Understanding Immune System Disorders: Symptoms, Causes, and Risk Factors
This article explores the key signs, underlying causes, and risk factors associated with immune system disorders. It highlights symptoms like cold extremities, dry eyes, fatigue, and mild fever, all of which can indicate immune dysfunction. Causes such as medication effects, malnutrition, and genetic factors are discussed. Understanding these aspects helps in early detection and management of immune-related health issues, emphasizing the importance of prompt medical attention for proper care.
Sponsored
The immune system functions as the body's defense mechanism, safeguarding against various illnesses. A robust immune system enhances the body's ability to prevent diseases, while a compromised immune system or immunodeficiency requires prompt attention.
Symptoms
Cold extremities
Inflamed blood vessels can prevent warmth in fingers, toes, nose, and ears, causing skin to turn pale or blue under cold conditions. When circulation improves, skin reverts to its normal color, a condition known as Raynaud’s phenomenon, common in immune disorders.
Dry Eyes
Autoimmune conditions like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can cause dry, gritty, or red eyes, sometimes with blurry vision. Difficulty crying and eye pain are also typical symptoms.
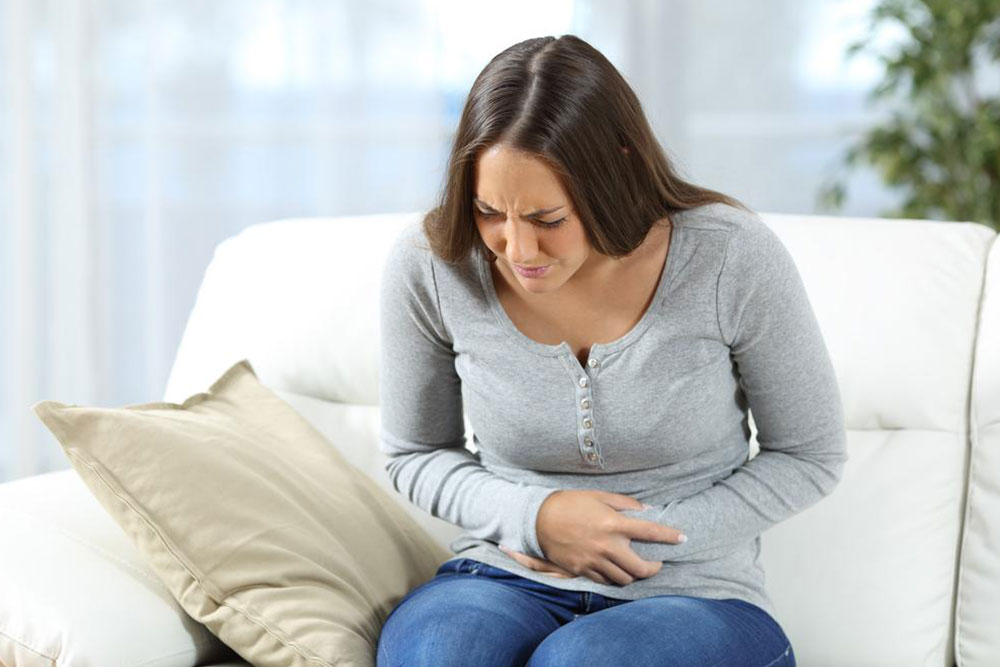
Persistent Fatigue
Ongoing tiredness despite adequate sleep may indicate immune dysfunction. Muscle and joint aches often accompany this feeling of exhaustion.
Mild Fever
Elevated body temperature might signal immune activation due to infection or autoimmune response. Persistent low-grade fever warrants medical evaluation.
Causes
Medications
Extended use of certain drugs, especially in cancer treatments, can suppress immune responses, leading to disorders.
Poor Nutrition
Malnutrition hampers cell-mediated immunity and antibody production, increasing vulnerability.
Additional Factors
Inherited conditions, limited environmental exposure, and infections also contribute to immune system issues.
Risk Factors
Gender
Women are more susceptible to autoimmune diseases compared to men.
Age
Young and middle-aged individuals are predominantly affected in autoimmune conditions.
Other Risks
Family history, prior infections, and environmental exposures can elevate risk levels.