Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
This article explores effective management strategies for rheumatoid arthritis, highlighting medication options like NSAIDs, DMARDs, biologics, and JAK inhibitors. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and physical therapy to reduce symptoms, slow disease progression, and maintain joint function. Proper treatment can help patients achieve remission, reduce pain, and improve mobility, enabling a better quality of life despite RA's chronic nature.
Sponsored

Effective Approaches to Rheumatoid Arthritis Management
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune condition that leads to joint inflammation and potential long-term damage. To prevent joint deterioration, healthcare providers design personalized treatment plans comprising medications and physical therapy.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
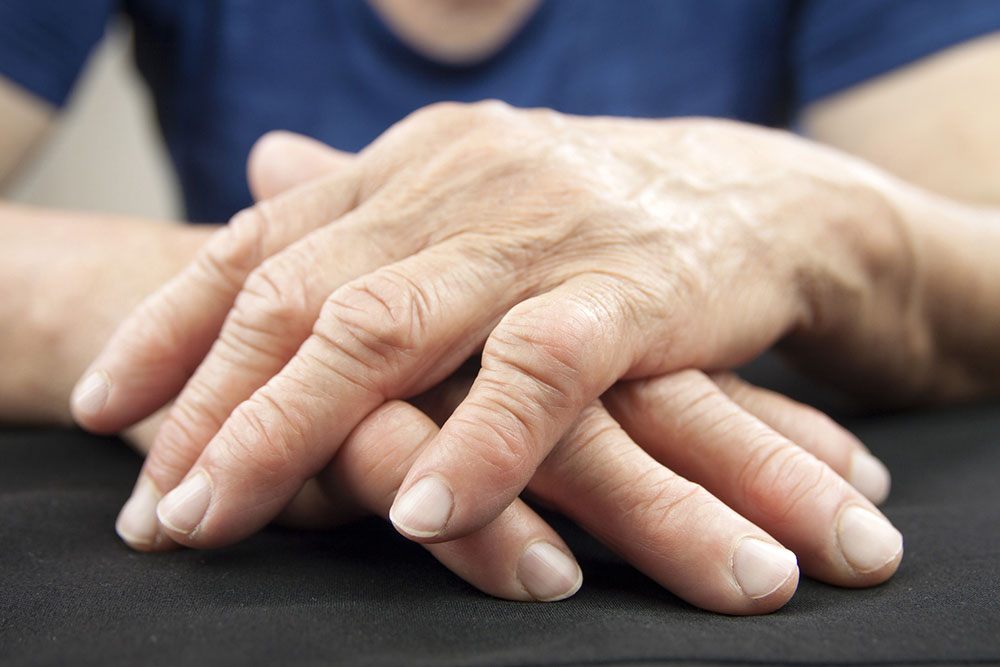
RA occurs when the immune system mistakenly targets joint tissues, especially the synovium, which lines and lubricates joints. This immune attack results in inflammation, pain, and tissue damage. The synovium's deterioration can eventually harm cartilage and bones if untreated.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial because, although there is no cure for RA, treatment can control symptoms and slow progression.
Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis
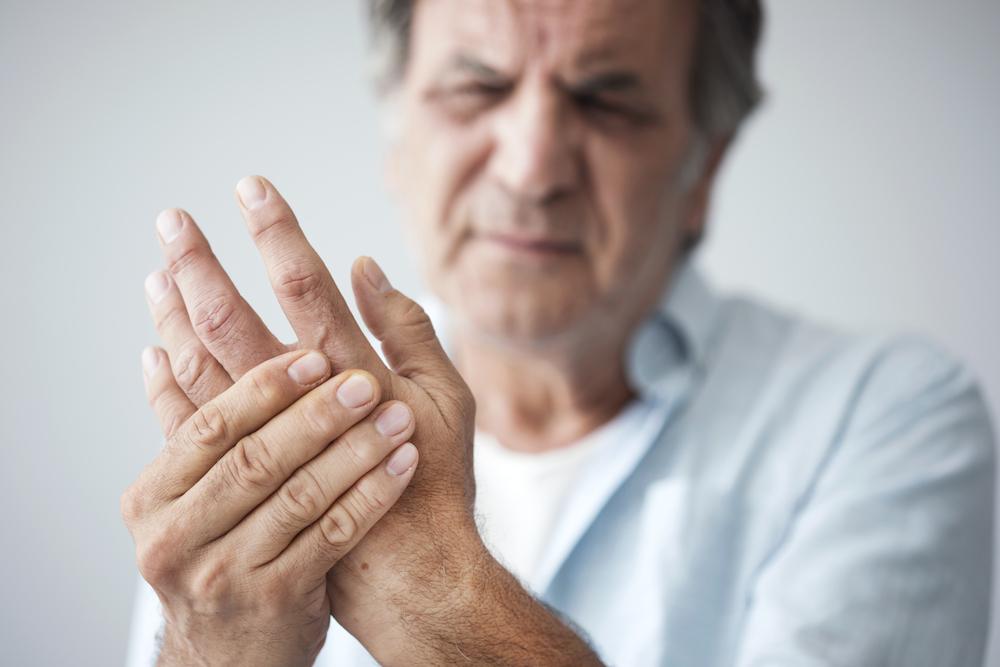
Managing RA involves reducing pain, minimizing inflammation, delaying joint damage, and achieving remission periods where symptoms are minimal or absent. Treatment often starts with pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications, progressing to disease-modifying drugs to alter the disease course.
