Understanding Secondary Hyperhidrosis: Causes and Treatments
Secondary hyperhidrosis is excessive sweating caused by underlying health conditions, with symptoms affecting larger body areas. Diagnosis involves identifying health issues, and treatments include medications, Botox, laser and microwave therapies, or surgery. Consulting a doctor is crucial for effective management.
Sponsored

Secondary hyperhidrosis differs from primary hyperhidrosis by being caused by an underlying health condition. Unlike primary hyperhidrosis, which typically presents as localized sweating, secondary hyperhidrosis results in widespread excessive sweating that occurs during wakefulness and is not confined to one area. It often signals other medical issues rather than being a standalone disorder.
Causes and Diagnosis
Many health conditions can contribute to generalized sweating, such as medication side effects, hormonal changes like pregnancy or menopause, obesity, thyroid problems, diabetes, heart conditions, Parkinson’s disease, lymphoma, and gout. Accurate diagnosis involves identifying the root cause through medical evaluations and tests. Patients are encouraged to report episodes of excessive sweating to their healthcare providers promptly.
Therapies and Approaches
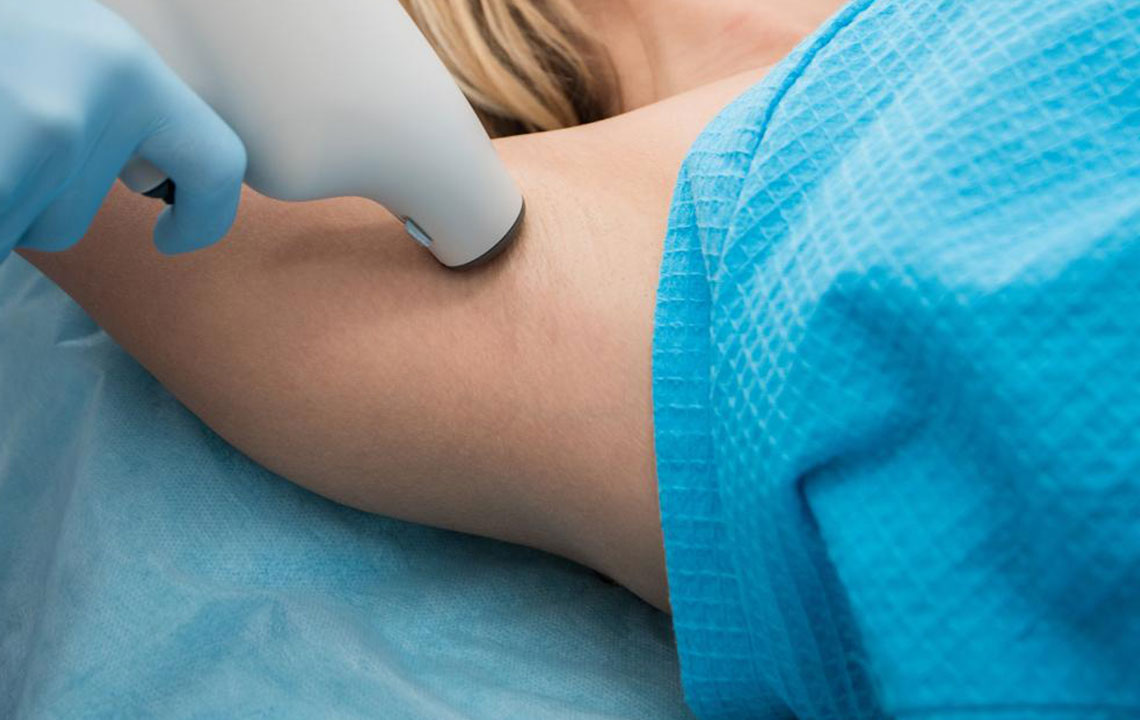
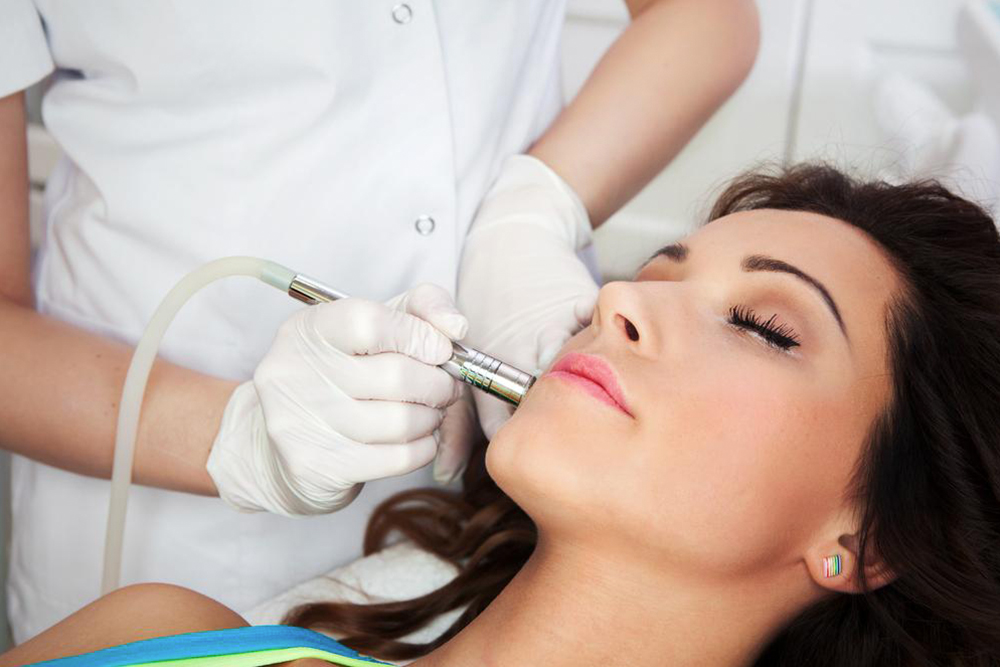
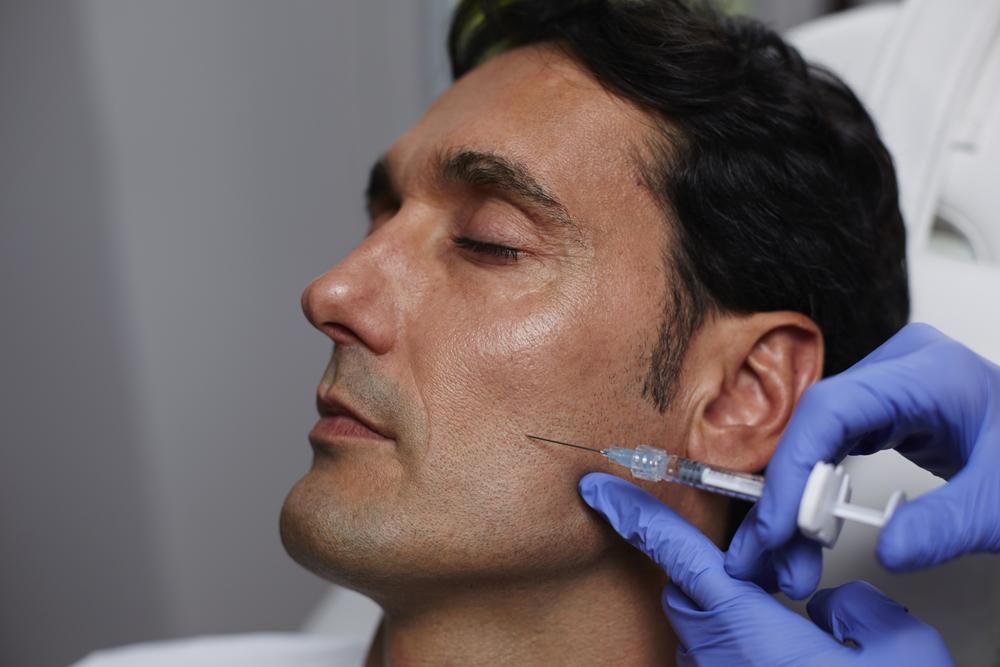
Treatment aims to improve comfort while investigating underlying causes. Mild cases may be managed with antiperspirants containing low or prescription-strength aluminum chloride. For more severe instances, advanced options are available. Botulinum toxin (Botox) injections temporarily block nerve signals responsible for sweating, especially in the underarm area, providing relief for over a year. Microwave and laser therapies are also used to destroy sweat glands in the underarm region, offering longer-lasting results. In stubborn cases, surgical options like thoracic sympathectomy, which involves severing nerves that trigger sweating, may be considered, though these procedures carry risks. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential to choose the safest and most effective treatment plan.