Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management
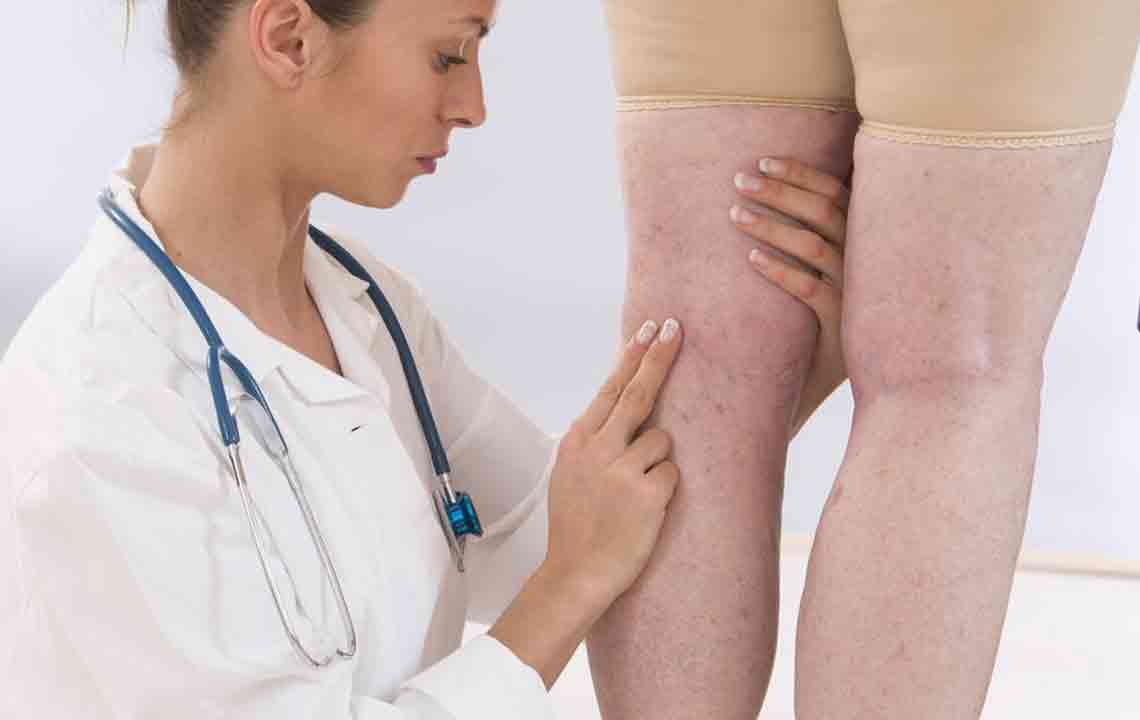
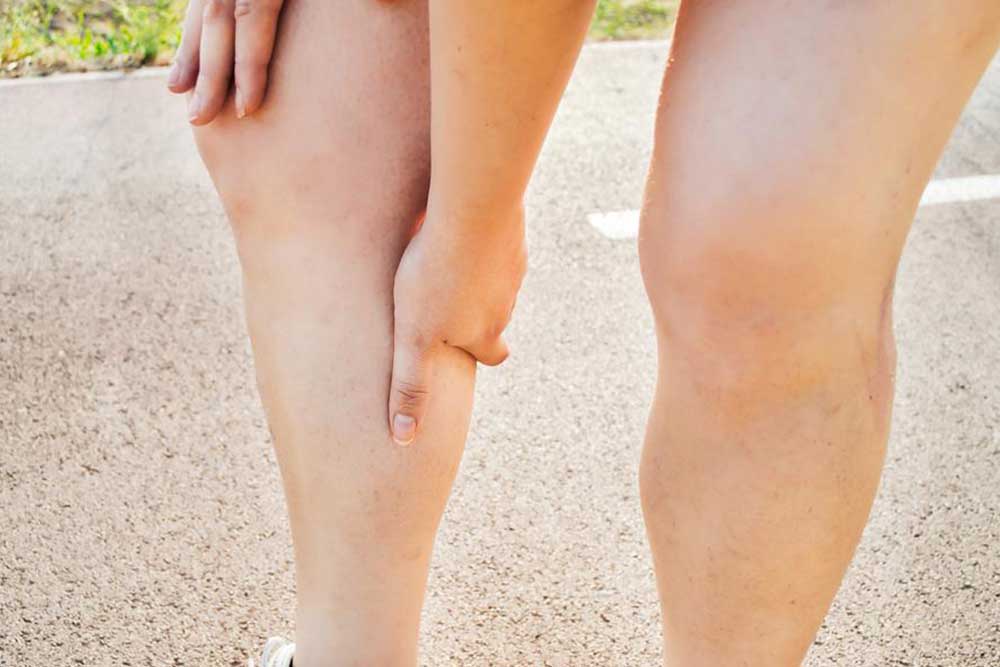
Deep vein thrombosis involves blood clot formation in deep veins, mainly in the legs or pelvis, requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms include swelling, pain, and skin discoloration. Risk factors encompass obesity, pregnancy, smoking, and age. Treatment options include anticoagulants, clot dissolvers, and compression stockings. Early detection is vital to prevent severe complications like pulmonary embolism. Lifestyle changes and medical management play key roles in prevention and recovery. Consult a healthcare professional if symptoms arise for effective intervention.
