Understanding Psoriasis: Symptoms and Variations
Learn about psoriasis, a chronic skin condition affecting over 130 million people globally. Explore its common symptoms, hereditary nature, and the various types—including plaque, inverse, erythrodermic, pustular, guttate, and nail psoriasis. While incurable, symptom management is possible through various treatments. Understanding the different forms helps in early diagnosis and effective care, reducing the risk of associated health issues such as psoriatic arthritis and metabolic conditions.
Sponsored

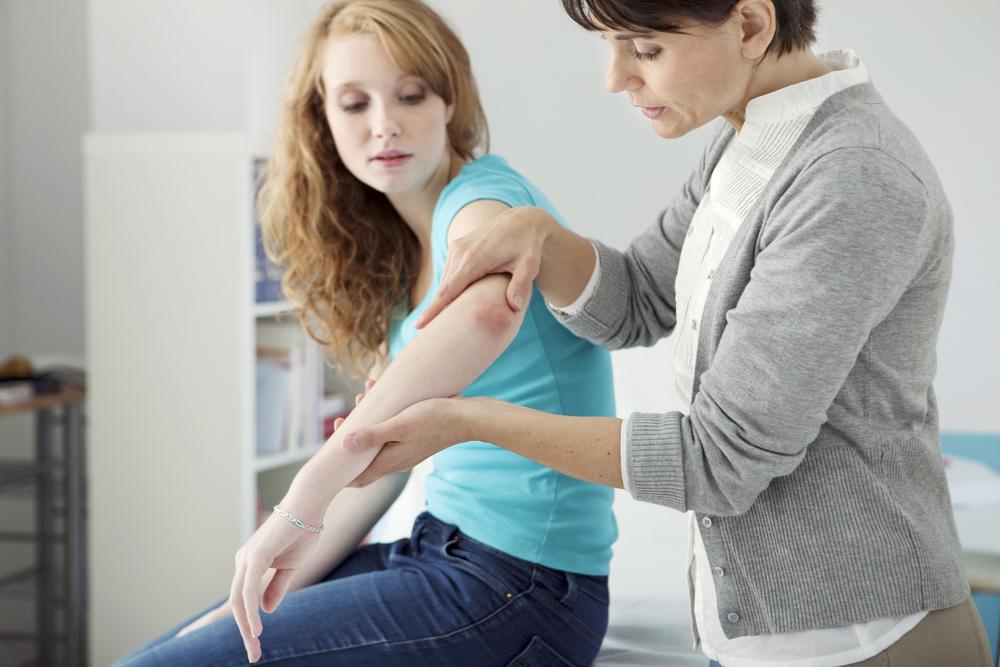
Psoriasis is a persistent skin disorder characterized by red, flaky patches covered with silvery scales. Commonly affecting areas like the scalp, knees, and elbows, it can also involve nails, trunk, and legs. Although not contagious, psoriasis is hereditary with no current prevention methods. It can vary from mild to severe and is linked to other health issues such as cardiovascular disease, Type 2 diabetes, and psoriatic arthritis, which affects about 15% of sufferers. While incurable, treatment options help manage symptoms effectively.
Types of Psoriasis
This condition manifests in different forms depending on location, severity, and individual factors. The recognized types include:
Chronic Plaque Psoriasis: The most prevalent form, featuring red patches with silvery scales that can cause itching or pain and may appear anywhere on the body, including mucous membranes or genitals.
