Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis: Symptoms, Detection, and Management
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition involving blood clots in deep veins, often in the legs or pelvis. Recognizing symptoms like swelling, pain, and discoloration is vital. Risk factors include age, pregnancy, smoking, and sedentary lifestyle. Diagnosis involves physical exams and imaging tests. Treatment options such as blood thinners, clot busters, and compression stockings are effective. Early intervention and healthy habits like regular exercise are key to prevention and management. Consult healthcare providers promptly if symptoms emerge to avoid life-threatening complications.
Sponsored

Recognizing and Managing Deep Vein Thrombosis
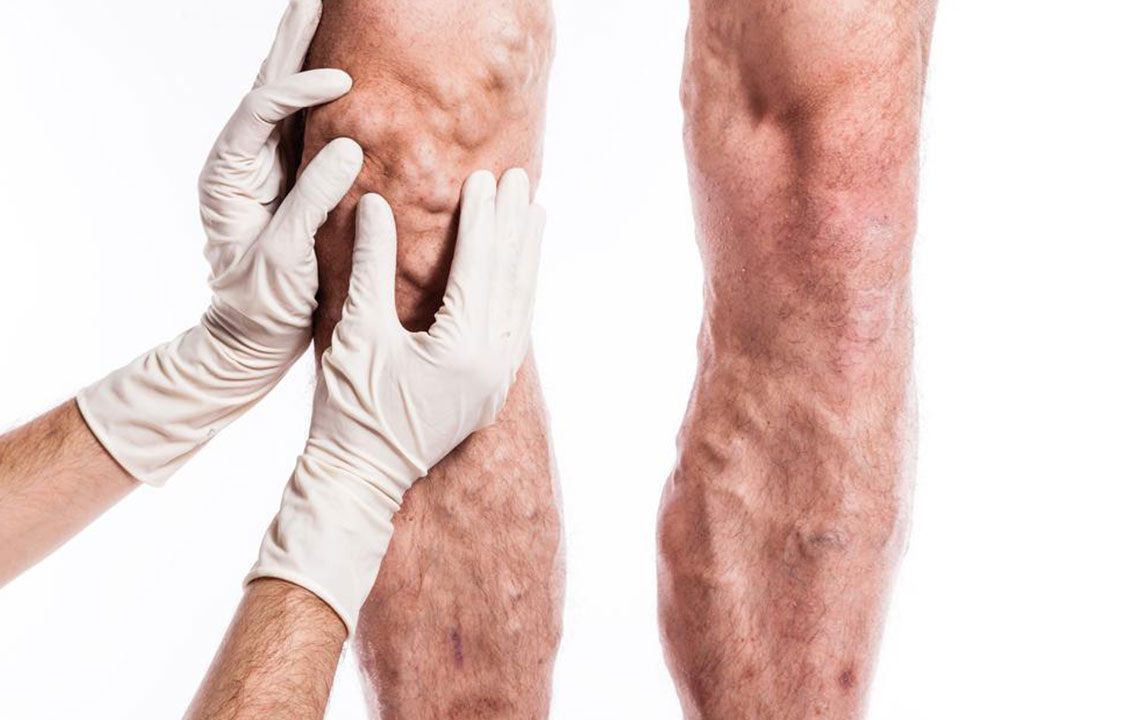
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot forms in the deep veins of the body, typically in the legs or pelvis. This condition can be life-threatening if untreated. While DVT can develop anywhere, common sites include the thighs and groin areas. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications such as pulmonary embolism.
Who is at Elevated Risk?
Individuals with a history of heart attack or stroke are more susceptible to blood clots.
Overweight individuals may have increased estrogen levels, promoting clot formation.
Pregnant women face higher risks, making blood clots a leading cause of maternal mortality.
Smokers and those involved in drug use are more vulnerable.
People over 60 are at greater risk.
Family history of blood clots increases susceptibility.
Sedentary lifestyles or prolonged sitting can lead to DVT.