Pain Relievers and NSAIDs
Initial treatment typically includes analgesics and NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, to control pain and swelling. For patients with gastrointestinal risks, COX-2 inhibitors may be prescribed as safer options.
Steroids
Medications like prednisone provide rapid relief from inflammation but are recommended only temporarily due to potential side effects.
DMARDs
Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs, including methotrexate and leflunomide, target immune responses to slow disease progression and joint damage. They help extend remission phases and preserve joint function.
Biologic Therapies
Biologics such as abatacept and anakinra specifically target immune system components responsible for inflammation, reducing systemic side effects associated with broader immunosuppressants.
JAK Inhibitors
These novel drugs interfere with Janus-kinase enzymes to diminish immune activation and inflammation.
While these medications are effective, they carry risks of adverse effects, which require careful medical supervision. Doctors tailor treatment plans based on individual health profiles, monitoring for side effects and adjusting therapy accordingly.
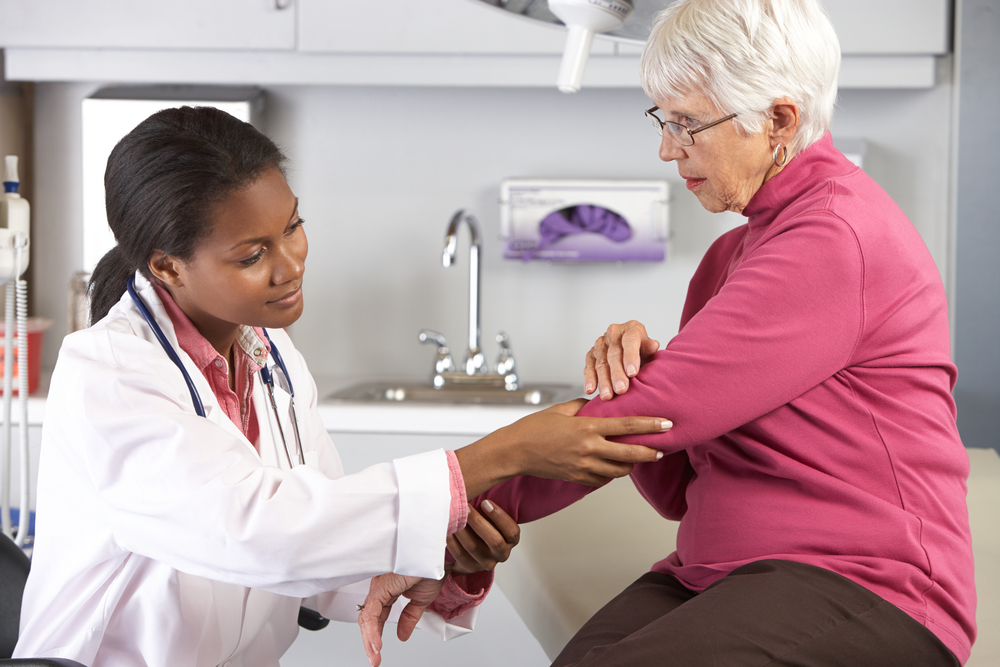
In addition to medication, physical therapy plays a vital role. Physiotherapists recommend exercises and routines to maintain joint flexibility, reduce stiffness, strengthen muscles, and improve overall function. Specialized activities like warm water exercises can ease discomfort. They might also suggest assistive devices or footwear to support mobility and daily tasks.
Managing RA is a long-term process that involves medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments. While the disease can cause joint deformities and impair mobility, a comprehensive treatment approach significantly enhances quality of life, alleviating pain and preventing joint damage.