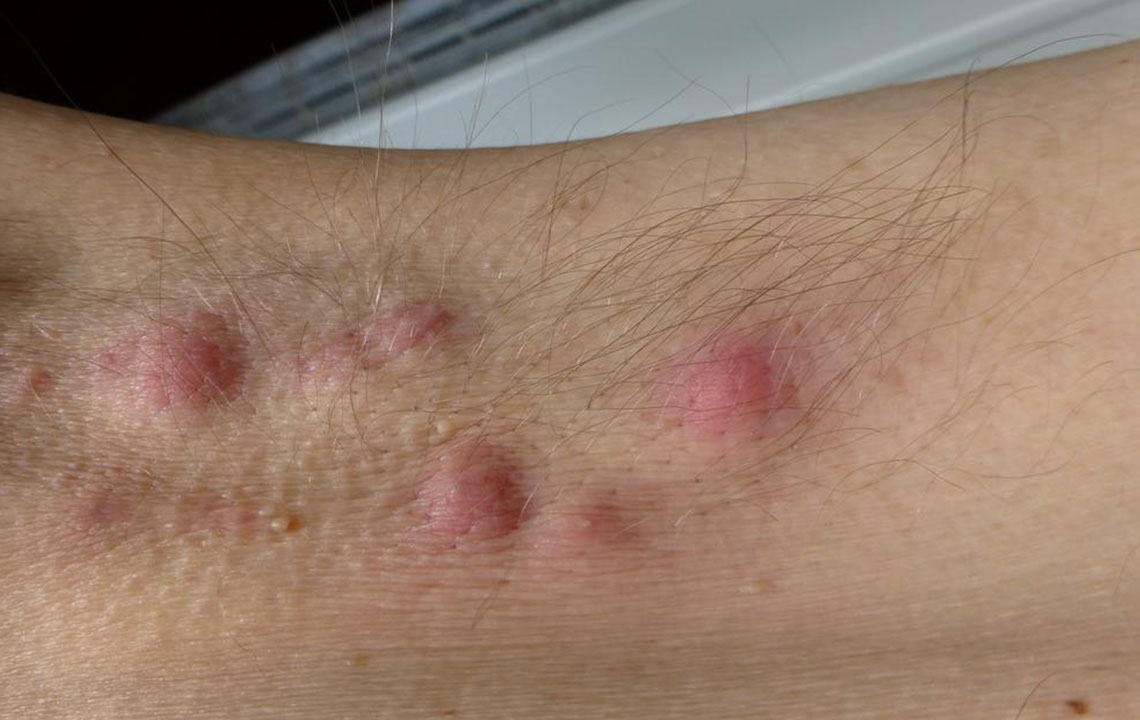
Inverse or Flexural Psoriasis: Presents as shiny, smooth patches in skin folds like the groin, behind the knees, or underarms. Often coexists with other psoriasis types.
Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A rare but severe form, covering the entire body with a red, peeling rash that is intensely itchy and painful.
Pustular Psoriasis: Characterized by white pustules on red skin, this severe type can localize on hands and feet or cover larger areas, accompanied by symptoms like muscle weakness, chills, and fever. Types include acropustulosis, palmoplantar pustulosis, and von Zumbusch.
Guttate Psoriasis: Often triggered by strep infections, it appears as small dot-like lesions on both children and adults.
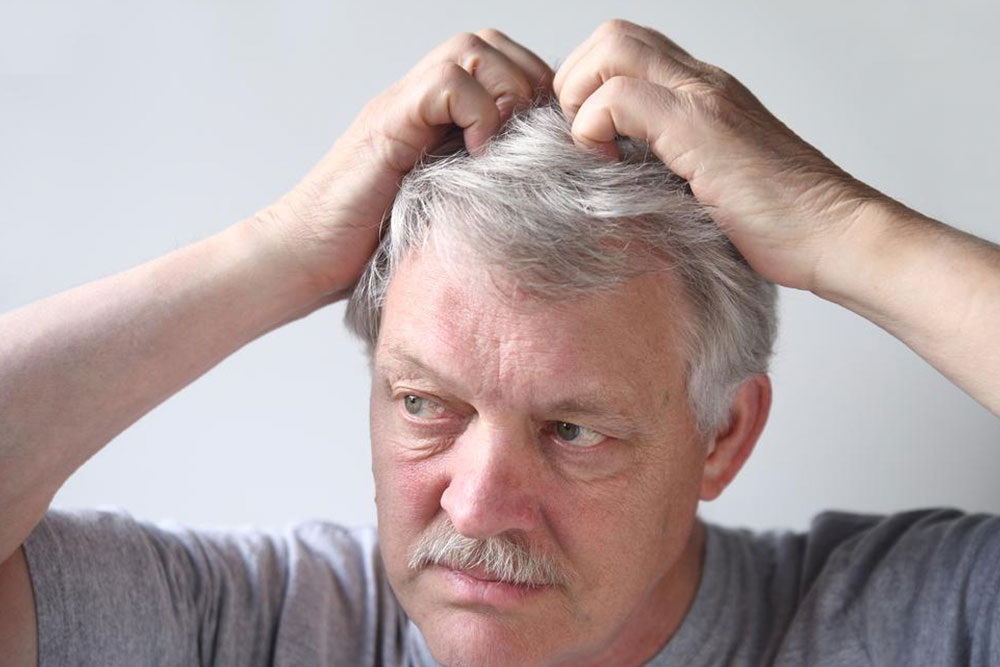
Nail Psoriasis: Not officially a separate type but affects fingernails and toenails, causing discoloration, pitting, and detachment, leading to nail loss.