and prompt consultation with an orthopedic specialist are essential for effective management.