Common Causes and Triggers of Gout-Related Foot Pain
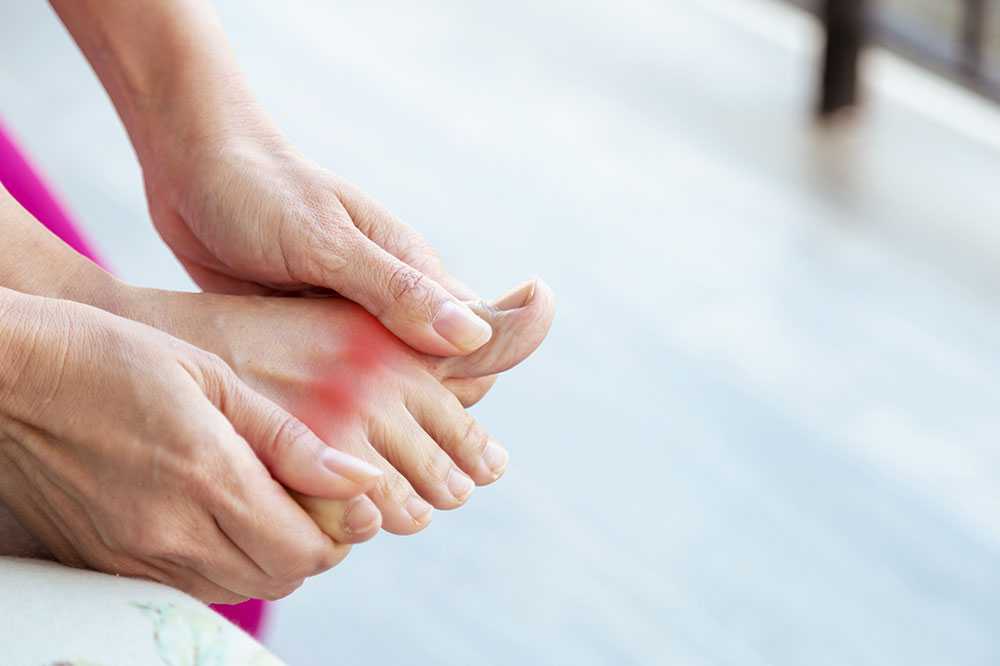
Gout causes sudden foot pain due to uric acid crystal buildup. Common triggers include purine-rich foods, dehydration, sugary drinks, alcohol, and certain medications. Managing these factors alongside medication helps prevent flare-ups and alleviates discomfort. Proper hydration and stress management are also key to control gout symptoms effectively.
Sponsored
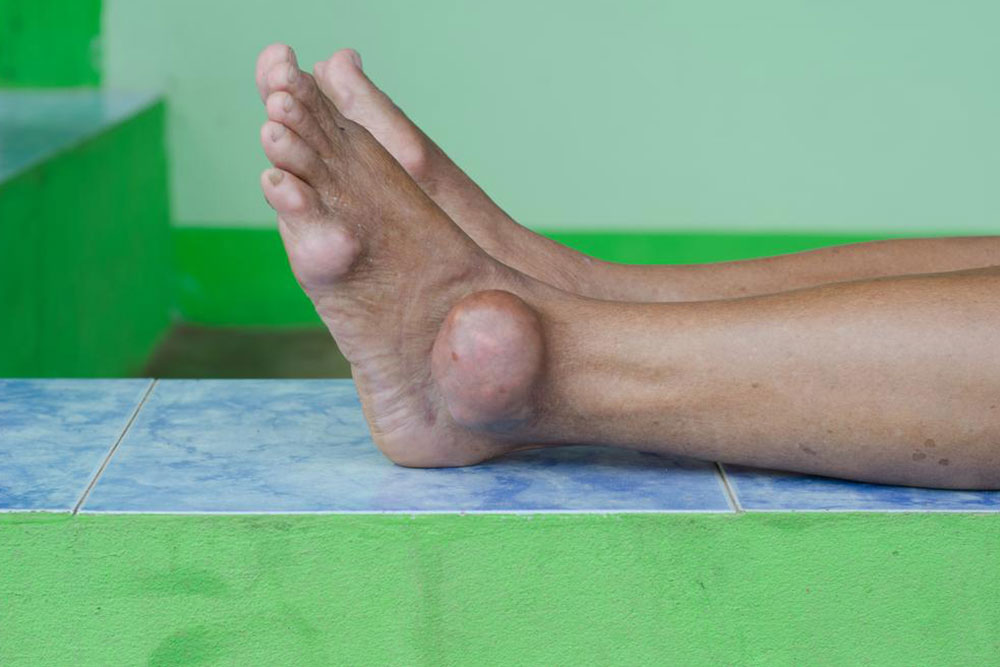
Gout is a form of arthritis marked by sudden, intense pain, swelling, and redness in joints, typically affecting the big toe. It results from uric acid crystals forming in joint spaces, caused by excess uric acid from purine breakdown. When the kidneys can't eliminate uric acid efficiently, or the body produces too much, hyperuricemia develops, leading to gout attacks. Managing gout involves medication and avoiding certain triggers to reduce flare-ups and foot discomfort.
Triggers that can worsen gout include:
Foods high in purines, such as bacon, turkey liver, sardines, shellfish, salmon, and vegetables like spinach, mushrooms, and asparagus.
Dehydration, which reduces kidney function and uric acid clearance.
Sugar-sweetened beverages, especially those with high fructose corn syrup, which promote uric acid production.
Alcohol, particularly beer, which contributes to increased uric acid levels and inflammation.
Beer is converted into lactic acid, hindering kidney efficiency in removing uric acid. Crash dieting or low-calorie plans can cause protein breakdown, raising uric acid levels. Certain blood pressure medications may also elevate gout risk. Stress has been linked to gout attacks as it depletes vitamin B5, essential for uric acid elimination. To effectively manage gout foot pain, along with medications, it's crucial to avoid these triggers and maintain hydration and stress levels.