Effective Strategies for Managing Psoriasis
Discover effective management strategies for psoriasis, including topical treatments, phototherapy options, and their benefits and side effects. Learn how to tailor therapies to individual needs for optimal skin health.
Sponsored

Approaches to managing psoriasis
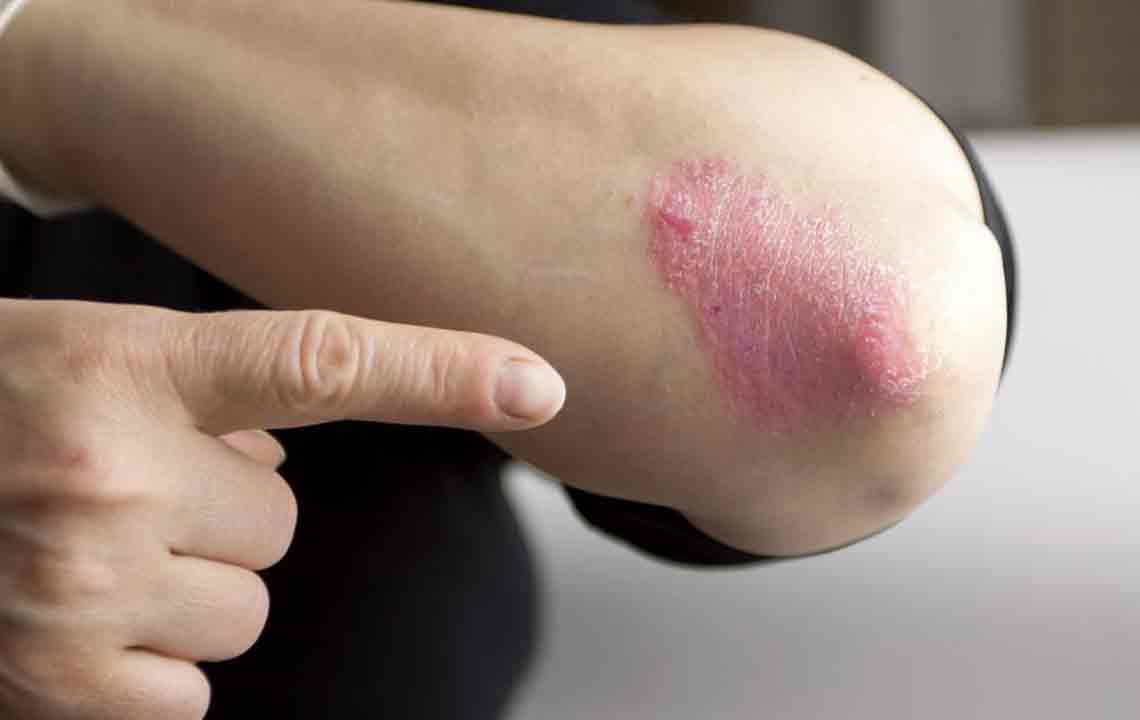
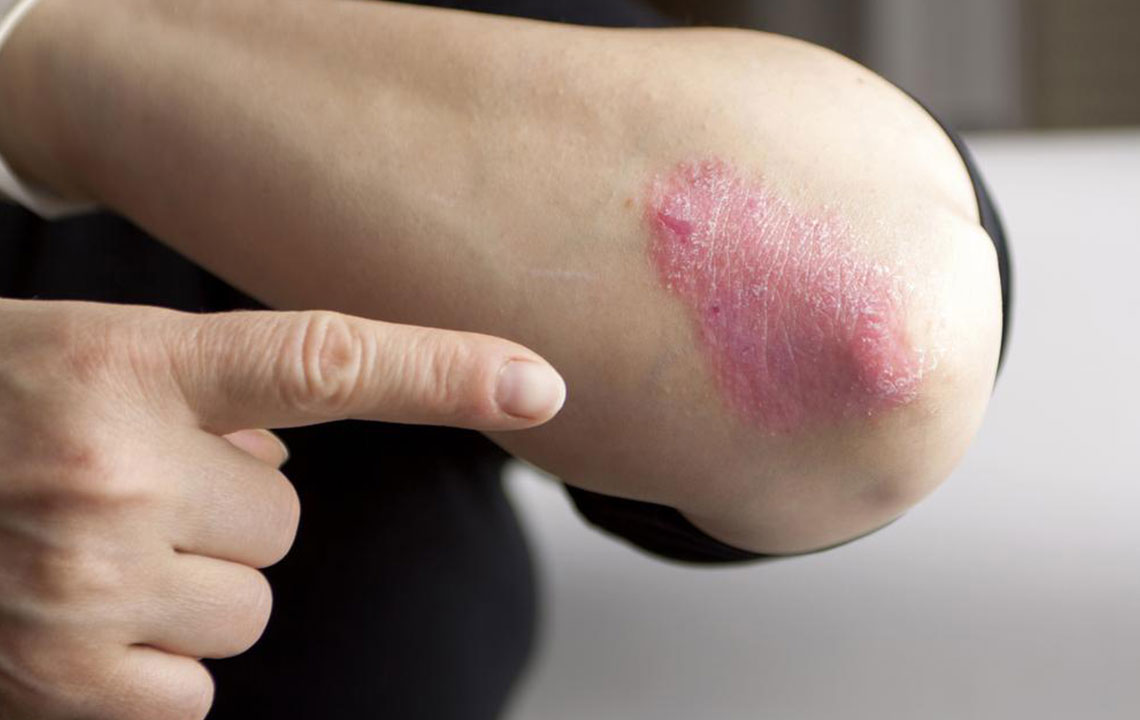
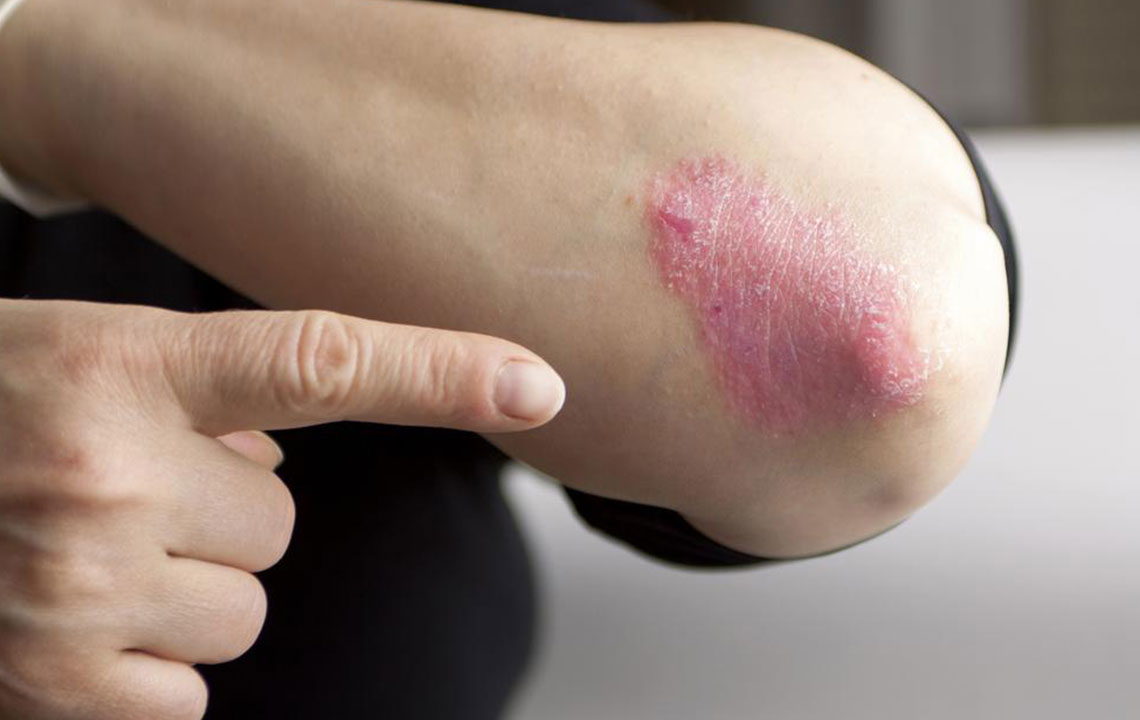
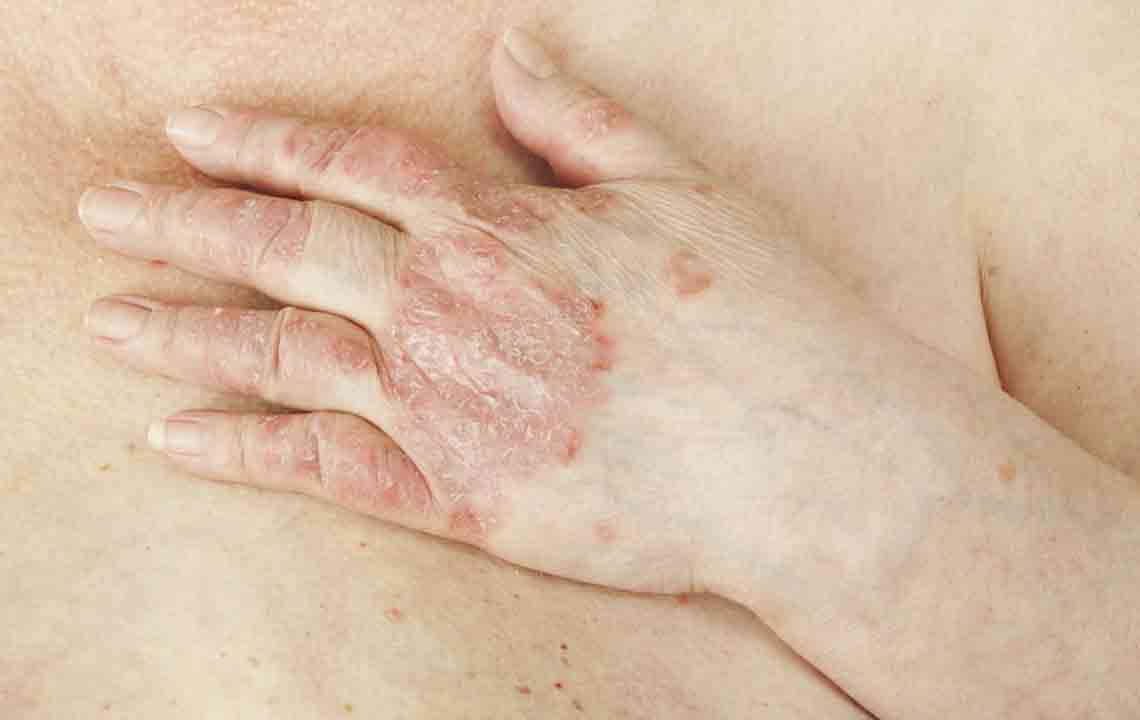
Psoriasis is a common skin disorder characterized by red patches, itching, and thick, silvery scales. Though there is no cure, various treatments focus on alleviating symptoms. The choice depends on severity and individual response to therapy.
Here is an overview of treatment options for psoriasis.
What are topical therapies for psoriasis?
Patients with psoriasis often require medications directly applied to affected skin areas.
Topical treatments are generally safe, especially when targeting localized lesions.
Since each person’s condition varies, a universal topical medication can't be prescribed with certainty, and effectiveness may differ.
