Six Nutritional Strategies to Alleviate Arthritis Discomfort
This article explores six dietary choices that can help manage arthritis symptoms by reducing inflammation and alleviating joint pain. Incorporating fatty fish, garlic, ginger, broccoli, walnuts, and berries into your diet can provide natural relief and improve joint health. Learn how these foods support anti-inflammatory processes and contribute to better management of arthritis for a healthier lifestyle.
Sponsored

Arthritis encompasses a range of joint disorders that cause stiffness, swelling, and pain across diverse populations. Common types include rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks joint tissues, and osteoarthritis, often caused by joint overuse. Dietary choices can play a vital role in managing symptoms by reducing inflammation and easing joint pain. Here are six foods that can support arthritis sufferers in controlling their symptoms naturally and effectively.
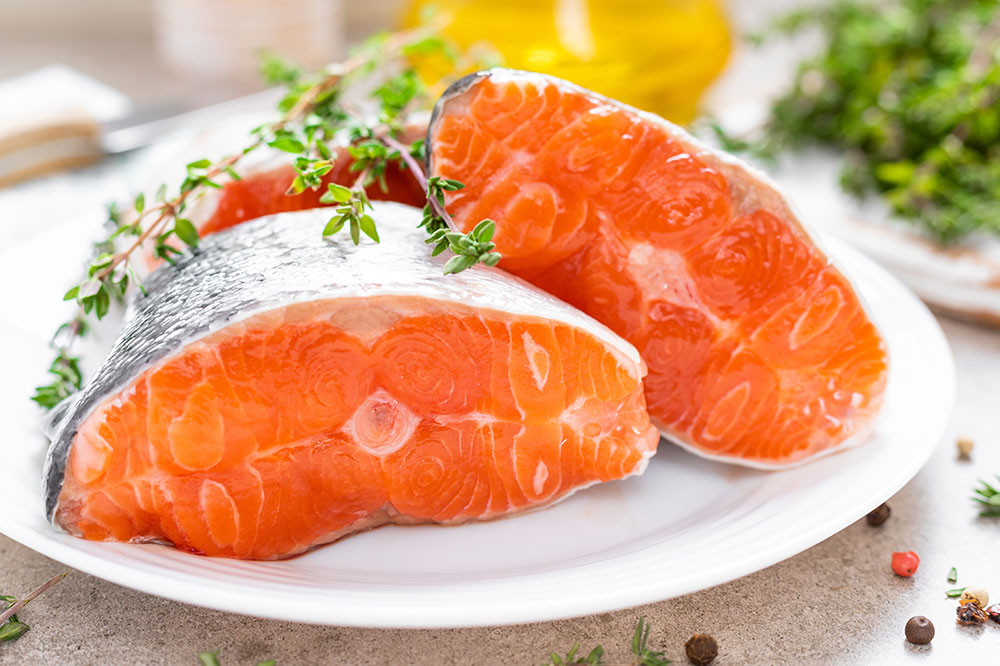
Omega-3 Rich Fish: Fish like salmon, sardines, mackerel, and trout are loaded with omega-3 fatty acids that combat inflammation. Research indicates that regular consumption reduces joint stiffness, pain, and inflammatory markers. Additionally, their vitamin D content may help lower rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. The American Heart Association recommends eating at least two servings of fatty fish weekly for optimal anti-inflammatory benefits.
Allicin-Packed Garlic: Beyond its culinary appeal, garlic offers numerous health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting properties. Its compounds may help lower arthritis-related inflammation and strengthen immune responses.
Ginger: Known for its spicy warmth, ginger has been demonstrated to alleviate knee pain in arthritis patients. Its active components inhibit the production of inflammatory substances, making it a natural remedy for joint discomfort. Fresh, dried, or powdered ginger can be incorporated into various dishes and teas.
Cruciferous Vegetables: Vegetables like broccoli contain sulforaphane, a compound that reduces inflammation. Studies show that including broccoli in your diet can lower levels of inflammatory markers, aiding in joint health.
Walnuts: These nutrient-dense nuts are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants that help decrease inflammation. Regular walnut consumption has been associated with reduced rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and lower inflammatory indicators.
Berries: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, berries help combat inflammation. Consuming at least two servings weekly has been linked to a 14% decrease in blood inflammatory markers. Their plant compounds rutin and quercetin provide additional health benefits.