Comprehensive Guide to Hepatitis C: FAQs and Insights
This comprehensive guide addresses common questions about Hepatitis C, including causes, survival, testing, prevention, and recent treatments. Understanding these key aspects can help in effective management and prevention of the disease, which affects the liver and has significant health implications. Recent advances have improved diagnosis and treatment outcomes, making awareness and early intervention crucial for those at risk.
Sponsored

Understanding Hepatitis C: Common Questions and Essential Information
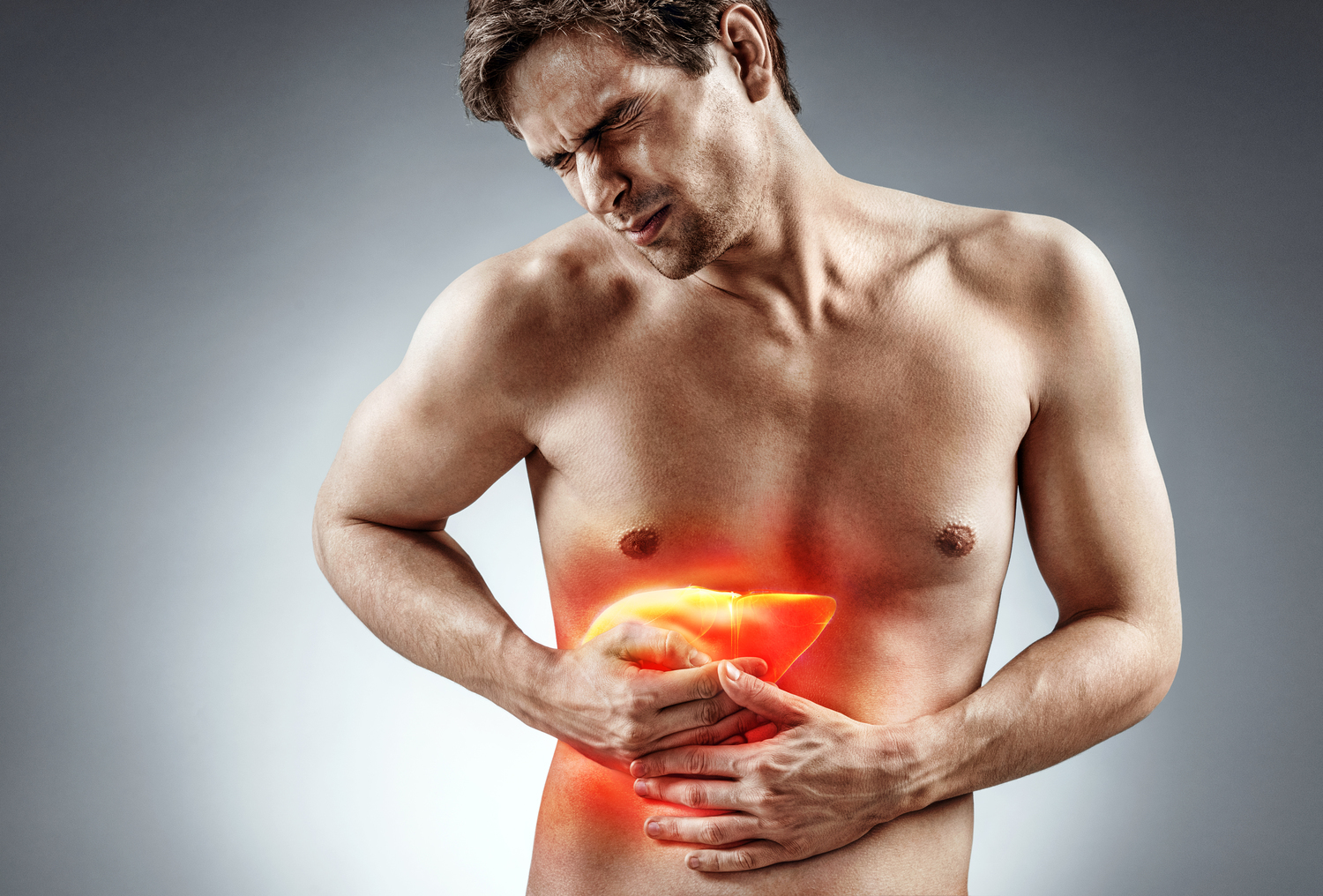
Hepatitis C is a persistent viral infection that affects the liver, varying from mild discomfort to severe, long-term liver damage. It is highly contagious and can lead to chronic illness if not managed properly.
What are primary causes of Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C spreads mainly through contact with infected blood. Sharing needles, contaminated medical equipment, or exposure to blood during procedures can transmit the virus. Body art practices like tattooing with unsterilized needles also pose risks. Unprotected sexual contact with an infected individual is another significant mode of transmission.
How long does the virus survive outside the body?
Research indicates that hepatitis C can live outside the body under certain conditions. It remains viable on surfaces at room temperature for over sixteen hours and can survive in syringes for up to sixty-three days, though it typically disintegrates after about three days. This resilience underscores the importance of proper sterilization and handling practices.
What tests are available to diagnose Hepatitis C?
The most common screening is the OraQuick antibody test, delivering results in approximately twenty minutes through a simple fingerstick blood sample. While a positive antibody test suggests exposure, confirmatory tests are necessary to determine active infection. Consulting healthcare professionals for thorough diagnostics is recommended for accurate assessment and treatment planning.
How can Hepatitis C transmission be prevented?
The key to prevention lies in avoiding contact with infected blood. This includes not sharing needles, razors, toothbrushes, or any items that may contain blood. Practicing safe tattooing and piercing procedures, using sterilized equipment, and practicing safe sex—especially during menstruation or if one partner has open injuries—are essential preventative measures.
What are the latest treatments and their effectiveness?
New antiviral medications, approved by the FDA, have revolutionized Hepatitis C treatment. These drugs significantly shorten therapy from about twenty-four weeks to as little as eight weeks, with cure rates exceeding ninety percent when used correctly. Advances in treatment options offer hope for effective management and potential eradication of the virus.