Diet Tips for Managing Diabetes: Foods to Eat and Avoid
This guide emphasizes dietary choices vital for diabetes management. It explains the different types of diabetes, highlights foods to avoid like high-starch and processed foods, and recommends healthier options such as whole grains, lean proteins, and vegetables. Adopting these dietary habits along with lifestyle modifications can help control blood sugar levels effectively and reduce health risks associated with diabetes.
Sponsored

Diet Guidance for Diabetes Management
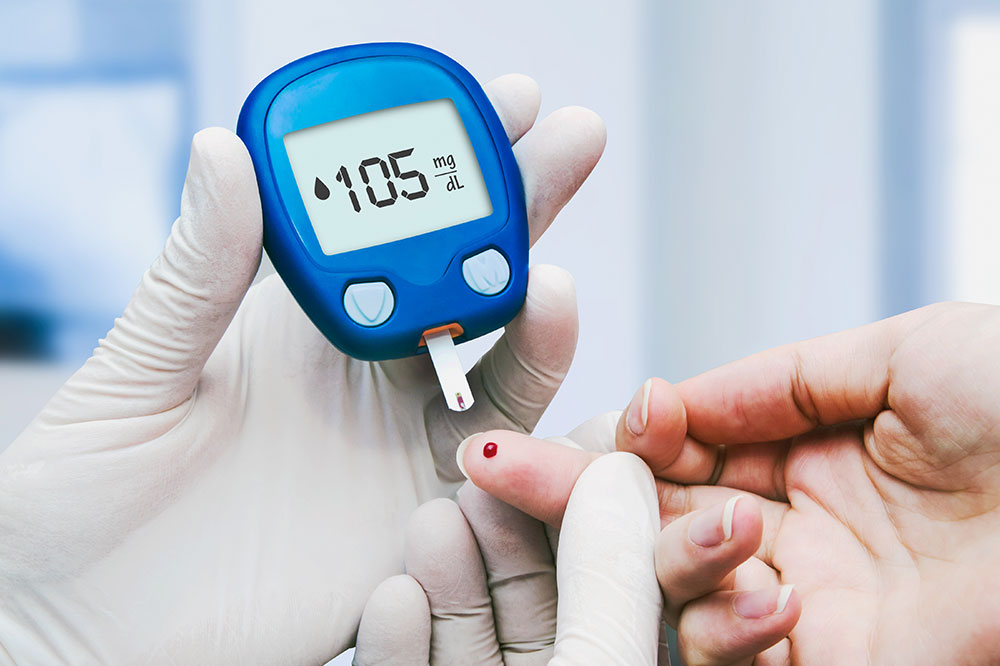
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a widespread health condition affecting millions globally. Derived from Greek, 'diabetes' means siphon, and 'mellitus' signifies sweet, highlighting sugar's presence in urine and blood. A 2013 study reported approximately 382 million individuals living with the disease worldwide.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes can affect anyone regardless of age or background. Contrary to earlier beliefs that it mainly affects middle-aged adults, recent data shows young people are also at risk.
The primary types are type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and typically resolves after childbirth.
Type 1 diabetes:
Also called insulin-dependent diabetes, this form results when the body's immune system fails to produce insulin. Often diagnosed in youth, it presents symptoms like excessive thirst, frequent urination, sudden weight fluctuations, blurred vision, fatigue, and increased hunger.
Smoking and alcohol intake worsen cardiovascular risks in diabetics. Quitting these habits and adopting a balanced diet, regular exercise, and proper medication can greatly improve health.
Type 2 diabetes:
This type arises when the body doesn't produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to it. It's prevalent among adults, often linked to unhealthy lifestyles, poor diet, stress, inactivity, obesity, and related health issues. It can be managed by lifestyle changes, weight loss, medication, and blood sugar monitoring. However, it's a progressive condition that may require insulin therapy over time.
Certain foods exacerbate diabetes symptoms; hence, avoiding high glycemic index foods, processed items, and unhealthy fats is crucial. Examples include white flour products, sugary snacks, and red meats.