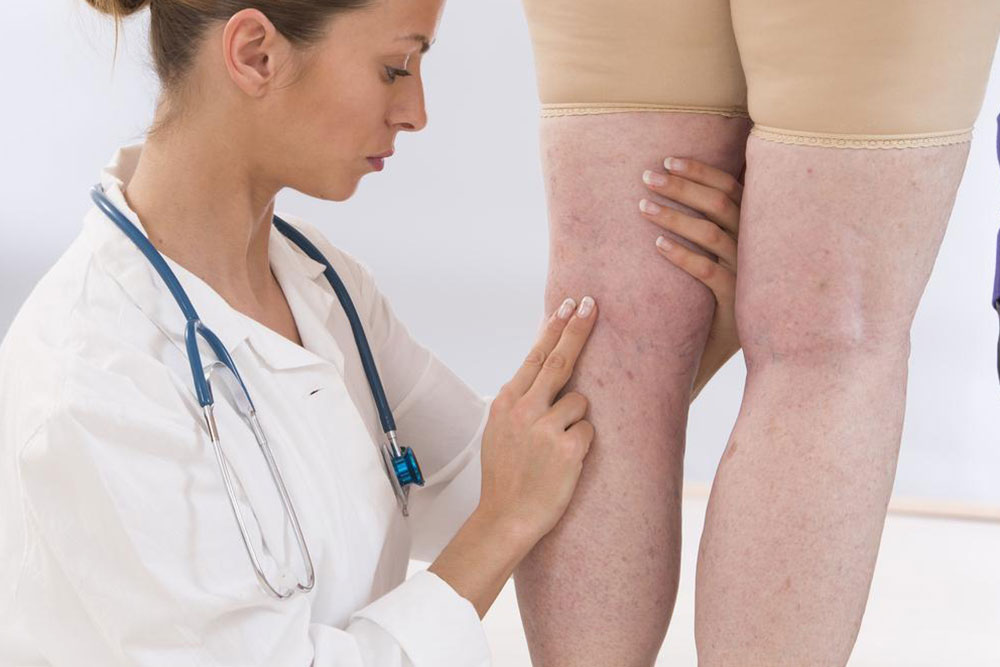
Discoloration, pale or bluish skin over the affected area
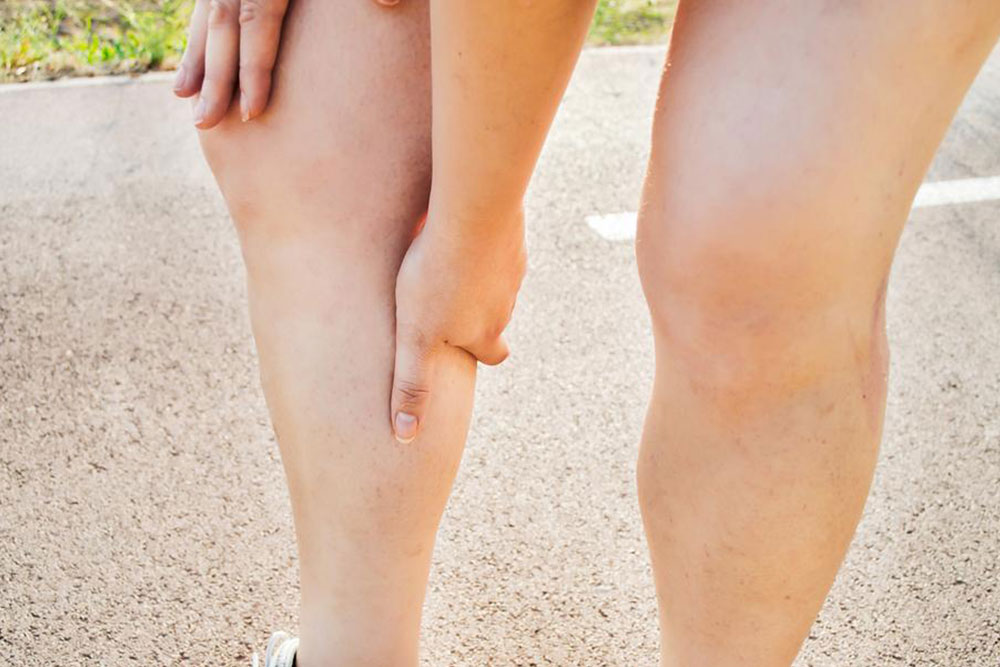
Swelling in the leg or arm
Intense, unexplained pain in the limb
Tenderness and discomfort in the affected area
Noticeable enlargement of veins
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Tips to Prevent DVT
Capsaicin-rich cayenne pepper can enhance circulation.
