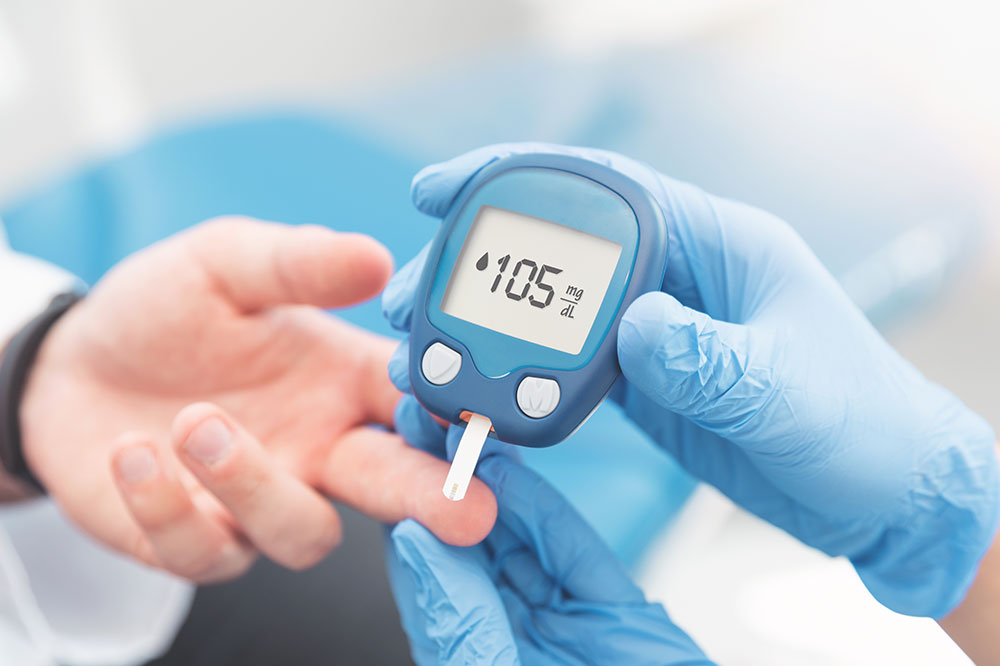
Essential Tests for Diabetes Detection and Monitoring
Discover the key diagnostic tests for diabetes, including Random Blood Sugar, A1C, Fasting Blood Sugar, and OGTT. Learn their procedures, benefits, and when to use each for effective monitoring and management of blood glucose levels. Regular screening is essential for at-risk individuals to prevent complications and maintain optimal health.
Sponsored
Maintaining regular screening is crucial for individuals at risk of diabetes or currently living with the condition. Monitoring blood sugar levels helps prevent complications and manage the disease effectively. Regardless of age, those with a family history of diabetes or heart issues should undergo routine testing. Several diagnostic methods are available to assess blood glucose levels, each suited for different situations and needs.
Random Blood Glucose Test
This test involves a simple blood sample taken without fasting. It provides quick insights into blood sugar levels at any time of day but may lack precision.
Hemoglobin A1C Test
Often recommended for ongoing management, the A1C test measures average blood sugar over months. No fasting required, but accuracy may be affected by conditions like anemia.
Fasting Blood Sugar Test
Requires fasting overnight, with only water allowed. It helps assess blood glucose after a period of rest from food consumption.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
After fasting, a sugary solution is consumed, and blood sugar is tested regularly over a few hours. This is particularly useful for diagnosing gestational diabetes.
Regular testing is vital in managing blood sugar levels. Consult your healthcare provider to determine the most suitable tests for your health needs and take proactive steps if levels are abnormal.