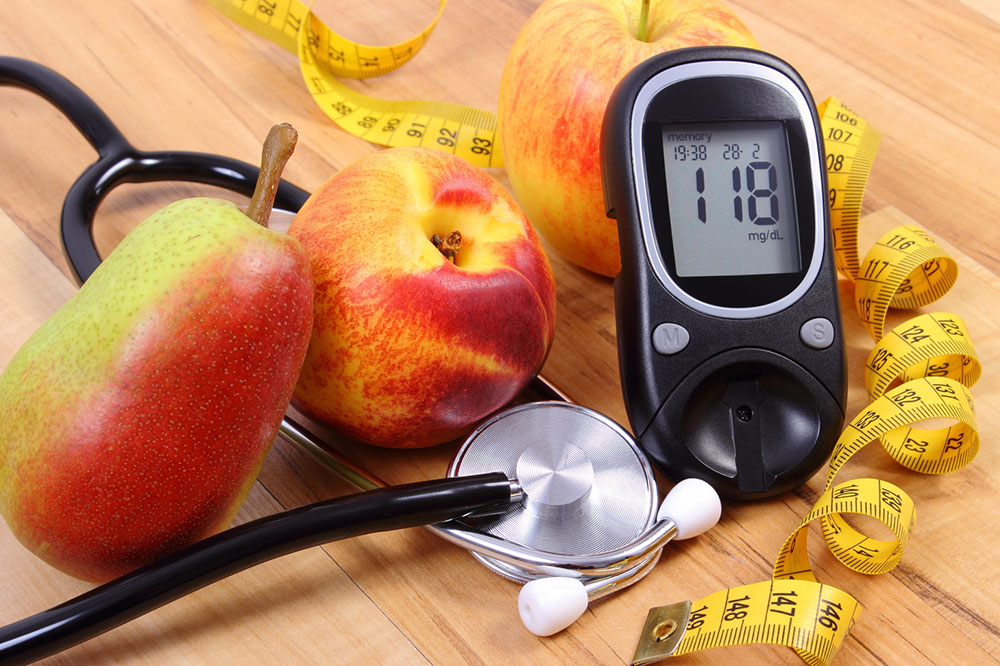
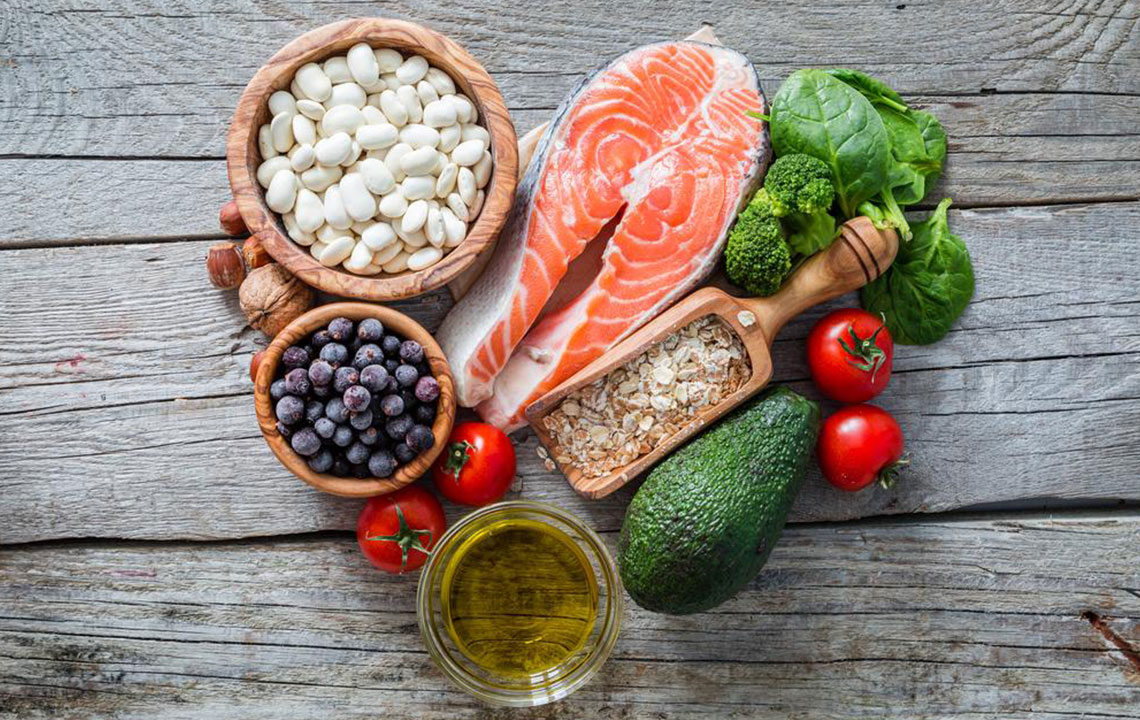
High-starch foods like white rice, white bread, and processed cereals should be replaced with whole grains such as brown rice, oats, millet, and high-fiber cereals.
Protein sources like fish, poultry, beans, nuts, and soy are safer choices than red meats, which can worsen insulin resistance.
Fruits low in sugar, green leafy vegetables, and avoiding canned or processed foods are recommended.
Managing carbohydrate intake and choosing nutrient-rich foods can help control blood glucose levels and prevent complications.