Some treatments may require adjustment due to side effects or limited efficacy. Certain medications can be combined, but some should not be used together, as they may interfere. Others may need to be used alongside additional therapies to enhance results.
Common topical treatments include:
Topical corticosteroids are used for mild psoriasis to reduce inflammation and soothe itching.
Vitamin D analogs, such as calcipotriene, help slow skin cell production. They come in cream form containing vitamin D.
Anthralin helps smooth skin by removing scales and slowing cell growth.
Retinoids derived from vitamin A diminish inflammation when applied topically.
Salicylic acid, available over-the-counter or by prescription, reduces scaling and promotes the shedding of dead skin cells. It can be combined with other treatments for better effectiveness.
Coal tar helps decrease scaling, itching, and inflammation.
Moisturizers alleviate dryness, scaling, and discomfort.
Sunlight phototherapy for psoriasis
Ultraviolet (UV) light, with wavelengths between 290-400 nm, can positively affect psoriatic skin by modifying immune responses.
This approach is often used when topical therapies are insufficient, covering over 5-10% of the body’s surface.
Natural sunlight exposure, under controlled conditions, helps regulate skin cell activity, reducing scaling and inflammation.
While sunlight contains UV rays, controlled exposure is essential to avoid overexposure and side effects.
Proper guidance ensures safe and effective sunlight therapy for psoriasis patients.
How UV-B phototherapy combats psoriasis
Controlled doses of UVB light, either natural or artificial, help manage mild to moderate psoriasis symptoms.
UVB therapy is effective for widespread or stubborn patches unresponsive to topical treatments.
Potential side effects include redness, dry skin, and irritation, which can be mitigated with topical moisturizers.
Narrowband UV-B, a more potent form, is often preferred for its efficiency.
Typically administered several times weekly until symptoms improve.
Some practitioners combine UVB with coal tar therapy (Goeckerman method) to enhance effectiveness, as coal tar increases skin’s UV absorption.
Possible side effects of topical therapies
Skin irritation or dermatitis
Headaches
Skin thinning or atrophy
Potential viral infections