Consuming garlic cloves supports healthy blood flow.
Ginger helps in breaking down clot-forming fibrins.
Foods high in vitamin E, like nuts and leafy greens, promote smooth circulation.
Adding cinnamon, which contains anticoagulant compounds, can help thin the blood.
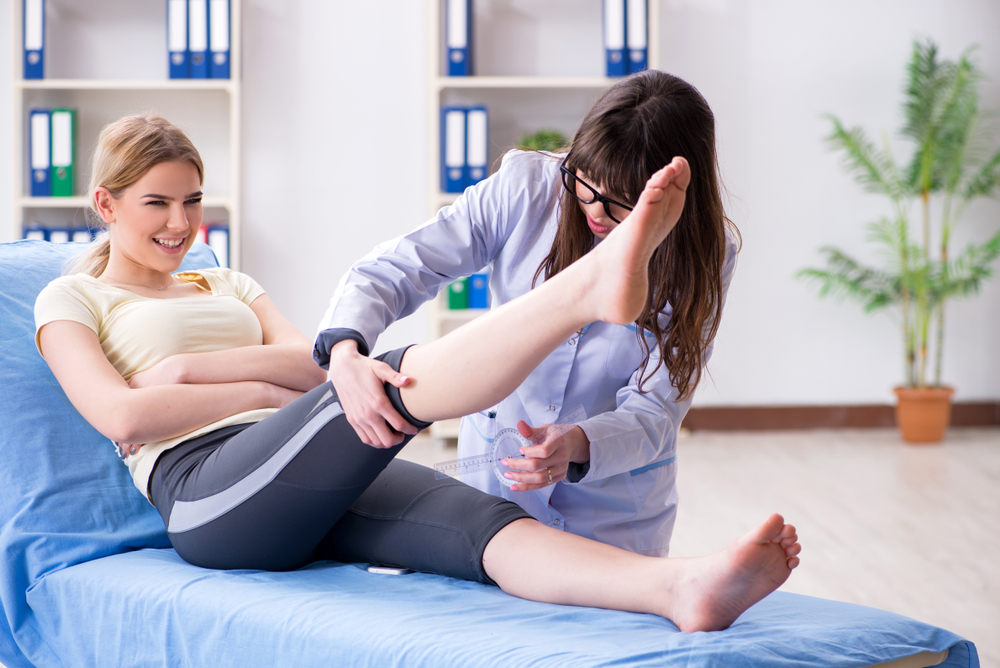
DVT Diagnosis Methods
Healthcare providers begin with symptom evaluation and physical examination, checking for swelling, tenderness, or discoloration. Diagnostic tests such as ultrasound, blood tests, venography, or imaging scans like CT or MRI may be recommended to confirm the presence of a clot.
Effective Treatment Approaches for DVT
Anticoagulants or blood thinners like apixaban, rivaroxaban, warfarin, and others prevent new clot formation.
Clot-busting medications may be administered in severe cases to dissolve existing clots.
Venous filters are inserted to intercept clots traveling to lungs.
Wearing compression stockings helps reduce swelling and discomfort.
Top Medical Centers for DVT Care
Rehabilitation Hospital of Denton
Presbyterian Hospital of Denton
Ubh Denton
UT Southwestern / Clements University Hospital
University General Hospital Dallas
Denton Regional Medical Center
Walnut Hill Medical Center
Medstar Georgetown University Hospital
Medstar National Rehabilitation Hospital
Medstar Washington Hospital Center
Providence Hospital
Psychiatric Institute of Washington
Zale Lipshy University Hospital