Key Lifestyle Tips to Manage Rheumatoid Arthritis Effectively
This guide provides essential tips for managing rheumatoid arthritis through diet and lifestyle modifications. It emphasizes avoiding refined sugars, processed foods, high red meat consumption, gluten, overexertion, and uncomfortable footwear. Implementing these strategies can help reduce inflammation, alleviate joint pain, and improve overall quality of life for those affected by rheumatoid arthritis. Staying informed and making mindful choices are key to effective disease management.
Sponsored

Essential Avoidances for Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
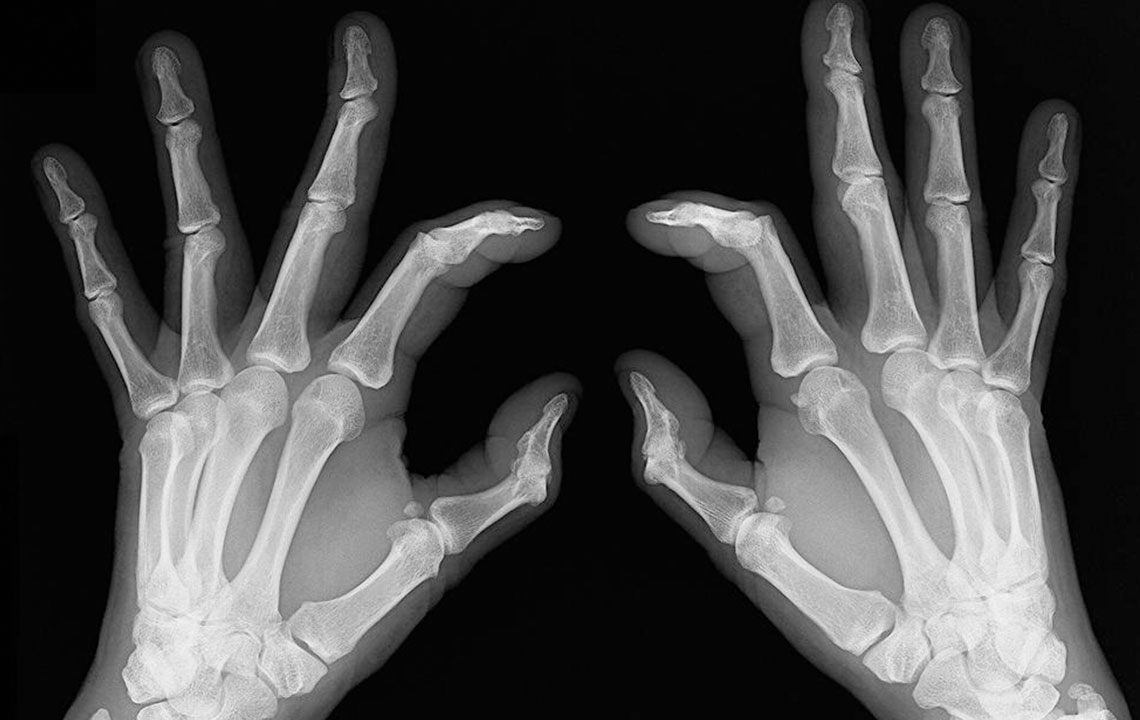
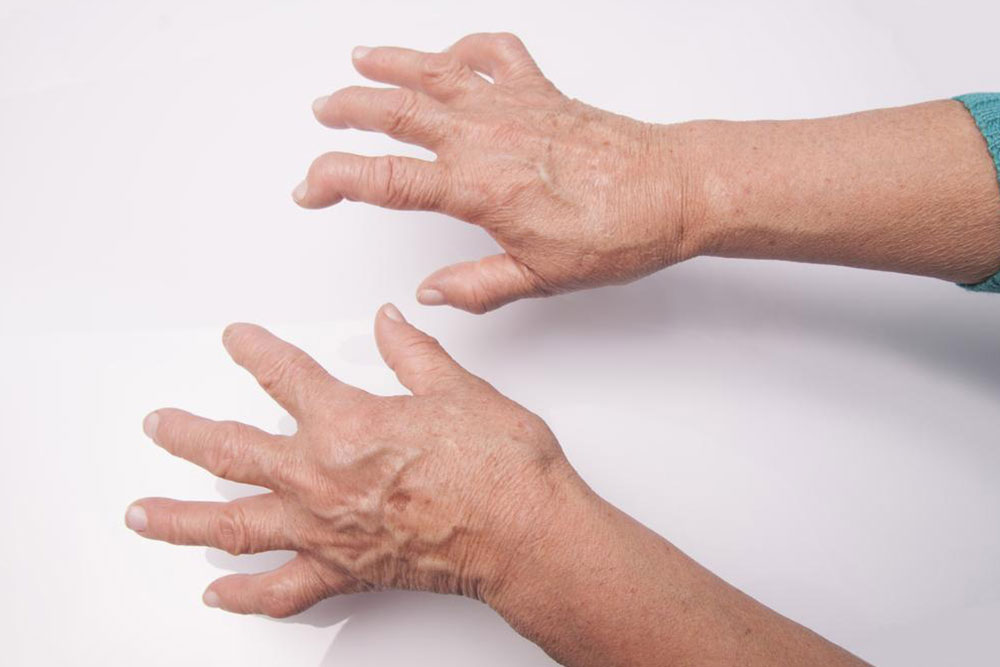
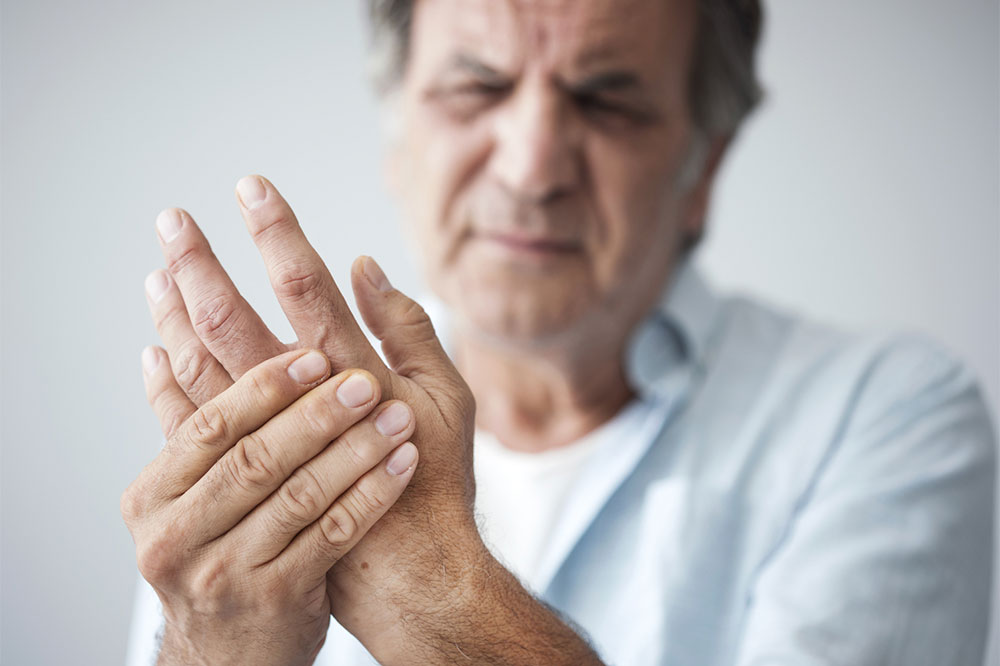
Rheumatoid arthritis is a persistent inflammatory disorder that affects individuals across all age groups. It often causes joint pain in areas like the wrists, ankles, feet, and fingers, which can severely impact daily life. Though treatments are accessible, modifying your diet and habits can significantly improve symptoms. This article highlights the foods and lifestyle habits to steer clear of to better control rheumatoid arthritis.
Added Sugars
Consuming foods high in refined sugars, such as sodas and sweets, can worsen arthritis symptoms. Scientific studies link excess sugar intake to increased inflammation and discomfort in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Limiting sugar not only helps manage symptoms but also reduces the risk of developing the condition.
Processed and Packaged Foods
Foods like cereals, baked goods, and ready-to-eat items often contain preservatives, excessive salt, and artificial additives that promote inflammation. Avoiding these can lessen joint pain and lower the risk of cardiovascular issues associated with rheumatoid arthritis.
Red and Processed Meats
Consuming large amounts of red and processed meats may boost inflammation and aggravate arthritis symptoms. Instead, consider plant-based protein sources to support joint health and reduce inflammation.
Gluten-containing Foods
Proteins present in wheat, barley, and rye may elevate inflammation levels. While research is ongoing, some patients find that reducing gluten intake alleviates their symptoms. An anti-inflammatory diet often includes gluten-free options for better management.
Beyond dietary adjustments, certain lifestyle habits should be avoided to prevent symptom exacerbation.
Overexertion
Pushing your body too hard can lead to increased fatigue and joint pain. It’s essential to rest adequately, take frequent breaks, and engage in gentle activities suitable for your condition.
Inappropriate Footwear
Wearing supportive, comfortable shoes minimizes joint stress and eases pain, helping you maintain mobility and reduce discomfort associated with rheumatoid arthritis.