Understanding Erectile Dysfunction: Symptoms, Causes, and Risk Factors
This article provides essential insights into erectile dysfunction, covering symptoms, causes, and risk factors. Understanding these elements helps in early diagnosis and proper management. It highlights the importance of medical consultation if symptoms persist and emphasizes lifestyle changes to reduce risks. An overview of hormonal, neurological, cardiovascular, and psychological factors offers a comprehensive understanding of ED, facilitating better health decisions. Regular screening and healthy habits are vital for maintaining sexual health and overall well-being.
Sponsored

Learn about the indicators, origins, and contributing factors of erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction refers to the inability to achieve or sustain an erection or to reach ejaculation. Causes can be emotional or physical, affecting not just sexual performance but also leading to stress, poor self-esteem, or depression. Recognizing symptoms is crucial for early intervention.
Signs to watch for include
Consistent difficulty in getting an erection
Trouble maintaining an erection during intimacy
Lowered sexual desire
Other related issues may involve delayed, premature ejaculation, or inability to orgasm despite stimulation. If symptoms persist beyond two months, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable.
Common causes of erectile dysfunction
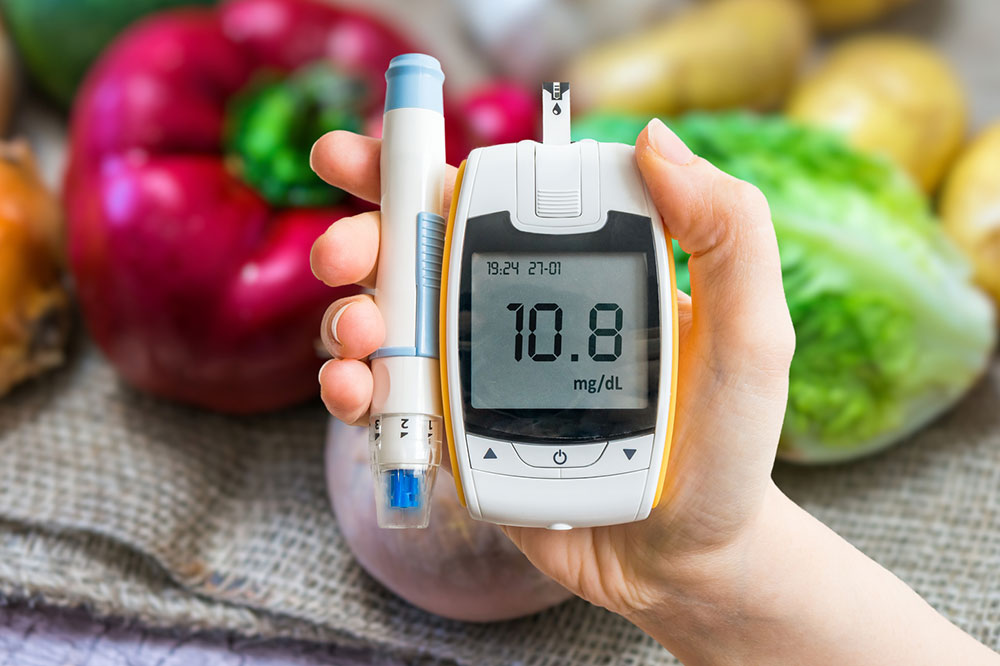
Hormonal and endocrine disorders
Conditions like diabetes affect hormone balance, impair blood flow, and damage nerves, all of which can lead to ED.
Medication side effects
Certain drugs may interfere with blood circulation, contributing to ED; always consult a doctor before stopping or changing medications.
Neurological issues
Nerve-related conditions such as Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis, or brain injuries can disrupt signals necessary for an erection. Surgery or trauma to the prostate can also cause nerve damage.
Cardiovascular conditions
Heart-related issues like clogged arteries, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol reduce penile blood flow, leading to ED.
Psychological and lifestyle factors
Emotional states like depression, anxiety, or stress hinder sexual arousal. Substance abuse, including alcohol, illicit drugs, or performance anxiety, also increase risk.
Risk factors for erectile dysfunction
Smoking - Contributes to arterial hardening, thus decreasing blood flow to the penis.
Obesity - Excess weight increases blood vessel disease risks, impacting erectile function.
Stress - Mental stress impedes relaxation, affecting the ability to achieve an erection.