Sponsored
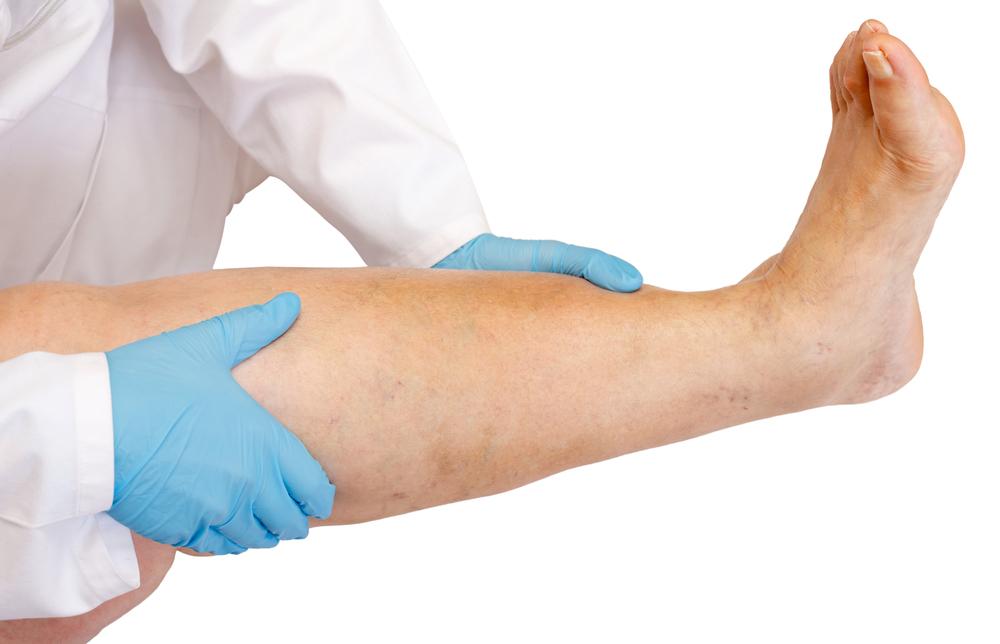
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Recognizing Symptoms, Diagnostic Methods, and Treatment Options
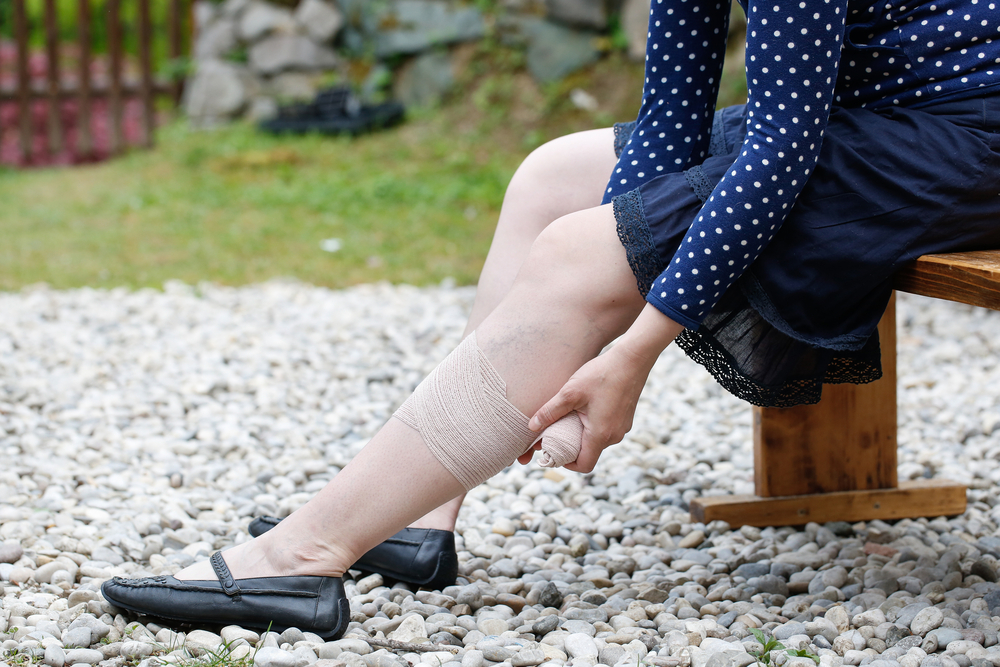
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the thighs or pelvis. This condition can pose serious health risks if not promptly addressed. DVT symptoms vary, but common signs include swelling, pain, discoloration, and enlarged veins in the affected limb. Risk factors include obesity, pregnancy, smoking, advanced age, and family history. Diagnosis often involves ultrasound, blood tests, or imaging scans. Treatment focuses on anticoagulant medications, clot busting drugs, compression therapy, and preventive measures.
Maintaining an active lifestyle, healthy diet, and regular medical check-ups can reduce DVT risk. If you experience symptoms, seek medical attention immediately to prevent complications such as pulmonary embolism.